Key Points
CC-90009 selectively degrades GSPT1, resulting in acute AML apoptosis and elimination of disease-driving LSCs.
The anti-AML activity of CC-90009 is regulated by the ILF2/ILF3 complex, the mTOR pathway, and the integrated stress response pathway.
Abstract
A number of clinically validated drugs have been developed by repurposing the CUL4-DDB1-CRBN-RBX1 (CRL4CRBN) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex with molecular glue degraders to eliminate disease-driving proteins. Here, we present the identification of a first-in-class GSPT1-selective cereblon E3 ligase modulator, CC-90009. Biochemical, structural, and molecular characterization demonstrates that CC-90009 coopts the CRL4CRBN to selectively target GSPT1 for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Depletion of GSPT1 by CC-90009 rapidly induces acute myeloid leukemia (AML) apoptosis, reducing leukemia engraftment and leukemia stem cells (LSCs) in large-scale primary patient xenografting of 35 independent AML samples, including those with adverse risk features. Using a genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screen for effectors of CC-90009 response, we uncovered the ILF2 and ILF3 heterodimeric complex as a novel regulator of cereblon expression. Knockout of ILF2/ILF3 decreases the production of full-length cereblon protein via modulating CRBN messenger RNA alternative splicing, leading to diminished response to CC-90009. The screen also revealed that the mTOR signaling and the integrated stress response specifically regulate the response to CC-90009 in contrast to other cereblon modulators. Hyperactivation of the mTOR pathway by inactivation of TSC1 and TSC2 protected against the growth inhibitory effect of CC-90009 by reducing CC-90009-induced binding of GSPT1 to cereblon and subsequent GSPT1 degradation. On the other hand, GSPT1 degradation promoted the activation of the GCN1/GCN2/ATF4 pathway and subsequent apoptosis in AML cells. Collectively, CC-90009 activity is mediated by multiple layers of signaling networks and pathways within AML blasts and LSCs, whose elucidation gives insight into further assessment of CC-90009s clinical utility. These trials were registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02848001 and #NCT04336982).
Introduction
Small-molecule degraders that hijack an E3 ubiquitin ligase to target disease-driving proteins for degradation are emerging as a promising therapeutic modality.1-3 Substantial advancements in this field are reflected by the development of immunomodulatory (IMiD) drugs, next-generation cereblon E3 ligase modulating (CELMoD) agents, and numerous heterobifunctional proteolysis-targeting chimeras.4-11 Acting as “molecular glue,” cereblon-modulating agents repurpose the CRL4CRBN E3 ubiquitin ligase to promote the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of cereblon neosubstrates.12-17 Molecular insights into the mechanism of action of immunomodulatory drugs in multiple myeloma and myelodysplastic syndrome with deletion of chromosome 5q accelerated the identification of novel cereblon neosubstrates14-17 and laid out a solid foundation for the discovery and development of next-generation cereblon modulators. Recently, a number of novel neosubstrates of IMiDs including ZFP91, SALL4, and WIZ were discovered,18-22 and several novel cereblon modulators, such as CC-122, CC-220, and CC-885 targeting well-established or novel cereblon neosubstrates, were developed to treat various hematological malignancies.5-7
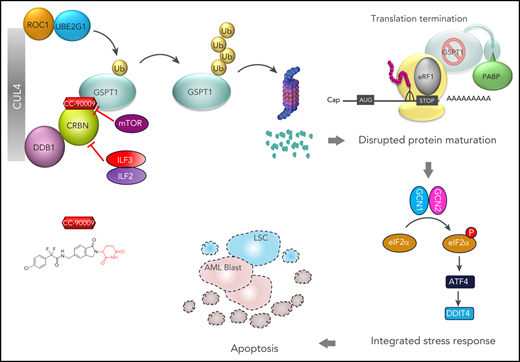
Although several promising therapies have been developed for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) that target specific genetic and epigenetic mutations,23-25 effective options for patients with poor risk cytogenetic features, or relapsed and refractory disease are still needed. GSPT1 is a small GTPase, which forms a complex with the translation termination factor eRF1 to mediate translation termination. GTP hydrolysis by GSPT1 promotes a conformational change in eRF1, thereby triggering peptide release from the ribosome-bound transfer RNA adjacent to a stop codon.26 Inactivation of the eRF1/GSPT1 complex results in translational read-through.27 GSPT1 was also known to recruit UPF1 to stalled ribosomes to induce nonsense-mediated decay of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) containing premature stop codons.28 Targeted degradation of GSPT1 by CC-885 elicits broad antitumor activity in AML.5 However, the clinical development of CC-885 was challenging owing to unmanageable off-target toxicities associated with the degradation of multiple neosubstrates including GSPT1, CK1α, HBS1L, IKZF1 (Ikaros), and IKZF3 (Aiolos). Moreover, although the degradation of GSPT1 is required for the anti-AML activity of CC-885, the missing mechanistic link between GSPT1 degradation and the subsequent anti-AML effect further hindered the development of CC-885.5 Here, we describe the discovery of a GSPT1-selective CELMoD agent (CC-90009), the mechanisms of its action, and preclinical efficacy across a wide spectrum of primary AML patient samples.
Methods
Genome-wide CRISPR screen
A total of 6 × 108 U937 cells stably expressing Cas9 protein were inoculated with a small guide RNA (sgRNA) library-containing lentiviral supernatant at a multiplicity of infection of 0.3 according to the Cellecta CRISPR screening guide. Cells were grown in 2-L flasks with agitation and at least 200 million cells were kept after each passage to exceed the 150,000 library complexity by more than 1000-fold, maintaining library representation. CC-90009 was replenished after the first 5 days of treatment. A total of 9 × 107 cell pellets were collected in technical duplicates at day 3 and day 12 postinfection for genomic DNA isolation and sequencing library preparation.
Detailed materials and methods can be found in the supplemental Methods, available on the Blood Web site.
Results
Identification of CC-90009, a novel CELMoD agent that possesses potent anti-AML activity
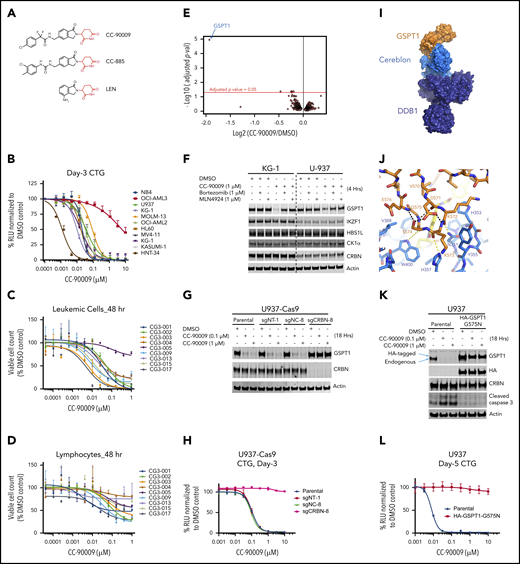
To identify compounds that possess anti-AML activity in a library of cereblon modulators, we performed a CellTiter-Glo cell viability screen in 11 human AML cell lines, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from healthy donors, and THLE-2, a hepatocyte cell line expressing phenotypic characteristics of normal adult liver epithelial cells. We identified a novel CELMoD agent, CC-90009, which demonstrated potent antiproliferative activity in 10 of 11 cell lines (Figure 1A-B; supplemental Figure 1A), with much less effect on the cell viability of PBMCs and THLE-2. By contrast, CC-885 was cytotoxic in all tested cell lines and PBMCs, whereas lenalidomide and pomalidomide showed no activity (supplemental Figure 1A-B). The antiproliferative effect of CC-90009 is associated with apoptosis induction in all tested AML cell lines except OCI-AML3 (supplemental Figure 1C). CC-90009 resistance in OCI-AML3 is associated with insufficient GSPT1 degradation, and RNA interference-mediated partial GSPT1 knockdown restored CC-90009 activity (supplemental Figure 1D).
