Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT
Anticoagulation in hospitalized patients with COVID-19
In this Blood Spotlight, Kreuziger and colleagues summarize the clinical consequences of thromboinflammation in COVID-19, examine the trial data addressing treatment and prophylaxis with anticoagulants, and provide a synthesis of guidelines. Their summary provides practical assistance for physicians now caring for hospitalized patients with COVID-19 and presents a framework for the integration of new data as further prospective evidence emerges.
REVIEW ARTICLE
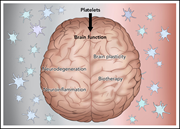
The multifaceted role of platelets in mediating brain function
Burnouf and Walker review the role of the platelets in brain function and disease beyond hemostasis. They identify involvement in the pathophysiology of various neurological inflammatory and degenerative diseases and how platelets and platelet extracellular vesicles potentially could be used in treatment.
HOW I TREAT
How I approach smoldering multiple myeloma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Using 2 illustrative cases and critically reviewing the pertinent literature, Vaxman and Gertz discuss their approach to patients with smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM). The authors highlight the heterogeneity among patients with SMM and the strengths and limitations of data from clinical trials of interventions, and they provide useful practical recommendations for monitoring and making decisions about treatment for this disease.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Enduring undetectable MRD and updated outcomes in relapsed/refractory CLL after fixed-duration venetoclax-rituximab
Clinical Trials & Observations
Kater and colleagues report on 5-year outcomes for patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) when treated with fixed-duration venetoclax-rituximab (VenR) in a pivotal randomized trial. Over 50% of patients who completed a 3-year VenR treatment have not progressed, and median time to next treatment is 58 months. Of 43% of patients with no measurable residual disease (MRD) at completion of VenR, 39% remained MRD-negative 3 years later, emphasizing the durability of the benefits for many patients.
GENE THERAPY
Comparative effectiveness of ZUMA-5 (axi-cel) vs SCHOLAR-5 external control in relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
As yet, there are no randomized studies of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy versus standard therapy in patients with multiple relapsed follicular lymphoma. To provide early insight into comparative efficacy, Ghione et al used propensity scoring analysis on prespecified prognostic factors with standardized mortality weighting to match patients in the SCHOLAR-5 retrospective registry to those in the ZUMA-5 study of axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel). These insights suggest superiority in response rate with axi-cel with longer times to the next treatment and improved progression-free and overall survival.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
A TCR mimic CAR T cell specific for NDC80 is broadly reactive with solid tumors and hematologic malignancies
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
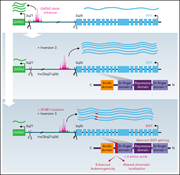
Aberrant EVI1 splicing contributes to EVI1-rearranged leukemia
PHAGOCYTES, GRANULOCYTES, AND MYELOPOIESIS
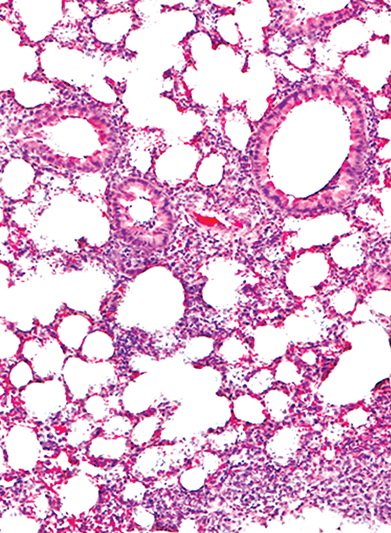
Unique characteristics of lung-resident neutrophils are maintained by PGE2/PKA/Tgm2-mediated signaling
Bae et al studied lung-resident neutrophils in mice, characterizing the resting state and responses to inflammatory stimuli of this unique population. The authors found that lung neutrophils are primarily immunosuppressive in health, and they defined a prostaglandin E2-regulated pathway leading to the generation and maintenance of the immunosuppressive state of lung neutrophils that helps protect lung tissues from collateral damage during inflammation. These insights provide potentially new opportunities for therapy of acute respiratory distress syndrome.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
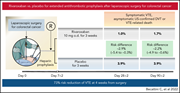
Rivaroxaban vs placebo for extended antithrombotic prophylaxis after laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancer
Clinical Trials & Observations
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a common adverse event following surgery, with risks related to the nature of the surgery, the presence of cancer, and other comorbidities. In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with patients having laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancer, Becattini et al demonstrated that the addition of 3 weeks of rivaroxaban to 1 week of low molecular weight heparin reduces the relative risk of VTE by 73% without increasing the bleeding risk. This finding establishes a new standard of prophylaxis for this surgical scenario.
TRANSPLANTATION
Genetic testing in severe aplastic anemia is required for optimal hematopoietic cell transplant outcomes
Clinical Trials & Observations
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HCT) is recommended as a curative therapy for patients with aplastic anemia, but outcomes vary. McReynolds and colleagues studied genetic data on 732 adults undergoing HCT for severe aplastic anemia. The authors identified that 7% had an unrecognized inherited bone marrow failure disorder, which is associated with poor overall survival post-HCT, including a 5-fold risk of toxic death. Patients with inherited syndromes must be identified prospectively and may need disease-specific transplant regimens to improve their outcomes.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
An updated list of drugs suspected to be associated with immune thrombocytopenia based on the WHO pharmacovigilance database
Clinical Trials & Observations
Ruxolitinib is more effective than other JAK inhibitors to treat VEXAS syndrome: a retrospective multicenter study
Clinical Trials & Observations
VEXAS syndrome (vacuoles in myeloid progenitors, E1 ubiquitin activating enzyme, X-linked, autoinflammatory manifestations and somatic) is an autoinflammatory condition caused by somatically acquired UBA1 mutations. Heiblig et al report on an international retrospective analysis of 30 patients with VEXAS syndrome treated with different Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, finding encouraging evidence supporting the use of the JAK1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib with clinical remissions and reductions in steroid use seen in the majority of patients.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Hematoxylin and eosin–stained lung tissue from a mouse pretreated with H89 before intratracheal instillation of lipopolysaccharide. Blockage of the PGE2-induced PKA pathway restrains lung neutrophil formation and exacerbates lung damage in an experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome model. See the article by Bae et al on page 889.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals








uMRD: “the” endpoint or “an” endpoint for CLL?
Clinical Trials & Observations