Issue Archive
Table of Contents
EDITORIAL
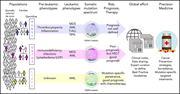
Introduction to a review series on secondary leukemia
In this commissioned series of reviews introduced by Associate Editor Jean Soulier, experts provide new insights into the pathobiology of secondary acute myeloid leukemias arising in diverse genetic or acquired, benign or malignant hematologic disorders.
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
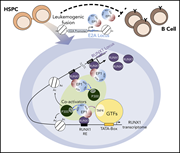
E2A-PBX1 functions as a coactivator for RUNX1 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
In a study reported in this Plenary Paper, Pi and colleagues used unbiased genomic profiling approaches and mechanistic studies to identify the direct and indirect target sites of the oncogenic fusion protein E2A-PBX1 in t(1,19)-positive pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. They revealed how E2A-PBX1 acts in concert with RUNX1 to enforce transcriptome alterations underpinning the development of leukemia.
REVIEW SERIES
Secondary Leukemia
Secondary leukemia in patients with germline transcription factor mutations (RUNX1, GATA2, CEBPA)
In this commissioned series of reviews introduced by Associate Editor Jean Soulier, experts provide new insights into the pathobiology of secondary acute myeloid leukemias arising in diverse genetic or acquired, benign or malignant hematologic disorders.
Secondary myelodysplastic syndrome and leukemia in acquired aplastic anemia and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
In this commissioned series of reviews introduced by Associate Editor Jean Soulier, experts provide new insights into the pathobiology of secondary acute myeloid leukemias arising in diverse genetic or acquired, benign or malignant hematologic disorders.
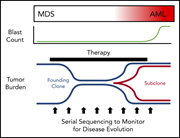
Genetics of progression from MDS to secondary leukemia
In this commissioned series of reviews introduced by Associate Editor Jean Soulier, experts provide new insights into the pathobiology of secondary acute myeloid leukemias arising in diverse genetic or acquired, benign or malignant hematologic disorders.
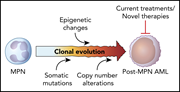
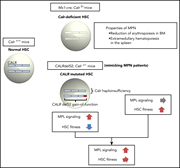
Leukemia secondary to myeloproliferative neoplasms
In this commissioned series of reviews introduced by Associate Editor Jean Soulier, experts provide new insights into the pathobiology of secondary acute myeloid leukemias arising in diverse genetic or acquired, benign or malignant hematologic disorders.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
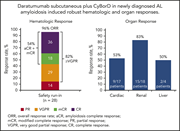
Daratumumab plus CyBorD for patients with newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis: safety run-in results of ANDROMEDA
Clinical Trials & Observations
Palladini et al provide early results of a prospective trial of subcutaneous daratumumab in combination with cyclophosphamide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone as first-line therapy for AL amyloidosis. They report that the regimen has high complete hematological and organ response rates and that toxicity is as expected with these classes of drugs.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
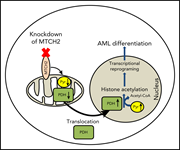
Mitochondrial carrier homolog 2 is necessary for AML survival
Arising in a screen to identify mitochondrial gene products necessary for the growth of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells, mitochondrial carrier homolog 2 (MTCH2) is shown to influence the differentiation of AML cells by toggling histone acetylation downstream of regulation of pyruvate metabolism.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
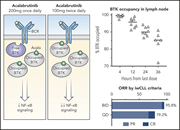
Clinical and biological implications of target occupancy in CLL treated with the BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib
Clinical Trials & Observations
In a randomized phase 2 trial of acalabrutinib in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), Sun et al documented that twice-daily dosing achieves higher Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) occupancy and pathway inhibition in lymph nodes than once-daily dosing and established the rate of BTK resynthesis in CLL cells. Both findings support the rationale for twice-daily dosing with this drug.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Calreticulin haploinsufficiency augments stem cell activity and is required for onset of myeloproliferative neoplasms in mice
Shide and colleagues separated the functional roles of loss of a normal CALR allele and gain of a mutant CALR allele in murine models of CALR-driven essential thrombocythemia, providing insights into the development of some myeloproliferative neoplasms and stem cell biology.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
The role of AGK in thrombocytopoiesis and possible therapeutic strategies
Jiang et al used murine models to reveal critical nonenzymatic roles for acylglycerol kinase (AGK) in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet biogenesis by enhancing JAK2/STAT3 signaling triggered by thrombopoietin.
TRANSPLANTATION
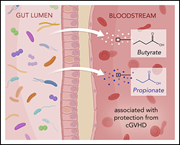
The microbe-derived short-chain fatty acids butyrate and propionate are associated with protection from chronic GVHD
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Markey and colleagues investigated the relationship between the gastrointestinal microbiome and chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD), revealing that lower systemic concentrations of microbe-derived butyrate and propionate are associated with a higher chance of developing cGVHD in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Tocilizumab not associated with increased infection risk after CAR T-cell therapy: implications for COVID-19?
Clinical Trials & Observations
RBCs prevent rapid PIEZO1 inactivation and expose slow deactivation as a mechanism of dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis
Impact of anticoagulation prior to COVID-19 infection: a propensity score–matched cohort study
Tremblay and colleagues asked whether patients receiving either routine anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy for existing conditions prior to becoming ill with COVID-19 have different outcomes from patients receiving neither therapy. After matching for existing comorbidities, this retrospective observational study finds no evidence for an effect of prediagnosis anticoagulation on mortality.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Immunofluorescence image of megakaryocytes derived from the fetal liver of an Agkf/f mouse. Megakaryocytes were stained with tubulin antibodies (conjugated with Alexa Fluor 488 [green]), DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole [blue]), and Stat3 antibodies (conjugated with rhodamine [red]). See the article by Jiang et al on page 119.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals


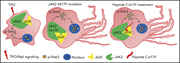

Oncogenesis by E2A-PBX1 in ALL: RUNX and more