CC-90009, a GSPT1-selective cereblon modulator, induces cereblon-and GSPT1-dependent anti-AML activity. (A) The chemical structures of CC-90009, CC-885, and lenalidomide (LEN) with the glutarimide ring shown in red. (B) The antiproliferative effect of CC-90009 in AML cell lines. Cells were incubated with DMSO or CC-90009 at the indicated concentrations. At day 3, cell proliferation was assessed by the Cell-Titer Glo (CTG) assay. (C-D) The effect of CC-90009 on cell viability of leukemic cells (C) and normal lymphocytes (D) in bone marrow aspirates of AML patients. Cells were treated with DMSO or increasing concentrations of CC-90009 for 48 hours. Cells were then stained with fluorescently labeled antibodies and Annexin-V, followed by flow cytometry to determine the cell number of live leukemic cells and lymphocytes. Data shown in panels C and D are presented as the percentage of viable cell counts in CC-90009-treated patient samples relative to DMSO controls. (E) Volcano plot of differentially abundant proteins in response to CC-90009 treatment relative to DMSO control. KG1 cells were treated with DMSO or 100 nM CC-90009 for 4 hours and subjected to tandem mass tag proteomics analysis. The x-axis indicates the log2–fold change of CC-90009 vs DMSO control for each protein. P values were corrected for multiple hypothesis testing using the Benjamini-Hochberg method to arrive at an adjusted P value (adj-P; also known as a false discovery rate). The y-axis is the -log10 (adj-P) values indicating statistical significance such that proteins lying above the dotted red line are statistically significant findings with adj-P <.05. (F) Immunoblot analysis of KG1 and U937 cells treated with DMSO or CC-90009 for 4 hours. Where indicated, cells were pretreated with mortezomib or MLN4924 or 30 minutes. (G-H) Immunoblot analysis (G) and cell proliferation (H) of U937-Cas9 parental cells or cells stably transduced with lentiviral vectors expressing a nontargeting sgRNA (sgNT-1), an sgRNA targeting a noncoding region (sgNC-8), or an sgRNA targeting CRBN (sgCRBN-8). Cells were treated with DMSO or CC-90009 at indicated concentrations. Crystal structure of GSPT1 in complex with cereblon, DDB1 and CC-90009. (I) Surface representation of the complex with DDB1 shown in purple, cereblon in blue, and GSPT1 in orange. The position of CC-90009 is shown with an arrow. (J) GSPT1 interaction with cereblon is mediated by a β-hairpin loop. Hydrogen bond interactions between cereblon and the GPST1 β-hairpin are shown as yellow dashes. (K-L) Immunoblot analysis (K) and cell proliferation (L) of U937 parental cells or cells stably expressing HA-GSPT1-G575N. Cells were treated with DMSO or CC-90009 at the indicated concentrations. Data in panels B-D, G, and L are shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD), n = 3 technical replicates. Result shown in all figure panels is representative of 3 biological replicates.
CC-90009, a GSPT1-selective cereblon modulator, induces cereblon-and GSPT1-dependent anti-AML activity. (A) The chemical structures of CC-90009, CC-885, and lenalidomide (LEN) with the glutarimide ring shown in red. (B) The antiproliferative effect of CC-90009 in AML cell lines. Cells were incubated with DMSO or CC-90009 at the indicated concentrations. At day 3, cell proliferation was assessed by the Cell-Titer Glo (CTG) assay. (C-D) The effect of CC-90009 on cell viability of leukemic cells (C) and normal lymphocytes (D) in bone marrow aspirates of AML patients. Cells were treated with DMSO or increasing concentrations of CC-90009 for 48 hours. Cells were then stained with fluorescently labeled antibodies and Annexin-V, followed by flow cytometry to determine the cell number of live leukemic cells and lymphocytes. Data shown in panels C and D are presented as the percentage of viable cell counts in CC-90009-treated patient samples relative to DMSO controls. (E) Volcano plot of differentially abundant proteins in response to CC-90009 treatment relative to DMSO control. KG1 cells were treated with DMSO or 100 nM CC-90009 for 4 hours and subjected to tandem mass tag proteomics analysis. The x-axis indicates the log2–fold change of CC-90009 vs DMSO control for each protein. P values were corrected for multiple hypothesis testing using the Benjamini-Hochberg method to arrive at an adjusted P value (adj-P; also known as a false discovery rate). The y-axis is the -log10 (adj-P) values indicating statistical significance such that proteins lying above the dotted red line are statistically significant findings with adj-P <.05. (F) Immunoblot analysis of KG1 and U937 cells treated with DMSO or CC-90009 for 4 hours. Where indicated, cells were pretreated with mortezomib or MLN4924 or 30 minutes. (G-H) Immunoblot analysis (G) and cell proliferation (H) of U937-Cas9 parental cells or cells stably transduced with lentiviral vectors expressing a nontargeting sgRNA (sgNT-1), an sgRNA targeting a noncoding region (sgNC-8), or an sgRNA targeting CRBN (sgCRBN-8). Cells were treated with DMSO or CC-90009 at indicated concentrations. Crystal structure of GSPT1 in complex with cereblon, DDB1 and CC-90009. (I) Surface representation of the complex with DDB1 shown in purple, cereblon in blue, and GSPT1 in orange. The position of CC-90009 is shown with an arrow. (J) GSPT1 interaction with cereblon is mediated by a β-hairpin loop. Hydrogen bond interactions between cereblon and the GPST1 β-hairpin are shown as yellow dashes. (K-L) Immunoblot analysis (K) and cell proliferation (L) of U937 parental cells or cells stably expressing HA-GSPT1-G575N. Cells were treated with DMSO or CC-90009 at the indicated concentrations. Data in panels B-D, G, and L are shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD), n = 3 technical replicates. Result shown in all figure panels is representative of 3 biological replicates.
