Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
The megakaryocytic transcription factor ARID3A suppresses leukemia pathogenesis
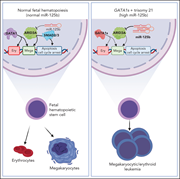
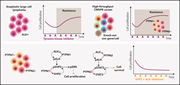
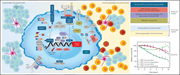
Up to 30% of patients with trisomy 21 develop transient abnormal myelopoiesis (TAM), and many progress to acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL), both in association with mutations in the GATA-1 transcription factor. In a Plenary Paper, Alejo-Valle et al demonstrate that miR-125b on chromosome 21 synergizes with mutant GATA-1 to promote leukemogenesis through the repression of ARID3A. Restoring ARID3A expression restores megakaryocytic differentiation and blocks the expansion of GATA-1mutant stem cells.
REVIEW ARTICLE
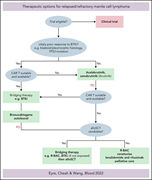
Therapeutic options for relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma
Eyre et al review the current state of the art of the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma that relapses after immunochemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation. They discuss Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors and the mechanisms of BTK inhibitor resistance, chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, and subsequent novel therapies.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Efficacy of a third BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine dose in patients with CLL who failed standard 2-dose vaccination
Clinical Trials & Observations
Herishanu and colleagues evaluated the efficacy of a third dose of COVID-19 vaccine in 172 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who were seronegative after 2 previous doses. Seropositivity was achieved in 25%, with 40% of off-therapy or therapy-naïve patients but only 12% of patients on anti-B-cell therapy responding. This study supports repeated vaccine dosing in this high-risk population but also underscores the need for continued careful protective practices and availability of antibody treatment in nonresponders.
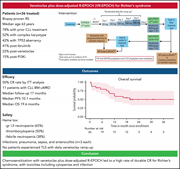
Venetoclax plus dose-adjusted R-EPOCH for Richter syndrome
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Richter syndrome responds poorly to chemotherapy and has a median survival of 3 to 6 months. Davids et al report results of a phase 2 trial of venetoclax plus chemoimmunotherapy in 26 patients. Complete response was achieved in 50% of patients, with a median overall survival of 19.6 months.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
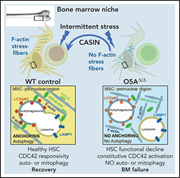
Autophagy in mesenchymal progenitors protects mice against bone marrow failure after severe intermittent stress
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
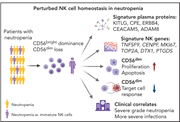
Perturbed NK-cell homeostasis associated with disease severity in chronic neutropenia
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Tyrosine phosphatases regulate resistance to ALK inhibitors in ALK+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) frequently carries anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene fusions, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) can treat ALCL that relapses after chemotherapy. However, TKIs are not curative and relapses occur. Using a genomic loss-of-function screen, Atabay et al found that resistance is driven by PTPN1 and PTPN2 through binding and phosphorylation of ALK and the ALK signaling mediator SHP2, leading to hyperactivity of SHP2, MAPK, and JAK/STAT signaling. Blockade of SHP2 increases sensitivity of ALCL to the ALK inhibitor crizotinib.
Genetic and phenotypic attributes of splenic marginal zone lymphoma
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL) is a heterogeneous disorder with variable clinical outcomes. Bonfiglio et al report on a genetic and phenotypic analysis of SMZL, defining 2 major and 2 minor genetic clusters with divergent gene expression signatures and clinical outcomes. They also characterize 2 micro environmental phenotypes based on immune cell infiltration, one immune suppressive and the other immune excluded. This new classification provides insights for future targeted therapies.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
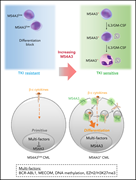
MS4A3 promotes differentiation in chronic myeloid leukemia by enhancing common β-chain cytokine receptor endocytosis
Although chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in chronic phase responds to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), leukemia stem cells persist and provide a source for relapse upon discontinuation of TKIs. Zhao et al performed a meta-analysis of published CML transcriptomes, identifying low expression of MS4A3 as a prominent feature in TKI-resistant stem cells and blasts. They demonstrate that MS4A3 promotes differentiation by increasing cytokine receptor expression, suggesting that overexpression of MS4A3 should overcome TKI resistance.
PHAGOCYTES, GRANULOCYTES, AND MYELOPOIESIS
Heterozygous variants of CLPB are a cause of severe congenital neutropenia
Severe congenital neutropenia (SCN) is a rare congenital disorder associated with agranulocytosis that has been linked to mutations in several different genes. Warren and colleagues report that heterozygous missense mutations in caseinolytic peptidase B (CLPB) are a novel cause of SCN. Unlike the pathophysiology of most forms of SCN, this mutation does not cause activation of the unfolded protein response and intramedullary apoptosis but causes apoptosis related to mitochondrial dysfunction.
LETTER TO BLOOD
CAR T-cell therapy in primary central nervous system lymphoma: the clinical experience of the French LOC network
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
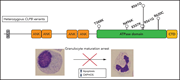
Chronic myeloid leukemia cells (LAMA-84) were transduced with MS4A3-EGFP (green) and stained by immunofluorescence to detect the lysosomal marker LAMP1 (red). The cell nucleus is labeled with DAPI (40′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; blue). This image shows the spatial proximity between MS4A3 and lysosomes. See the article by Zhao et al on page 761.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals




Posttranscriptional Arid3a deregulation in AMKL