Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
REVIEW ARTICLE
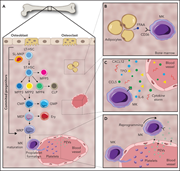
The bone marrow niche from the inside out: how megakaryocytes are shaped by and shape hematopoiesis
Stone et al explore the interconnectiveness of regulation of megakaryopoiesis and regulation of the bone marrow microenvironment in a timely and unique review. In particular, they focus on the now-recognized multiple and divergent pathways from hematopoietic stem cells to mature megakaryocytes and how this is influenced by, and influences, the stem cell niche.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
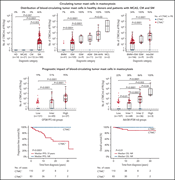
Sustained minimal residual disease negativity in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma and the impact of daratumumab in MAIA and ALCYONE
Clinical Trials & Observations
San Miguel et al evaluated the impact of dynamic, rather than single-point, assessment of measurable/minimal residual disease (MRD) by next-generation sequencing at a sensitivity of 10−5 during remission on outcome in over 1400 patients in 2 randomized trials of first-line myeloma therapy. MRD negativity sustained over 12 months is associated with superior progression-free survival over either MRD positivity or nonsustained MRD negativity, regardless of frontline treatment regimen.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
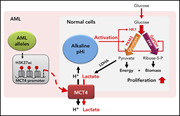
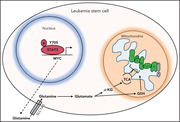
Proton export alkalinizes intracellular pH and reprograms carbon metabolism to drive normal and malignant cell growth
Increased cellular pH is recognized as a metabolic adaptation by malignant cells. Man and colleagues report that cellular proton balance regulates the proliferation of hematopoietic progenitors and that this is enhanced in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells through overexpression of the monocarboxylate transporter MCT4. Inhibition of proton export eradicates leukemia-initiating cells in vivo but does not affect normal hemopoiesis, suggesting a future therapeutic approach for AML.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
PI3Kδ/γ inhibition promotes human CART cell epigenetic and metabolic reprogramming to enhance antitumor cytotoxicity
Funk et al report a potential solution to the problem of exhausted T cells in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) limiting the efficacy of autologous chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy. Adding the PI3Kδ/γ inhibitor duvelisib to CAR T-cell cultures from these patients enriches T-stem cell memory and CD8+ CAR T-cell generation and increases in vivo cellular expansion and anti-CLL activity in model systems. This approach is amenable to clinical testing.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
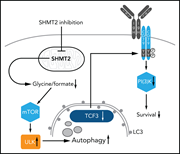
SHMT2 inhibition disrupts the TCF3 transcriptional survival program in Burkitt lymphoma
PEG10 amplification at 7q21.3 potentiates large-cell transformation in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Frequency and prognostic impact of blood-circulating tumor mast cells in mastocytosis
Clinical Trials & Observations
The STAT3-MYC axis promotes survival of leukemia stem cells by regulating SLC1A5 and oxidative phosphorylation
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
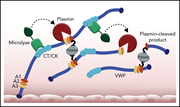
Microlyse: a thrombolytic agent that targets VWF for clearance of microvascular thrombosis
von Willebrand factor (VWF) platelet-binding activity is proteolytically regulated by ADAMTS13, with congenital or acquired deficiency in ADAMTS13 causing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) due to an increase in thrombogenic VWF multimer lengths. de Maat and colleagues describe a novel thrombolytic agent that fuses the protease domain of urokinase and a VWF-binding nanobody, thereby targeting plasminogen activation to the VWF surface and degrading fibrin-poor microthrombi. They report amelioration of disease without perturbation of hemostasis in a murine model of TTP.
TRANSPLANTATION
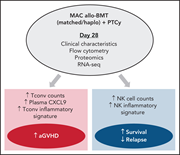
Signatures of GVHD and relapse after posttransplant cyclophosphamide revealed by immune profiling and machine learning
McCurdy et al provide a comprehensive analysis of immune reconstitution after haploidentical and sibling donor allografts using posttransplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy) as graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis. Speed of conventional CD4+ T cell recovery and activation and metabolic signatures are risk markers for acute GVHD. Early natural killer (NK) cell recovery is associated with less relapse, while loss of NK and CD8+ T-cell inflammatory signaling predominates in relapsing patients. These data may inform future interventions following PTCy to improve outcomes.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Neutrophil and platelet increases with luspatercept in lower-risk MDS: secondary endpoints from the MEDALIST trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Aged healthy mice acquire clonal hematopoiesis mutations
Chin and colleagues used detailed mutational analysis of aged mice and transplantation to evaluate the mouse as a model of clonal hematopoiesis (CH). Their data suggest that while murine hematopoietic stem cells acquire mutations in CH-associated genes when aged and CH clones can expand after transplantation (as in humans), these are rare events. Nevertheless, genetically manipulated murine models mimicking human CH are feasible and may prove useful in the future.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
It shows our therapeutic protein Microlyse (green) binding to strings of von Willebrand factor and platelets (red) on vascular endothelial cells (blue) that are pathogenic in the disease thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. See the article by de Maat et al on page 597.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





Sustained minimal residual disease in myeloma
Clinical Trials & Observations