The anti-AML activity of CC-90009 was further evaluated using the PharmaFlow assay on a panel of diagnostic bone marrow samples obtained from 9 AML patients.29 Rapid and highly efficient loss of viable leukemic cells was detected in 8 of 9 patient samples at 48 hours posttreatment with CC-90009 (Figure 1C), and nearly all leukemic cells were eliminated within 96 hours (supplemental Figure 1E). By contrast, CC-90009 showed much lower activity against normal lymphocytes obtained from the same patient (Figure 1D; supplemental Figure 1E-F).
Next, we assessed the effect of CC-90009 on the global proteome in KG-1 AML cells using mass spectrometry. CC-90009 treatment reduced the GSPT1 protein abundance with minimal effect on the rest of the proteome (Figure 1E), and immunoblotting confirmed the specific degradation of GSPT1 but not other known CC-885 neosubstrates including IKZF1, HBS1L, and CK1α (Figure 1F). The CC-90009-induced GSPT1 downregulation can be blocked by proteasomal inhibition with bortezomib, or inactivation of the CRL4CRBN complex with MLN4924 or CRBN knockout (Figure 1F-G; supplemental Figure 1G-H). Moreover, CC-90009 promoted the binding of cereblon to GSPT1 but not IKZF1 when added directly into the binding assays performed with cell extracts, whereas lenalidomide exhibited binding selectivity toward IKZF1 over GSPT1 (supplemental Figure 2A). The cereblonY384A/W386A(YWAA)12,13,30 mutant defective in binding cereblon modulators cannot interact with GSPT1 or IKZF1 in the presence of CC-90009 or lenalidomide, respectively (supplemental Figure 2A). These data suggest that CC-90009 specifically recruits GSPT1 to cereblon for ubiquitination and degradation.
Targeted degradation of GSPT1 by CC-90009 via a glycine-containing degron mediates the anti-AML activity
To further define the molecular basis of CC-90009’s activity, we cocrystalized it in complex with GSPT1, DDB1, and cereblon (Figure 1I-J; supplemental Figure 2B-C). The overall binding mode of DDB1-cereblon-GSPT1-CC-90009 is similar to the previously reported structure of DDB1-cereblon-GSPT1-CC-885 (PDB: 5HXB).5 GSPT1 interaction with cereblon and CC-90009 is mediated by a β-hairpin degron loop formed by GSPT1 residues 568 through 576 (Figure 1J). Hydrogen bond interactions are formed between the backbone carbonyls of GSPT1 residues K572, K573, and S574 and cereblon residues N351, H357, and W400, respectively (Figure 1J). The glutarimide moiety of CC-90009 binds the cereblon tritryptophan pocket,12,13 presenting the isoindolinone ring above the cereblon surface such that it forms Van der Waals and hydrophobic interactions with GSPT1 residue G575 (supplemental Figure 2C). As observed with CC-885, the GSPT1 G575N mutation conferred complete resistance to CC-90009-induced degradation (Figure 1K; supplemental Figure 2E-F). CC-90009 extends from the isoindolinone, making a hydrogen bond interaction between the difluoroacetamide moiety and the side chain of cereblon residue H353 and positioning the chlorophenyl moiety proximal to the β-sheet core of GSPT1 domain 3 (supplemental Figure 2C). A notable difference in the side chain position of cereblon residue E377 is observed relative to the CC-885 structure, suggesting a lack of interaction between E377 and CC-90009, which might contribute to the differential substrate selectivity of CC-90009 and CC-885 (supplemental Figure 2D).
Although ablation of CRBN completely abolished the antiproliferative effect of CC-90009 in U937, OCI-AML2, and MOLM-13 (Figure 1H; supplemental Figure 1G-H), it is possible that the anti-AML activity of CC-90009 is mediated through GSPT1 and/or additional substrate(s) that cannot be detected by mass spectrometry owing to technological limitations. To explore this hypothesis, we determined the antiproliferative effect of CC-90009 in U937, OCI-AML2 and MOLM-13 parental cells, and cells stably overexpressing GSPT1-G575N. GSPT1 stabilization completely inhibited the response to CC-90009 (Figure 1L; supplemental Figure 2E-F), ruling out the participation of other substrates in the anti-AML effect of CC-90009. Moreover, RNA interference-mediated GSPT1 knockdown led to rapid loss of cell fitness in U937 cells (supplemental Figure 2G), consistent with our previous observations.5 Thus, GSPT1 degradation is both necessary and sufficient to account for the anti-AML activity of CC-90009.
Genome-wide CRISPR screen reveals the mechanism of action of CC-90009 in AML
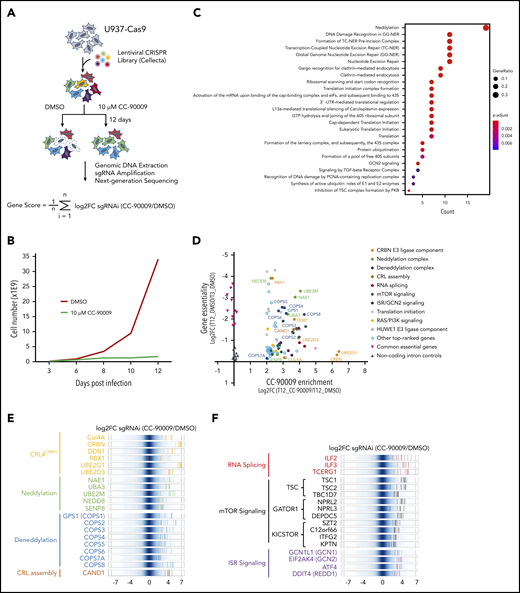
To further elucidate the mechanism of action of CC-90009 in AML, we performed a genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screen to delineate genes and pathways that govern the response to CC-90009 (Figure 2A). U937 cells stably expressing Cas9 were transduced with a pooled lentiviral library targeting ∼19,000 protein-encoding genes, followed by treatment with CC-90009 or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). As expected, CC-90009 treatment led to cell growth arrest and significantly affected the sgRNA distribution as compared with DMSO control (Figure 2B; supplemental Figure 3A).
