Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
SF3B1-mutant MDS as a distinct disease subtype: a proposal from the International Working Group for the Prognosis of MDS
Clinical Trials & Observations
The World Health Organization’s classification of hematopoietic and lymphoid tumors has worked to integrate morphology and genetics, but del(5q) remains the only molecularly defined subtype of myelodysplasia (MDS). In a Special Report that is also this issue’s Plenary Paper, the International Working Group for the Prognosis of MDS makes the case for designating SF3B1-mutant MDS as a second molecularly defined subtype with good prognosis and increased likelihood of response to luspatercept.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
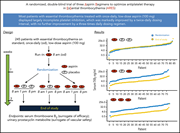
A randomized double-blind trial of 3 aspirin regimens to optimize antiplatelet therapy in essential thrombocythemia
Clinical Trials & Observations
Treatment with once-daily aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid [ASA]) is recommended in essential thrombocythemia (ET) based on efficacy studies in polycythemia vera, but ASA may not provide sufficient platelet inhibition in ET because of increased platelet activation. Rocca et al compared efficacy of ASA in suppressing thromboxane excretion with once-, twice-, and 3-times–daily dosing. Twice-daily dosing has superior antiplatelet activity compared to once-daily dosing, with no further improvement with treatment 3 times daily.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
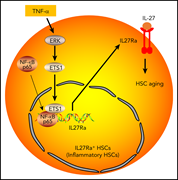
Aging-induced IL27Ra signaling impairs hematopoietic stem cells
Aging-associated changes in hematopoietic stem cells lead to myeloid skewing, anemia of aging, and increased risk of myeloid malignancy. He et al confirmed that these changes are closely linked to increased expression of inflammatory cytokines, demonstrating that an age-associated increase in tumor necrosis factor α leads to increased expression of interleukin 27 receptor α (IL27Ra) and that these IL27Ra+ stem cells have impaired reconstitution capacity and increased myeloid skewing.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
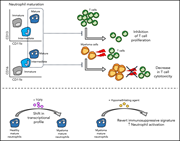
Immunogenomic identification and characterization of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells in multiple myeloma
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are a subset of mature neutrophils that promote tumor growth through suppression of T-cell responses. Perez et al characterize MDSCs in multiple myeloma, proposing a combination of markers to identify this subpopulation and correlating their frequency with inferior progression free survival.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
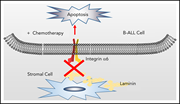
Integrin α6 mediates the drug resistance of acute lymphoblastic B-cell leukemia
Stromal adhesion mediated by integrin α6 has been implicated in both drug resistance and central nervous system migration of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) cells. The authors demonstrated that blocking α6 induces apoptosis in B-ALL cells and increases their sensitivity to chemotherapy, suggesting that α6 is a potential novel target for B-ALL therapy.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
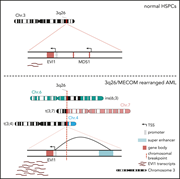
Atypical 3q26/MECOM rearrangements genocopy inv(3)/t(3;3) in acute myeloid leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) associated with inv(3)/t(3;3) is recognized as a distinct form of AML associated with poor prognosis. Ottema and colleagues dissected the genotypic and functional characteristics of atypical 3q26/MECOM rearrangements in AML, demonstrating that they have a similar pattern of gene expression to inv(3)/t(3;3) and suggesting that all 3q26-rearranged AML should be viewed as a single entity.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
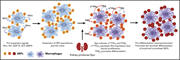
Epo receptor signaling in macrophages alters the splenic niche to promote erythroid differentiation
Chen and colleagues present a novel paradigm of the role of erythropoietin (Epo) in stress hematopoiesis. Using a mouse model, they demonstrated that Epo acts to modulate macrophages in the erythropoietic niche to suppress Wnt expression, suppressing Wnt-induced proliferation of early progenitors, and to increase production of prostaglandin E2, inducing erythroid progenitors to differentiate.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
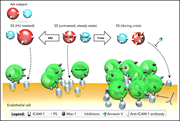
Plasma microparticles of sickle patients during crisis or taking hydroxyurea modify endothelium inflammatory properties
Garnier and colleagues studied erythrocyte-derived microparticles (MPs) isolated from the plasma of patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) before and after hydroxyurea treatment and during vaso-occlusive crisis. They demonstrated that increased phosphatidylserine (PS) expression on SCD MPs increases endothelial ICAM-1 and neutrophil adhesion at baseline, and this was markedly increased during crisis. Furthermore, PS expression was decreased by hydroxyurea, suggesting a novel effect in preventing crisis.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Integrin α6 is highly expressed in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). Immunohistochemical staining of integrin α6 (red), which was coexpressed with a pan–B-cell marker, CD79a (brown), in a bone marrow biopsy sample of a minimal residual disease–positive B-ALL patient. See the article by Gang et al on page 210.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals



SF3B1: the lord of the rings in MDS