Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
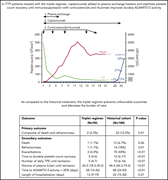
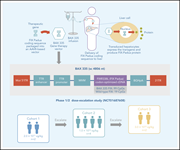
A regimen with caplacizumab, immunosuppression, and plasma exchange prevents unfavorable outcomes in immune-mediated TTP
Clinical Trials & Observations
Plasma exchange and immunosuppression have been the standard treatment for acquired immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) for the last 3 decades. In a Plenary Paper, Coppo and colleagues provide evidence that translates clinical trial data into everyday clinical practice for the potential addition of the anti–von Willebrand factor nanobody caplacizumab to that standard.
REVIEW ARTICLE
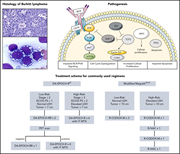
The treatment of Burkitt lymphoma in adults
Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is an uncommon but distinctive, highly aggressive lymphoma. Crombie and LaCasce review its clinical, pathologic, and genomic features and discuss standard and emerging treatment options for adult patients with BL.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Flotetuzumab as salvage immunotherapy for refractory acute myeloid leukemia
Clinical Trials & Observations
Uy and colleagues report the results of a multicenter phase 1/2 study of flotetuzumab, a dual-affinity (CD3ε and CD123) retargeting (DART) protein, in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The drug brings together effector T cells and target cells (CD123-expressing AML blasts). Preliminary efficacy data indicate an 18% complete response rate at the recommended phase 2 dose; higher rates are seen in less heavily pretreated patients and in AMLs with high immune infiltration.
DARTs point the way forward in AML
Clinical Trials & Observations
GENE THERAPY
BAX 335 hemophilia B gene therapy clinical trial results: potential impact of CpG sequences on gene expression
Clinical Trials & Observations
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
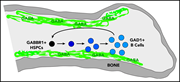
The neurotransmitter receptor Gabbr1 regulates proliferation and function of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, but its receptor is also expressed by hematopoietic progenitors. In genetic and pharmacological experiments, Shao et al show that GABA and its receptor can regulate murine and human stem cell function, including function in transplant models. These data suggest that the GABA receptor is an attractive new molecular target for intervention to enhance human stem cell engraftment.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Identification of MALT1 feedback mechanisms enables rational design of potent antilymphoma regimens for ABC-DLBCL
Fontan and colleagues report a functional genomics screen that identifies genes and pathways that augment or interfere with the efficacy of a MALT1 inhibitor. Building on these insights, they demonstrate that simultaneous MALT1 and MTORC1 inhibition triggers synergistic killing in both in vitro and in vivo models of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). These data should inform interpretation of observations in ongoing early-phase trials of MALT1 inhibitors.
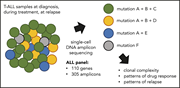
Single-cell DNA amplicon sequencing reveals clonal heterogeneity and evolution in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
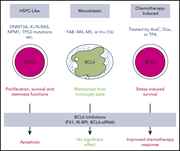
BCL6 maintains survival and self-renewal of primary human acute myeloid leukemia cells
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
Effect of hydroxyurea exposure before puberty on sperm parameters in males with sickle cell disease
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
In these two short reports, the authors approach the issue of whether hydroxyurea (HU) use in young males has major irreversible effects on sperm production. Joseph et al analyzed and compared sperm parameters in male patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) who were exposed or not exposed to HU before puberty. They report semen abnormalities in all patients but no differences between groups. Independently, Gille et al provide evidence for the lack of in vivo HU-related decreases in the spermatogonial pool in biopsy specimens from young males with SCD but evidence for a negative effect of SCD itself. Together, these reports suggest that the use of HU in young males does not adversely affect fertility.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
Structural, functional, and mechanistic insights uncover the fundamental role of orphan connexin-62 in platelets
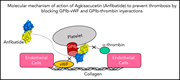
Structure of the platelet glycoprotein Ib receptor in complex with a novel antithrombotic agent
Brief Report
Agkisacucetin is a novel venom-derived antithrombotic drug candidate currently in phase 2 clinical trials. To understand its mechanism of action, Wang and colleagues solved the crystal structure of the glycoprotein Ib α chain (GPIbα) N-terminal domain in complex with agkisacucetin, revealing that the drug can sterically block the interaction of GPIb receptor with both von Willebrand factor and thrombin proteins, thereby inhibiting platelet function.
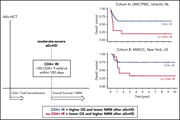
TRANSPLANTATION
CD4+ T-cell reconstitution predicts survival outcomes after acute graft-versus-host-disease: a dual-center validation
Clinical Trials & Observations
LETTER TO BLOOD
Hydroxyurea does not affect the spermatogonial pool in prepubertal patients with sickle cell disease
Clinical Trials & Observations
In these two short reports, the authors approach the issue of whether hydroxyurea (HU) use in young males has major irreversible effects on sperm production. Joseph et al analyzed and compared sperm parameters in male patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) who were exposed or not exposed to HU before puberty. They report semen abnormalities in all patients but no differences between groups. Independently, Gille et al provide evidence for the lack of in vivo HU-related decreases in the spermatogonial pool in biopsy specimens from young males with SCD but evidence for a negative effect of SCD itself. Together, these reports suggest that the use of HU in young males does not adversely affect fertility.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Overview of glycoprotein Ib α chain (GPIbα)– agkisacucetin interactions. GPIbα is colored in magenta and shown in cartoon representation. Agkisacucetin is shown in surface representation with electrostatic potential from –3.0 (red) to +3.0 (blue). See the article by Wang et al on page 844.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






TTP: the evolution of clinical practice