Identification of genes and pathways modulating the response to CC-90009 via CRIPSR/Cas9 screen. (A) Schematic showing the design of the genome-wide CRISPR screen to identify molecular determinants of CC-90009 response. At day 3 posttransduction, cells were treated with 10 µM CC-90009 or DMSO vehicle control for an additional 9 days, followed by amplification of sgRNA coding regions and next-generation sequencing. The log2 fold change (log2FC) in sgRNA read count in the CC-90009-treated sample as compared with DMSO control was designated as the enrichment score, and the average log2FC value of all sgRNAs for a gene of interest was used to quantify the effect of gene knockout on CC-90009 response. (B) Cell proliferation curve of U937-Cas9 cells transduced with the lentiviral sgRNA library and treated with DMSO or CC-90009. Three days posttransduction, cells were treated with DMSO or 10 µM CC-90009 for 9 days. (C) Pathway enrichment analysis of genes enriched by CC-90009 treatment with log2FC >2 and false discovery rate (FDR) <0.05 relative to DMSO control. The color and size of the dots represent adjusted significance level and gene ratio, respectively. Gene ratio refers to the number of input genes annotated to an individual pathway as a ratio of all input genes annotated to any Reactome pathway. (D) Scatter plot of 78 genes significantly enriched by CC-90009 (log2FC >2 and FDR <0.05). X-axis, CC-90009 enrichment score shown as log2FC (T12_CC-90009 vs T12_DMSO); y-axis, gene essentiality score shown as log2FC (T12_DMSO vs T3_DMSO). Some of these genes were grouped into 10 functional modules with different color coding. (E,F) Log2FC values of sgRNAs targeting CC-90009 enriched genes in the functional modules as indicated. Background shown in dark blue represents the log2FC values of all sgRNAs in the library. Each solid line with a color representing a functional module indicates the log2FC value of an individual sgRNA. Well-characterized genes known to be essential for the activity of the cereblon E3 ligase complex (E); novel genes that regulate the response to CC-90009 with no clear mechanistic understanding (F). Note that in panels E and F, multiple sgRNAs targeting each of these top-ranked genes were significantly enriched by CC-90009, strongly supporting the on-target gene knockout effect.
Identification of genes and pathways modulating the response to CC-90009 via CRIPSR/Cas9 screen. (A) Schematic showing the design of the genome-wide CRISPR screen to identify molecular determinants of CC-90009 response. At day 3 posttransduction, cells were treated with 10 µM CC-90009 or DMSO vehicle control for an additional 9 days, followed by amplification of sgRNA coding regions and next-generation sequencing. The log2 fold change (log2FC) in sgRNA read count in the CC-90009-treated sample as compared with DMSO control was designated as the enrichment score, and the average log2FC value of all sgRNAs for a gene of interest was used to quantify the effect of gene knockout on CC-90009 response. (B) Cell proliferation curve of U937-Cas9 cells transduced with the lentiviral sgRNA library and treated with DMSO or CC-90009. Three days posttransduction, cells were treated with DMSO or 10 µM CC-90009 for 9 days. (C) Pathway enrichment analysis of genes enriched by CC-90009 treatment with log2FC >2 and false discovery rate (FDR) <0.05 relative to DMSO control. The color and size of the dots represent adjusted significance level and gene ratio, respectively. Gene ratio refers to the number of input genes annotated to an individual pathway as a ratio of all input genes annotated to any Reactome pathway. (D) Scatter plot of 78 genes significantly enriched by CC-90009 (log2FC >2 and FDR <0.05). X-axis, CC-90009 enrichment score shown as log2FC (T12_CC-90009 vs T12_DMSO); y-axis, gene essentiality score shown as log2FC (T12_DMSO vs T3_DMSO). Some of these genes were grouped into 10 functional modules with different color coding. (E,F) Log2FC values of sgRNAs targeting CC-90009 enriched genes in the functional modules as indicated. Background shown in dark blue represents the log2FC values of all sgRNAs in the library. Each solid line with a color representing a functional module indicates the log2FC value of an individual sgRNA. Well-characterized genes known to be essential for the activity of the cereblon E3 ligase complex (E); novel genes that regulate the response to CC-90009 with no clear mechanistic understanding (F). Note that in panels E and F, multiple sgRNAs targeting each of these top-ranked genes were significantly enriched by CC-90009, strongly supporting the on-target gene knockout effect.
Pathway enrichment analysis of top-ranked genes yielded a few protein complexes and signaling cascades that regulate the response to CC-90009 (Figure 2C-D; supplemental Figure 3B; supplemental Tables 1 and 2). As expected, a significant fraction of CC-90009-enriched genes encode proteins known to be essential for the biological activities of all cereblon modulators, including subunits of the CRL4CRBN complex and the COP9 signalosome, ubiquitin conjugation enzymes UBE2D3 and UBE2G1, components of the NEDD8 conjugation pathway, and the Cullin Ring E3 ligase assembly factor CAND1 (Figure 2D-E).31-35 Additionally, we uncovered a few candidate genes that have not been previously reported to affect the response to other cereblon modulators. These include modulators of RNA alternative splicing including ILF2 and ILF3, suppressors of mTOR signaling including TSC1 and TSC2, and key components of the integrated stress response pathway including GCN1(GCN1L1), GCN2(EIF2AK4), and ATF4 (Figure 2C,F).
Loss of ILF2 or ILF3 blocks the maturation of full-length CRBN mRNA, thereby diminishing the response to CC-90009
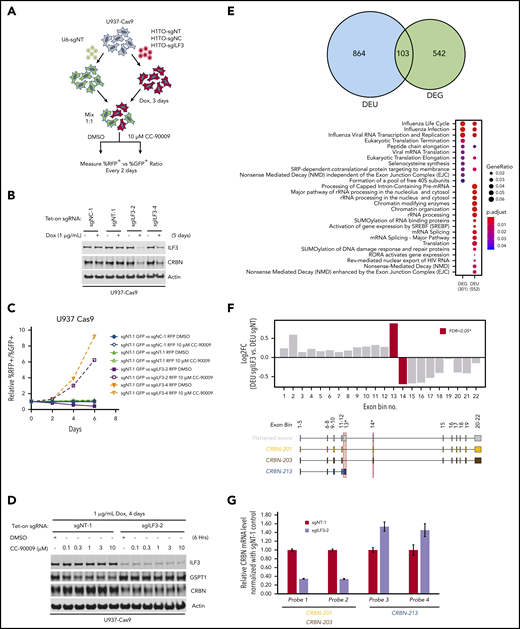
To ascertain if inactivation of ILF3 abrogates the response to CC-90009, we used a flow cytometry-based CRISPR competition assay to discern the effect of ILF3 knockout on cell fitness with or without CC-90009 treatment (Figure 3A). Doxycycline-induced expression of sgILF3, but not a control sgRNA, sgNT, or sgNC, triggered effective knockout of ILF3 in U937 cells, leading to significant enrichment of ILF3-depleted cells over control cells, consistent with the CRISPR screen (Figure 3B-C). ILF3 loss drastically reduced cereblon expression, and hence CC-90009-induced GSPT1 degradation and growth inhibition (Figure 3B,D; supplemental Figure 4C). ILF2(NF45) and ILF3(NF90) form a heterodimeric complex, which is known to regulate gene expression at multiple levels.36-40 ILF2 knockout displayed the same effect as did ILF3 knockout in U937 (supplemental Figure 4A-C). Additionally, the effects of ILF2 or ILF3 ablation on cereblon expression and CC-90009 response can also be observed in OCI-AML2 cells (supplemental Figure 4D-E).
