Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Subsequent malignant neoplasms among children with Hodgkin lymphoma: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
With improved survival of children with Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), attention has become increasingly focused on secondary effects of intensive therapy and efforts to reduce later secondary malignancy. Giulino-Roth and colleagues report that the 10-year incidence of secondary malignancy among children with HL treated with a response-adaptive therapy is low and nearly all restricted to patients with combined modality therapy, supporting efforts to safely minimize radiotherapy in HL treatment.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
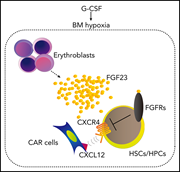
FGF-23 from erythroblasts promotes hematopoietic progenitor mobilization
Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF-23) is produced by osteocytes and regulates renal phosphate metabolism. Ishii and colleagues elucidate a novel role for FGF-23 in hematopoiesis, demonstrating that it is produced by erythroblasts in response to hypoxia, suppresses erythropoiesis, and increases hematopoietic stem cell mobilization by G-CSF by interfering with migration toward CXCL12.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
EBV-associated primary CNS lymphoma occurring after immunosuppression is a distinct immunobiological entity
Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) arises in both immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients. In immunosuppressed patients, it is typically Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) positive and has a very poor prognosis. Gandhi et al demonstrate that the landscape of EBV+ PCNSL has a completely distinct profile, lacking the mutations characteristic of EBV− PCNSL and displaying a tolerogenic microenvironment with high checkpoint gene expression that provides potential entry points for targeted therapy.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
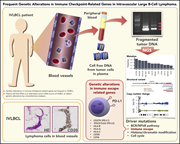
Frequent genetic alterations in immune checkpoint–related genes in intravascular large B-cell lymphoma
Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma (IVLBCL) is an extranodal lymphoma found in small blood vessels without lymphadenopathy. Shimada and colleagues performed whole-exome sequencing of cell-free plasma DNA (cfDNA) and tumor tissue, demonstrating that IVLBCL is associated with high levels of cfDNA and a high frequency of mutations, leading to increased PD-L1/PD-L2 expression. This suggests the potential for checkpoint blockade as a therapy for IVLBCL and further indicates that cfDNA may offer a biomarker for diagnosis and monitoring of tumor response.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
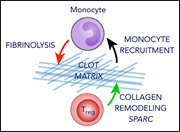
Specialized regulatory T cells control venous blood clot resolution through SPARC
Shahneh et al delineate a fascinating new intersection between the immune system and thrombosis, demonstrating a population of regulatory T cells (Tregs) that accumulate in venous clots and facilitate clot resolution through monocyte recruitment and induction of matrix metalloproteinase activity. Since anticoagulation works through blocking new clot formation, the authors suggest that inducing increased clot-associated Tregs could improve outcomes by directly facilitating rapid clot resolution.
TRANSPLANTATION
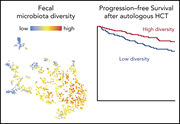
Fecal microbiota diversity disruption and clinical outcomes after auto-HCT: a multicenter observational study
In patients who undergo allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT), loss of fecal microbiota diversity is associated with increased graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and nonrelapse mortality (NRM). The authors investigated decreased fecal microbiota diversity in patients undergoing autologous HCT who do not develop GVHD and have low NRM. They demonstrate that autologous HCT patients also develop decreased fecal microbiota diversity, which is associated with decreased progression-free survival.
VASCULAR BIOLOGY
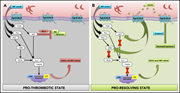
Targeting the AnxA1/Fpr2/ALX pathway regulates neutrophil function, promoting thromboinflammation resolution in sickle cell disease
There is compelling evidence that neutrophils play a critical role in thromboinflammation. Ansari et al focus on sickle cell disease and postulate that chronic inflammatory changes in neutrophils decrease inflammation resolution, contributing to thrombosis. They demonstrate that this reflects defective annexin A1–mediated resolution of inflammation and that administration of annexin A1 to sickle cell mice decreases cerebral thrombosis, suggesting a novel targetable pathway to decrease thromboinflammation in sickle cell disease.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Genetics of osteonecrosis in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and general populations
Microbiome markers are early predictors of acute GVHD in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
A lung biopsy specimen from a patient with intravascular large B-cell lymphoma (IVLBCL) who had chromosome 9p amplification was immunohistochemically stained using anti–PD-L1 antibody clone SP142, which recognizes the C-terminal region of PD-L1. PD-L1 staining correlates with the structural variant of the gene. See the article by Shimada et al on page 1491.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





Protect our children: Hodgkin lymphoma survivors
Clinical Trials & Observations