Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
HOW I TREAT
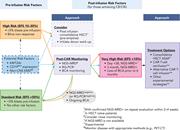
How I use risk factors for success or failure of CD19 CAR T cells to guide management of children and AYA with B-cell ALL
Myers and colleagues discuss their approach to therapy of relapsed pediatric and adolescent/young adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with respect to predictors of successful chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. Following a single patient through several relapses, the authors discuss clinical trial data and answer remaining questions regarding salvage therapy, bridging therapy, consolidation therapy, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for relapsed/refractory disease.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Venetoclax and idasanutlin in relapsed/refractory AML: a nonrandomized, open-label phase 1b trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Daver and colleagues report on a phase 1b trial combining venetoclax and the MDM inhibitor idasanutlin in patients with relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who are ineligible for cytotoxic chemotherapy. Composite complete remissions are seen in 25-40% of patients; however, response duration is short. Patients with AML bearing IDH1/2 and RUNX1 mutations respond better, and those with TP53 mutations do less well. Of note, 12 of 36 evaluable patients developed emergent TP53 mutation-bearing clones, almost all of which had been present at baseline but at very low variant allele frequency, suggesting a possible need to screen and select patients best suited for this combination.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
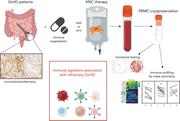
A unique immune signature in blood separates therapy-refractory from therapy-responsive acute graft-versus-host disease
van Halteren and colleagues used high-dimensional immune cell profiling to elucidate immune subsets, predicting development of acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) and its response to therapy. The authors report that myeloid and lymphoid subsets that home to the skin and gastrointestinal tract in aGVHD are detectable in the blood before the onset of symptoms and that these distinct cell populations persist over time in patients unresponsive to therapy. Such single-cell immune profiling may improve clinical decision-making in managing severe aGVHD.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Discovery of novel predisposing coding and noncoding variants in familial Hodgkin lymphoma
Familial cases of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) have long been recognized, but there is ongoing debate as to whether this reflects genetic predisposition or shared environmental factors. Flerlage et al report on whole genome sequencing of 234 individuals from 36 pedigrees with multiple first-degree relatives with HL identifying 44 HL risk variants in 28 pedigrees. Four variants were recurrent, but the others were private, occurring in only 1 family. This suggests that germline variants play a major role in familial recurrence of HL.
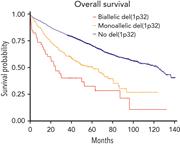
Biallelic deletion of 1p32 defines ultra-high-risk myeloma, but monoallelic del(1p32) remains a strong prognostic factor
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
In this month’s CME article, Schavgoulidze et al confirm the adverse impact of 1p32 deletion in patients newly diagnosed with multiple myeloma (NDMM). In a study of 2551 patients with NDMM, the 11% harboring del(1p32) have inferior progression-free and overall survival (OS). Biallelic del(1p32) confirmed a dramatically worse prognosis, with a median OS of only 25 months. Detection of biallelic del(1p32) at diagnosis defines an ultra–high-risk subgroup of NDMM.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
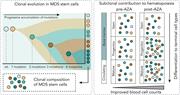
Contribution of mutant HSC clones to immature and mature cells in MDS and CMML, and variations with AZA therapy
Brief Report
Myelodysplastic neoplasms (MDS) and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) are driven by progressive acquisition of somatic mutations in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). Treatment with hypomethylating agents (HMA) often improves blood counts without decreasing clonal burden. Schnegg-Kaufmann and colleagues investigated whether this reflects a shift in mature cell populations toward those derived from unmutated or less mutated clones. Both before and after HMA treatment, mutational burden in mature cells is similar, suggesting that even highly mutated cells can give rise to mature progeny, indicating that cellular maturation can be improved without eliminating mutant HSCs.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
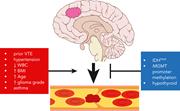
Determining venous thromboembolism risk in patients with adult-type diffuse glioma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a common complication of glioblastoma, but physicians are wary of anticoagulation due to the risk of bleeding. Burdett et al present a new prediction model for VTE risk in glioma based on clinical factors and tumor characteristics (including next-generation sequencing) from 258 patients, and the authors validated this model in 2 separate cohorts. They also created a web-based tool that may guide clinicians toward anticoagulation in a subgroup of patients.
TRANSPLANTATION
Prevention of acute GVHD using an orthogonal IL-2/IL-2Rβ system to selectively expand regulatory T cells in vivo
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Prognostic value and oncogenic landscape of TP53 alterations in adult and pediatric T-ALL
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Treatment with oIL2Rβ Tregs and oIL2 cytokine reduces acute graft-versus-host disease pathology in the colon. See the article by Ramos et al on page 1337.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






MDM2 and BCL-2: to p53 or not to p53?
Clinical Trials & Observations