Regulation of CRBN splicing and CC-90009 response by the ILF2 and ILF3 complex. (A-C) Assessment of the effect of ILF3 knockout on CC-90009 response by a flow cytometry-based CRISPR competition assay. U937 cells stably expressing Cas9 were infected with lentiviral vectors coexpressing RFP and a nontargeting sgRNA (sgNT-1), an sgRNA targeting a noncoding region (sgNC-1), or an sgRNA targeting ILF3 (sgILF3-2 or sgILF3-4). The expression of RFP is driven by an EF1a-HTLV hybrid promoter, whereas the expression of sgRNAs was under the control of a doxycycline-inducible H1/TO promoter. Three days after sgRNA induction with 1 μg/mL doxycycline, the cells were mixed at a 1:1 ratio with U937 Cas9 cells infected with a lentiviral vector constitutively expressing GFP and a nontargeting sgRNA (sgNT-1) and treated with DMSO or 10 μM CC-90009. The change of RFP+/GFP+ ratio was monitored by flow cytometry every 2 days thereafter. (A) Schematic design of the flow cytometry-based CRISPR competition assay. (B) Immunoblot analysis of U937-Cas9 cells inducibly expressing sgNT-1, sgNC-1, sgILF3-2, or sgILF3-4. Cells were treated with doxycycline (DOX) for 6 days. (C) The RFP+/GFP+ ratios of U937-Cas9 cells coexpressing RFP and sgNT-1, sgNC-1, sgILF3-2, or sgILF3-4 mixed with cells coexpressing GFP and sgNT-1 at each indicated timepoint were normalized to the RFP+/GFP+ ratio of the cell mixtures on day 0. (D) Immunoblot analysis of U937-Cas9 cells stably expressing sgNT-1 or sgILF3-2 under the control of the H1/TO promoter. Cells were treated with or without DOX for 4 days, followed by incubation with DMSO or an increasing concentration of CC-90009 for 6 hours. (E) RNA sequencing analysis of U937-Cas9 cells with inducible expression sgNT-1 or sgILF3-2 for 7 days. Evidence of differential splicing was observed in a total of 967 unique genes by up- and/or downregulated exon usage with ILF3 knockout in U937 cells, reaching a corrected significance level (FDR) <0.05. At the gene level, 791 genes were found to be significantly (FDR <0.05) up- or downregulated with ILF3 knockout. Top: Venn diagram showing the overlap of genes with significant differential exon usage (DEU; LHS) and genes with differential expression at the gene-level (DEG; RHS). Bottom: pathway enrichment analysis of DEU and DEG genes. The color and size of the dots represent adjusted significance level and gene ratio respectively. Gene ratio refers to the number of input genes annotated to an individual pathway as a ratio of all input genes annotated to any Reactome pathway. (F) DEU analysis revealed significant differential splicing of individual CRBN exons (red bars) with knockout of ILF3. An exon, which annotates to the truncated transcript, CRBN.213 (exon bin no.13), is significantly elevated (FDR, 0.02) with ILF3 knockout relative to NT controls. Conversely, exons downstream of this isoform are significantly underrepresented (FDR, 0.05; exon bin no. 14) in the ILF3 knockout cells relative to parental. (G) Quantitative PCR analysis of the expression levels of CRBN transcripts as indicated in U937-Cas9 cells with inducible expression sgNT-1 or sgILF3-2 for 7 days. Data in panel G are shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD), n = 4 technical replicates. Result shown in all figure panels is representative of 3 biological replicates.
Regulation of CRBN splicing and CC-90009 response by the ILF2 and ILF3 complex. (A-C) Assessment of the effect of ILF3 knockout on CC-90009 response by a flow cytometry-based CRISPR competition assay. U937 cells stably expressing Cas9 were infected with lentiviral vectors coexpressing RFP and a nontargeting sgRNA (sgNT-1), an sgRNA targeting a noncoding region (sgNC-1), or an sgRNA targeting ILF3 (sgILF3-2 or sgILF3-4). The expression of RFP is driven by an EF1a-HTLV hybrid promoter, whereas the expression of sgRNAs was under the control of a doxycycline-inducible H1/TO promoter. Three days after sgRNA induction with 1 μg/mL doxycycline, the cells were mixed at a 1:1 ratio with U937 Cas9 cells infected with a lentiviral vector constitutively expressing GFP and a nontargeting sgRNA (sgNT-1) and treated with DMSO or 10 μM CC-90009. The change of RFP+/GFP+ ratio was monitored by flow cytometry every 2 days thereafter. (A) Schematic design of the flow cytometry-based CRISPR competition assay. (B) Immunoblot analysis of U937-Cas9 cells inducibly expressing sgNT-1, sgNC-1, sgILF3-2, or sgILF3-4. Cells were treated with doxycycline (DOX) for 6 days. (C) The RFP+/GFP+ ratios of U937-Cas9 cells coexpressing RFP and sgNT-1, sgNC-1, sgILF3-2, or sgILF3-4 mixed with cells coexpressing GFP and sgNT-1 at each indicated timepoint were normalized to the RFP+/GFP+ ratio of the cell mixtures on day 0. (D) Immunoblot analysis of U937-Cas9 cells stably expressing sgNT-1 or sgILF3-2 under the control of the H1/TO promoter. Cells were treated with or without DOX for 4 days, followed by incubation with DMSO or an increasing concentration of CC-90009 for 6 hours. (E) RNA sequencing analysis of U937-Cas9 cells with inducible expression sgNT-1 or sgILF3-2 for 7 days. Evidence of differential splicing was observed in a total of 967 unique genes by up- and/or downregulated exon usage with ILF3 knockout in U937 cells, reaching a corrected significance level (FDR) <0.05. At the gene level, 791 genes were found to be significantly (FDR <0.05) up- or downregulated with ILF3 knockout. Top: Venn diagram showing the overlap of genes with significant differential exon usage (DEU; LHS) and genes with differential expression at the gene-level (DEG; RHS). Bottom: pathway enrichment analysis of DEU and DEG genes. The color and size of the dots represent adjusted significance level and gene ratio respectively. Gene ratio refers to the number of input genes annotated to an individual pathway as a ratio of all input genes annotated to any Reactome pathway. (F) DEU analysis revealed significant differential splicing of individual CRBN exons (red bars) with knockout of ILF3. An exon, which annotates to the truncated transcript, CRBN.213 (exon bin no.13), is significantly elevated (FDR, 0.02) with ILF3 knockout relative to NT controls. Conversely, exons downstream of this isoform are significantly underrepresented (FDR, 0.05; exon bin no. 14) in the ILF3 knockout cells relative to parental. (G) Quantitative PCR analysis of the expression levels of CRBN transcripts as indicated in U937-Cas9 cells with inducible expression sgNT-1 or sgILF3-2 for 7 days. Data in panel G are shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD), n = 4 technical replicates. Result shown in all figure panels is representative of 3 biological replicates.
