Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PERSPECTIVE
Distinguishing AML from MDS: a fixed blast percentage may no longer be optimal
Clinical Trials & Observations
In this Perspective, the late Elihu Estey, along with Robert P. Hasserjian and Hartmut Döhner, argues for approaching patients currently identified as having either low-blast-count acute myeloid leukemia (AML; blasts 20%-30%) or myelodysplasia (MDS) with excess blasts 2 (MDS-EB2; blasts 10%-19%) as having the umbrella entity AML-MDS. They suggest that this reflects biological reality and could allow flexibility for enrollment in trials of new therapies, thereby speeding studies translatable into clinical practice.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
All-trans retinoic acid plus low-dose rituximab vs low-dose rituximab in corticosteroid-resistant or relapsed ITP
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
In this month’s CME article, Wu et al report a novel approach to steroid resistant immune thrombocytopenia (ITP), demonstrating that all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) plus low-dose rituximab (LD-RTX) yields a higher rate of response than LD-RTX alone. Although responses are superior at 6 months, platelet counts declined in the combined treatment groups after 2 years. Further studies are warranted to elucidate the potential role of ATRA in combination with other therapies for refractory ITP.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
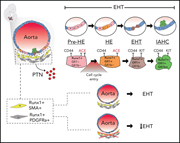
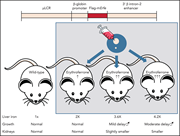
Murine AGM single-cell profiling identifies a continuum of hemogenic endothelium differentiation marked by ACE
Dissecting the molecular processes driving the formation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) from hemogenic endothelium is essential to developing approaches for in vitro generation of HSCs. Using Runx1 and GFi1/1b reporter mouse models, Fadlullah et al performed single-cell RNA sequencing and fluorescence-activated cell sorting analyses to generate a publicly available atlas of the endothelial-tohematopoietic transition (EHT) that should prove invaluable for future investigations of HSC development and in vitro generation.
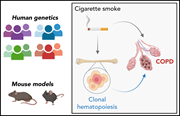
Association of clonal hematopoiesis with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) is an age-related phenomenon that induces inflammation. Since CHIP is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, Miller and colleagues investigated the association between CHIP and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), another age-related inflammatory process. Genomic analysis of 4 large cohorts with over 8400 patients with COPD shows that CHIP increases the risk of COPD incidence and severity. In a correlative mouse study, inactivation of Tet2, a common CHIP mutation, increases smoke exposure–induced emphysema.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
T-follicular helper cell expansion and chronic T-cell activation are characteristic immune anomalies in Evans syndrome
Evans syndrome (ES) is the co-occurrence of autoimmune hemolytic anemia and immune thrombocytopenia. Kumar et al investigated the immune profile of 24 pediatric patients with ES in comparison to 22 ITP patients and 24 healthy controls, analysing immunophenotype, gene expression, cytokine levels, and T-cell receptor repertoire. They demonstrate that ES has a unique profile, confirming that ES is a manifestation of a broader underlying immunopathologic process.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
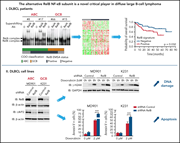
The alternative RelB NF-κB subunit is a novel critical player in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
ETV6-NCOA2 fusion induces T/myeloid mixed-phenotype leukemia through transformation of nonthymic hematopoietic progenitor cells
Single-route CNS prophylaxis for aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphomas: real-world outcomes from 21 US academic institutions
Clinical Trials & Observations
Prophylaxis to prevent central nervous system (CNS) relapse in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is widely used but has no defined standard of care. Orellana-Noia and colleagues assessed the efficacy of CNS prophylaxis in a retrospective multicenter analysis of 1162 patients. They demonstrate that the route of prophylaxis (intrathecal vs high-dose systemic therapy) does not affect relapse rate. CNS relapse remains very close to the rate predicted without prophylaxis, suggesting that the criteria and choice of therapy for CNS prophylaxis in DLBCL need to be reevaluated.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
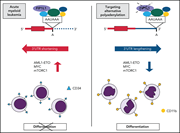
Alternative polyadenylation dysregulation contributes to the differentiation block of acute myeloid leukemia
Alternative polyadenylation (APA) is a posttransciprional modification that can alter transcript stability, localization, translation, and protein complex formation. Davis et al investigated APA dysregulation in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), demonstrating that AML blasts have global 3′ untranslated region (UTR) shortening and coding sequence lengthening that change gene expression patterns. Blocking FIP1L1, a regulator of cleavage and polyadenylation, induces differentiation of AML cells by promoting 3_ UTR lengthening, offering a novel pathway to target for the treatment of AML.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
Erythroid overproduction of erythroferrone causes iron overload and developmental abnormalities in mice
Erythroferrone (ERFE), which suppresses hepatic production of hepcidin, is induced in erythroid cells by erythropoietic cells in response to hemorrhage, hypoxia, and ineffective erythropoiesis. Coffey et al used transgenic mice with graded ERFE overexpression to demonstrate that ERFE induces dose-dependent iron overload, hepcidin deficiency, and impaired bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling, confirming that ERFE mediates iron overload when overproduced. Markedly elevated ERFE levels induced other abnormalities, suggesting that high ERFE levels can also impair BMP signaling during development.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
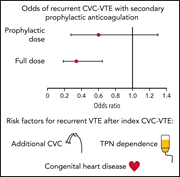
Prevention of recurrent thrombotic events in children with central venous catheter-associated venous thrombosis
Clinical Trials & Observations
Central venous catheters (CVCs) are a significant risk factor for pediatric venous thromboembolism (VTE). Clark et al performed a retrospective study of 373 patients with VTE to assess the value of secondary prophylaxis in preventing recurrent VTE. Recurrent VTE occurred in 17.4% of patients and was increased in patients with multiple CVC placements, congenital heart disease, and parenteral nutrition dependence. Full-dose, but not prophylactic, anticoagulation reduced recurrence risk by 65%.
LETTER TO BLOOD
DNMT3A overgrowth syndrome is associated with the development of hematopoietic malignancies in children and young adults
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Immunofluorescent staining of mouse E10.5 dorsal aorta (DA). RUNX1 is green, CD31 is red, and PDGFRa is gray. RUNX1+ cells in the endothelial lining of the DA are hemogenic endothelial cells. Mesenchymal RUNX1+ cells, which support hematopoiesis, are abundant in the ventral subaortic region. See the article by Fadlullah et al on page 343.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






An “ATRA-ctive” new treatment of ITP?
Clinical Trials & Observations