Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
HOW I TREAT
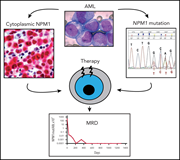
How I diagnose and treat NPM1-mutated AML
NPM1 mutations are present in approximately one-third of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients. With a series of 4 illustrative cases, Falini et al describe the diagnosis and treatment of NPM1-mutated AML, including diagnosis, primary therapy, the value of measurable residual disease monitoring, and the role of allogeneic stem cell transplantation.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
A phase 2 study of venetoclax plus R-CHOP as first-line treatment for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a heterogeneous disease with variable prognosis, with Bcl-2–overexpressing lymphoma having inferior outcomes when treated with standard R-CHOP therapy. Through indirect comparison, Morschhauser et al demonstrate that the addition of venetoclax to R-CHOP appears to improve progression-free survival in Bcl-2–overexpressing DLBCL at the expense of additional toxicity.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
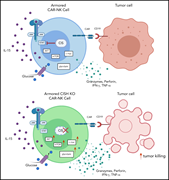
Targeting a cytokine checkpoint enhances the fitness of armored cord blood CAR-NK cells
The development of chimeric antigen receptor–natural killer (CAR-NK) cells for antitumor immunotherapy offers the attraction of preparing off-the-shelf cellular products, avoiding issues of autologous T-cell collection and engineering. Here the authors demonstrate that the activity of NK cells engineered to express a CAR plus IL-15 is enhanced by elimination of a cytokine checkpoint gene, promoting improved metabolic fitness and antitumor activity.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Efficacy and safety results from CheckMate 140, a phase 2 study of nivolumab for relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
The prognostic impact of infiltrating T cells and macrophages and the results in prior small studies have suggested that immune checkpoint inhibition could be effective in treating follicular lymphoma (FL). Armand and colleagues report results of a phase 2 study of nivolumab in relapsed or refractory FL. The results were disappointing, with only 4% response, but secondary analyses identify gene expression signatures predicting response that may inform future immunotherapeutic approaches.
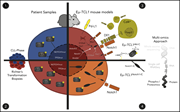
Active Akt signaling triggers CLL toward Richter transformation via overactivation of Notch1
Richter transformation (RT) is a rare but lethal complication of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Although it arises in the subset of patients with molecular features of high-risk disease, the majority of high-risk patients do not undergo transformation. Kohlhaas et al delineated a candidate pathway toward development of RT in patient samples and genetic studies using Eμ-TCL1 mice, demonstrating that constitutive AKT signaling interacts with Notch1 to promote RT, offering a potential biomarker for transformation and an entry point for directed therapy.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
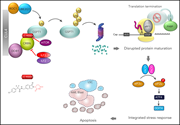
CC-90009, a novel cereblon E3 ligase modulator, targets acute myeloid leukemia blasts and leukemia stem cells
Modulation of protein degradation pathways to target disease-driving proteins has broad potential for a range of malignancies. Surka et al describe a novel small molecule that modulates cereblon E3 ligase to bind a specific protein, GSPT1, and induce its proteasomal degradation. Degradation of GSPT1 led to apoptosis in primary patient xenografts from 35 patients.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
TRANSFUSION MEDICINE
Platelet extracellular vesicles mediate transfusion-related acute lung injury by imbalancing the sphingolipid rheostat
About half of transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) is related to transfusion of allogeneic antibodies that damage the recipient endothelium, but nonimmune TRALI is not well understood; studies suggest it is increased in relation to platelet-storage time. McVey and colleagues related this storage lesion to platelet extracellular vesicles (EVs), demonstrating that time in storage increases the number of EVs and shifts their content toward ceramide, which disrupts the lung endothelial barrier.
TRANSPLANTATION
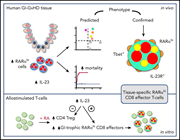
Retinoic acid–responsive CD8 effector T cells are selectively increased in IL-23–rich tissue in gastrointestinal GVHD
Ball and colleagues investigated the role of retinoic acid (RA)–responsive T cells in acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract in primary biopsy specimens and peripheral blood samples. They demonstrate that in the posttransplant inflammatory GI environment, increased interleukin-23 (IL-23) secretion facilitates trafficking of a population of RA-responsive CD8 effector T cells expressing T-bet and the IL-23 receptor and reduces CD4 regulatory T cells, offering a novel potential target for prevention of GI GVHD.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
A cocrystal structure of DDB1 (purple), cereblon (blue), GSPT1 (orange), and CC-90009 (yellow, inset), a novel cereblon E3 ligase modulator that targets acute myeloid leukemia blasts and leukemia stem cells. See the article by Surka et al on page 661.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals







Bcl-2 inhibition in DLBCL: “the times they are a-changing”?
Clinical Trials & Observations