To investigate the mechanism by which the ILF2/ILF3 complex regulates cereblon expression, we performed mRNA-sequencing on U937-Cas9 cells expressing sgNT and sgILF3. ILF3 loss significantly affected the expression level of 645 genes, many of which are related to influenza infection and replication (Figure 3E). Additionally, ILF3 loss drastically changed the level of alternatively spliced transcripts of 967 genes involved in several cellular functions including pre-mRNA and ribosomal RNA processing, chromatin modification, and non-sense-mediated mRNA decay (Figure 3E). This transcriptomic analysis revealed a drastic change of exon usage of CRBN, but not its total mRNA level, in response to ILF3 loss (Figure 3E-F; supplemental Table 3). Human CRBN has 15 splicing variants, 2 of which (CRBN-201 and CRBN-203) produce a full-length functional protein (supplemental Figure 4F). ILF3 knockout reduced the mRNA level of CRBN-201 and CRBN-203 and increased the level of splicing variant CRBN-213, which is composed of exons 1 through 4 and a cryptic exon 5 containing a premature stop codon (Figure 3F; supplemental Figure 4F). Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis confirmed the effect of ILF3 loss on cereblon alternative splicing without affecting its total mRNA level (Figure 3G; supplemental Figure 4G).
Hyperactivation of the mTOR signaling pathway attenuates the response to CC-90009 via blockage of GSPT1 degradation
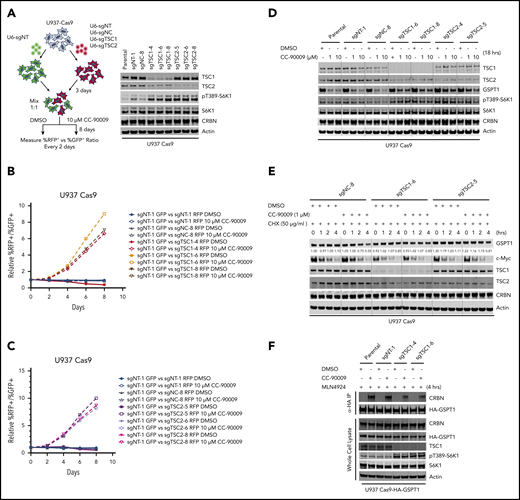
In response to amino acid and glucose stimulation, mTOR is translocated to the lysosomal surface, where it is activated by Rheb.41 The mTOR lysosomal translocation is negatively regulated by the KICSTOR complex and the GATOR1 complex, whereas Rheb is suppressed by the TSC complex.41 In the CRISPR screen, nearly every sgRNA targeting genes encoding subunits of the TSC complex, the GATOR1 complex, or the KICSTOR complex was enriched by CC-90009 treatment (Figure 2F). Knockout of TSC1 or TSC2 resulted in enhancement of S6K1 phosphorylation, indicating mTOR hyperactivation (Figure 4A; supplemental Figure 5A). Consistent with the CRISPR screen, TSC1 or TSC2 deficiency conferred a growth advantage in the presence of, but not in the absence of, CC-90009 in U937 and OCI-AML2, when tested in the CRISPR competition assay (Figure 4B-C; supplemental Figure 5B). TSC1 or TSC2 loss partially blocked CC-90009-induced GSPT1 degradation (Figure 4D; supplemental Figure 5C). Cotreatment with everolimus, an mTORC1 inhibitor, restored the CC-90009-induced degradation and growth inhibition (supplemental Figure 5D-E), suggesting that activation of the mTORC1 signaling attenuates the degradation of GSPT1, leading to diminished CC-90009 response.
Loss of TSC1 or TSC2 attenuates the response to CC-90009. A-C) Assessment of the effect of TSC1 or TSC2 knockout on CC-90009 response by a flow cytometry based CRISPR competition assay. U937 cells stably expressing Cas9 were infected with a lentiviral vector constitutively co-expressing GFP and sgNT-1, or with lentiviral vectors constitutively co-expressing RFP and sgNT-1, sgNC-8, or 1 of the 3 sgRNAs targeting TSC1 or TSC2 as indicated. Three days after infection, RFP and GFP cells were mixed at a 1:1 ratio and treated with DMSO or 10 μM CC-90009. The change of RFP+/GFP+ ratio was monitored by flow cytometry every 2 days thereafter. A) Left, schematic design of the flow cytometry based CRISPR competition assay. Right, confirmation of TSC1 or TSC2 knockout by immunoblot analysis. B) and C) The RFP+/GFP+ ratios of U937-Cas9 cells co-expressing RFP and sgNT-1, sgNC-8, or 1 of 3 sgRNAs targeting TSC1 (B) or TSC2 (C) mixed with cells co-expressing GFP and sgNT-1 at each indicated timepoint were normalized to the RFP+/GFP+ ratio of the cell mixtures on “Day 0”. D) and E) Immunoblot analysis of U937-Cas9 parental cells or cells stably expressing sgRNAs as indicated. Cells were treated with DMSO or CC-90009 in the absence (D) or presence (E) of cycloheximide. (F) Immunoblot analysis of anti-HA immunoprecipitates (top) or whole cell extracts (bottom) of U937-Cas9 parental cells or cells stably expressing the indicated sgRNAs. Cells were treated with MLN4924 and DMSO or CC-90009. Result shown in all figure panels is representative of 3 biological replicates.
Loss of TSC1 or TSC2 attenuates the response to CC-90009. A-C) Assessment of the effect of TSC1 or TSC2 knockout on CC-90009 response by a flow cytometry based CRISPR competition assay. U937 cells stably expressing Cas9 were infected with a lentiviral vector constitutively co-expressing GFP and sgNT-1, or with lentiviral vectors constitutively co-expressing RFP and sgNT-1, sgNC-8, or 1 of the 3 sgRNAs targeting TSC1 or TSC2 as indicated. Three days after infection, RFP and GFP cells were mixed at a 1:1 ratio and treated with DMSO or 10 μM CC-90009. The change of RFP+/GFP+ ratio was monitored by flow cytometry every 2 days thereafter. A) Left, schematic design of the flow cytometry based CRISPR competition assay. Right, confirmation of TSC1 or TSC2 knockout by immunoblot analysis. B) and C) The RFP+/GFP+ ratios of U937-Cas9 cells co-expressing RFP and sgNT-1, sgNC-8, or 1 of 3 sgRNAs targeting TSC1 (B) or TSC2 (C) mixed with cells co-expressing GFP and sgNT-1 at each indicated timepoint were normalized to the RFP+/GFP+ ratio of the cell mixtures on “Day 0”. D) and E) Immunoblot analysis of U937-Cas9 parental cells or cells stably expressing sgRNAs as indicated. Cells were treated with DMSO or CC-90009 in the absence (D) or presence (E) of cycloheximide. (F) Immunoblot analysis of anti-HA immunoprecipitates (top) or whole cell extracts (bottom) of U937-Cas9 parental cells or cells stably expressing the indicated sgRNAs. Cells were treated with MLN4924 and DMSO or CC-90009. Result shown in all figure panels is representative of 3 biological replicates.
