Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT
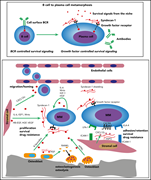
Syndecan-1 and stromal heparan sulfate proteoglycans: key moderators of plasma cell biology and myeloma pathogenesis
As B cells mature to plasma cells, they lose expression of the B-cell antigen receptor and become dependent on interactions with the microenvironment to sustain survival. In a Blood Spotlight, Ren et al review the central role of plasma cell syndecan-1 (CD138) and other stromal heparan sulfate-proteoglycans in the marrow microenvironment in supporting both normal and malignant cells, and they discuss how this pathway can be targeted for potential therapy for multiple myeloma.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
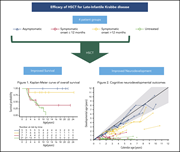
Long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for late-infantile Krabbe disease
Clinical Trials & Observations
Krabbe disease is a rare neurodegenerative glycogen storage disease, 80% of which presents in infancy (age 0 to 6 months). The only effective therapy is hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), which is most effective when performed early on asymptomatic infants. Yoon et al report on HSCT for patients diagnosed at 6 to 36 months of age, showing again that asymptomatic patients have improved survival and normal or near-normal development; even symptomatic patients derive some benefit.
Real-world experience with caplacizumab in the management of acute TTP
Clinical Trials & Observations
Dutt et al review the early real-world experience with caplacizumab for the treatment of acute immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) in a multicenter study of 85 patients.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Conditional expression of HGAL leads to the development of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in mice
Mutational landscape of gray zone lymphoma
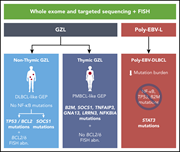
Gray zone lymphomas (GZLs) are B-cell neoplasms with features between those of classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Sarkozy et al compared the patterns of somatic mutations in Epstein-Barr virus–negative GZL, DLBCL, cHL, and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL). Mediastinal GZL has a distinct profile from GZL outside the mediastinum and displays mutational overlap with cHL and PMBCL, suggesting a common cell of origin.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Overcoming T-cell exhaustion in LCH: PD-1 blockade and targeted MAPK inhibition are synergistic in a mouse model of LCH
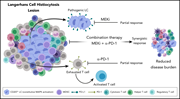
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is a myeloid malignancy comprising a small percentage of malignant dendritic cells embedded in an inflammatory infiltrate. Sengal and colleagues examined the inflammatory milieu, demonstrating a prominent exhausted T-cell infiltrate with high checkpoint receptor expression. Treatment of a mouse model of LCH with a single-agent mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibitor or anti-PD-1 decreased myeloid cells or lymphoid cells, respectively; combined therapy was synergistic in decreasing both populations, suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy for LCH.
Ivosidenib or enasidenib combined with intensive chemotherapy in patients with newly diagnosed AML: a phase 1 study
Clinical Trials & Observations
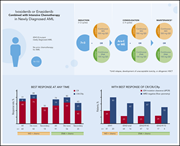
Ivosidenib and enasidenib are approved as single agents for relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with IDH1 and IDH2 mutations (mIDH1/2), respectively. Stein et al report a phase 1 study evaluating the efficacy and safety of these agents in combination with intensive chemotherapy for first-line therapy for mIDH AML. The therapy is well tolerated, and results are encouraging. A phase 3 trial is ongoing and will inform whether addition of targeted therapy results in superior remission rates and improved survival.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
A zinc transporter, transmembrane protein 163, is critical for the biogenesis of platelet dense granules
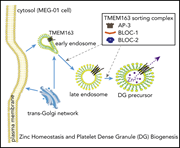
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS) is a recessive disorder associated with loss of dense granules in several tissues, including platelets and melanosomes. Yuan and colleagues observed that a novel platelet zinc transporter, transmembrane protein 163 (TMEM163), is reduced in HPS, and that deletion of TMEM163 in mice results in abnormal zinc accumulation and loss of dense granules. These results elucidate a link between zinc homeostasis and platelet granule formation.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
Rurioctocog alfa pegol PK-guided prophylaxis in hemophilia A: results from the phase 3 PROPEL study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Rurioctocog alfa pegol is a recombinant prolonged half-life factor VIII (FVIII) product that provides safe and efficacious prophylaxis targeting a trough FVIII level exceeding 1%. Klamroth et al report that targeting a trough of 8% to 12% provides superior control of bleeding episodes without new safety signals.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Increased incidence of germline PIEZO1 mutations in individuals with idiopathic erythrocytosis
Outcomes of patients with large B-cell lymphoma progressing after axicabtagene ciloleucel therapy
Clinical Trials & Observations
SSBP2-CSF1R is a recurrent fusion in B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia with diverse genetic presentation and variable outcome
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Transmembrane protein 163 (TMEM163; red) is located on the limiting membrane of luminal FluoZin-3–labeled granules (green), which are likely dense granule precursors in MEG-01 cells. See the article by Yuan et al on page 1804.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





Taking gray zone lymphomas out of the shadows