To understand whether the effect of mTOR activation on CC-90009-induced GSPT1 degradation can be ascribed to an increased rate of GSPT1 protein synthesis and/or a decreased rate of GSPT1 degradation, we determined the change of GSPT1 protein half-life in response to TSC1 or TSC2 loss in the presence or absence of CC-90009. Cotreatment with CC-90009 and cycloheximide, a protein synthesis inhibitor, downregulated GSPT1 expression and TSC1 or TSC2 loss largely abrogated this effect, whereas cycloheximide treatment alone showed little effect on GSPT1 protein level in U937 parental, TSC1−/− and TSC2−/− cells (Figure 4E). mTOR hyperactivation also exhibited the same effect on the degradation of hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged GSPT1 induced by CC-90009, as compared with that of endogenous GSPT1 (supplemental Figure 5F). By contrast, TSC1 or TSC2 deficiency affected neither the pomalidomide-induced degradation of IKZF1 nor the half-life of IKZF1 in the presence or absence of pomalidomide (supplemental Figure 5G-H); we reasoned that mTOR activation might limit the accessibility of GSPT1 by cereblon without affecting the activity of the CRL4CRBN ligase or the 26S proteasome. Consistent with this hypothesis, TSC1 loss significantly reduced the interaction between HA-tagged GSPT1 and endogenous cereblon induced by CC-90009 (Figure 4F).
GSPT1 degradation triggers the activation of the integrated stress response pathway resulting in acute apoptosis
The integrated stress response (ISR) is an evolutionarily conserved homeostatic pathway that is activated by the phosphorylation of the translation initiation factor eIF2α by 1 of 4 homologous stress-sensing kinases, PERK, GCN2, HRI, or PKR, resulting in the inhibition of global protein translation and preferential translation of ISR effectors including ATF4.42,43 GCN2 forms a complex with GCN1 on translating ribosomes and activates the ATF4 pathway when sensing cellular stresses.44 In the CRISPR screen, nearly all sgRNAs targeting GCN1, GCN2, as well as ATF4 and its downstream transcriptional target gene DDIT4 were significantly enriched by CC-90009 (Figure 3F), whereas enrichment of sgRNAs targeting other eIF2α kinases including PERK(EIF2AK3), HRI(EIF2AK1), and PKR(EIF2AK2) was not observed (supplemental Table 1). Using the CRISPR competition assay we confirmed that loss of GCN1, GCN2, ATF4, or DDIT4 protected the cells against CC-90009-induced growth inhibition in U937 and OCI-AML2 (Figure 5A-D; supplemental Figure 6A-G), suggesting that activation of the GCN2-mediated ISR plays a critical role in the anti-AML effect of CC-90009. Indeed, CC-90009 treatment triggered the rapid phosphorylation of eIF2α; accumulation of ATF4 and its transcriptional targets DDIT4, CHOP, and ATF3; and subsequent induction of apoptosis (Figure 5E; supplemental Figure 6H). Quantitative RT-PCR analysis confirmed the marked induction of ATF4 target genes ATF3, CHOP, and DDIT4 at the mRNA level upon CC-90009 treatment (Figure 5F; supplemental Figure 6I). CC-90009 resistance in OCI-AML3 cells is linked to insufficient GSPT1 degradation and ISR activation, and partial knockdown of GSPT1 completely restored the response (supplemental Figure 1D). Stabilization of GSPT1 completely blocked the CC-90009-induced ISR activation and apoptosis, whereas knockdown of GSPT1 was sufficient to activate ISR (supplemental Figure 2E-G).
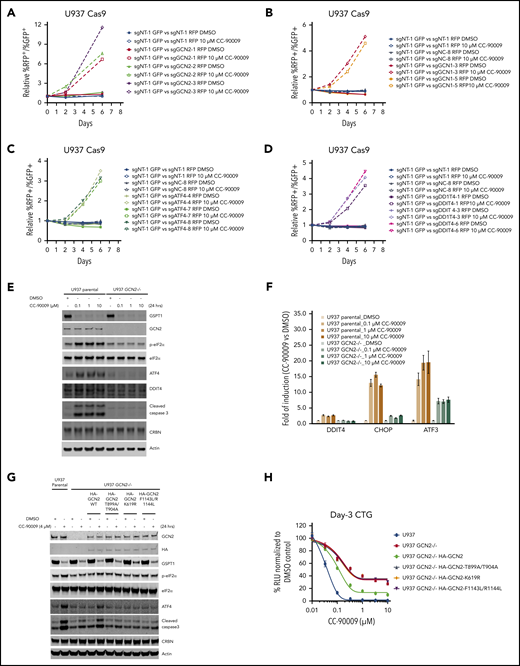
CC-90009 activates the GCN2-mediated integrated stress response and subsequent apoptosis in AML. Characterization of the role of (A) GCN2, (B) GCN1, (C) ATF4, and (D) DDIT4 in mediating CC-90009 response using a flow cytometry-based CRISPR competition assay. U937 cells stably expressing Cas9 were infected with a lentiviral vector constitutively coexpressing GFP and sgNT-1, or with lentiviral vectors constitutively coexpressing RFP and sgNT-1, sgNC-8, or 1 of the gene-specific sgRNAs as indicated. Three days after infection, RFP and GFP cells were mixed at a 1:1 ratio and treated with DMSO or 10 μM CC-90009. The change of RFP+/GFP+ ratio was monitored by flow cytometry every 2 days thereafter. The RFP+/GFP+ ratios of U937-Cas9 cells coexpressing RFP and sgNT-1, sgNC-8, or 1 of 3 sgRNAs targeting GCN2 (A), GCN1 (B), ATF4 (C), or DDIT4 (D) mixed with cells coexpressing GFP and sgNT-1 at each indicated timepoint were normalized to the RFP+/GFP+ ratio of the cell mixtures on day 0. (E-F) Immunoblot (E) or quantitative RT-PCR analysis (F) of U937 parental and GCN2−/− cells treated with DMSO or CC-90009 at the indicated concentrations for 24 hours. The U937 GCN2−/− cell line is derived from a single clone of U937 parental cells stably infected with a lentiviral CRISPR vector targeting GCN2 (see “Methods and materials”). (G) Immunoblot analysis of U937 parental cells and GCN2−/− cells with or without a stably transduced lentiviral vector expressing HA-tagged GCN2 wild-type or mutants as indicated. Cells were treated with DMSO or CC-90009 for 24 hours. (H) The effect of CC-90009 on proliferation of cells shown in panel G. On day 3 after CC-90009 treatment, cell proliferation was assessed by CTG. Data in panels F and G are shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD), n = 3 or 4 technical replicates. Result shown in all figure panels is representative of 3 biological replicates.
CC-90009 activates the GCN2-mediated integrated stress response and subsequent apoptosis in AML. Characterization of the role of (A) GCN2, (B) GCN1, (C) ATF4, and (D) DDIT4 in mediating CC-90009 response using a flow cytometry-based CRISPR competition assay. U937 cells stably expressing Cas9 were infected with a lentiviral vector constitutively coexpressing GFP and sgNT-1, or with lentiviral vectors constitutively coexpressing RFP and sgNT-1, sgNC-8, or 1 of the gene-specific sgRNAs as indicated. Three days after infection, RFP and GFP cells were mixed at a 1:1 ratio and treated with DMSO or 10 μM CC-90009. The change of RFP+/GFP+ ratio was monitored by flow cytometry every 2 days thereafter. The RFP+/GFP+ ratios of U937-Cas9 cells coexpressing RFP and sgNT-1, sgNC-8, or 1 of 3 sgRNAs targeting GCN2 (A), GCN1 (B), ATF4 (C), or DDIT4 (D) mixed with cells coexpressing GFP and sgNT-1 at each indicated timepoint were normalized to the RFP+/GFP+ ratio of the cell mixtures on day 0. (E-F) Immunoblot (E) or quantitative RT-PCR analysis (F) of U937 parental and GCN2−/− cells treated with DMSO or CC-90009 at the indicated concentrations for 24 hours. The U937 GCN2−/− cell line is derived from a single clone of U937 parental cells stably infected with a lentiviral CRISPR vector targeting GCN2 (see “Methods and materials”). (G) Immunoblot analysis of U937 parental cells and GCN2−/− cells with or without a stably transduced lentiviral vector expressing HA-tagged GCN2 wild-type or mutants as indicated. Cells were treated with DMSO or CC-90009 for 24 hours. (H) The effect of CC-90009 on proliferation of cells shown in panel G. On day 3 after CC-90009 treatment, cell proliferation was assessed by CTG. Data in panels F and G are shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD), n = 3 or 4 technical replicates. Result shown in all figure panels is representative of 3 biological replicates.
To determine if the ISR activation by CC-90009 is solely mediated by GCN2, we evaluated the effect of GCN2 ablation on CC-90009 response. GCN2 knockout inhibited eIF2α phosphorylation, induction of ATF4 and its target gene DDIT4, and caspase-3 cleavage in U937 cells treated with CC-90009 (Figure 5E-F). GCN2 loss largely, but not completely, blocked the induction of other ATF4 target genes ATF3 and CHOP (Figure 5F), suggesting the involvement of additional signaling pathways capable of inducing these 2 genes. Reintroduction of GCN2 wild-type, but not any of its enzymatically dead mutants T899A/T904A, K619R, and F1143L/R1144L, significantly restored the response to CC-90009 in U937 GCN2−/− cells (Figure 5G-H). Collectively, these findings suggest that the ISR activation following GSPT1 degradation at least partially modulates the anti-AML activity of CC-90009.
CC-90009 reduces leukemic engraftment in AML xenograft models
To further assess the antileukemia activity of CC-90009 across a spectrum of primary AML samples with extensive heterogeneity at the genetic, phenotypic, and clinical level, AML cells from 23 patients were treated in vitro with different concentrations of CC-90009 for 24 hours. Treatment with 100 nM CC-90009 reduced GSPT1 expression by >70% in 9 samples, 50% to 70% in 8 samples, and <50% in 6 samples (Figure 6A). Consistently, CC-90009 decreased viability and induced apoptosis of AML cells with good correlation to GSPT1 reduction (supplemental Figure 7A-B). CC-90009 was also cytotoxic to primitive AML progenitors evidenced by significantly decreased colony numbers (supplemental Figure 7C).
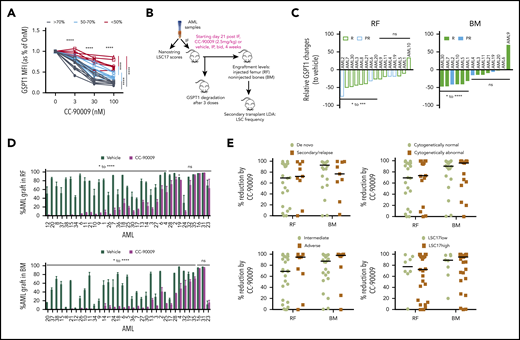
CC-90009 treatment reduces leukemic engraftment in AML xenograft models. (A) GSPT1 expression at 24 hours in culture with CC-90009 at indicated concentrations. Each line indicates data relative to 0 nM CC-90009 for an individual patient sample (n = 23). Lines in black, cyan, and red represent samples with >70%, 50% to 70%, and <50% GSPT1 reduction, respectively, at the 100-nM treatment dose. (B) Schematic experimental design for in vivo CC-90009 treatment. IF, intrafemoral transplantation; LDA, limiting dose assay; LSC17, a 17-gene leukemia stem cell signature. (C) Relative GSPT1 degradation to controls in the RF and BM of NOD.SCID mice engrafted with AML and treated with CC-90009 (n = 2-4 mice per treatment group). PR, partial responder; R, responder. (D) CD45+CD33+ AML engraftment levels in RF and BM of xenotransplanted mice treated with vehicle (dark green bars) or CC-90009 (purple bars) (n = 5 per treatment group). Bars represent mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of an individual patient sample. (E) Relative reduction in leukemic engraftment in mice treated with CC-90009 compared with controls, and transplanted with de novo or secondary or relapsed AML, normal or abnormal cytogenetics, MRC adverse or intermediate risk group, and high or low LS17 scores. Each dot represents an individual patient sample. Bars are the median values for each group. For panels C and E, relative change for each patient sample was calculated as (median of CC90009 – median of vehicle)/median of vehicle × 100. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, ****P < .0001. ns, not significant.
CC-90009 treatment reduces leukemic engraftment in AML xenograft models. (A) GSPT1 expression at 24 hours in culture with CC-90009 at indicated concentrations. Each line indicates data relative to 0 nM CC-90009 for an individual patient sample (n = 23). Lines in black, cyan, and red represent samples with >70%, 50% to 70%, and <50% GSPT1 reduction, respectively, at the 100-nM treatment dose. (B) Schematic experimental design for in vivo CC-90009 treatment. IF, intrafemoral transplantation; LDA, limiting dose assay; LSC17, a 17-gene leukemia stem cell signature. (C) Relative GSPT1 degradation to controls in the RF and BM of NOD.SCID mice engrafted with AML and treated with CC-90009 (n = 2-4 mice per treatment group). PR, partial responder; R, responder. (D) CD45+CD33+ AML engraftment levels in RF and BM of xenotransplanted mice treated with vehicle (dark green bars) or CC-90009 (purple bars) (n = 5 per treatment group). Bars represent mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of an individual patient sample. (E) Relative reduction in leukemic engraftment in mice treated with CC-90009 compared with controls, and transplanted with de novo or secondary or relapsed AML, normal or abnormal cytogenetics, MRC adverse or intermediate risk group, and high or low LS17 scores. Each dot represents an individual patient sample. Bars are the median values for each group. For panels C and E, relative change for each patient sample was calculated as (median of CC90009 – median of vehicle)/median of vehicle × 100. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, ****P < .0001. ns, not significant.
Next, the antileukemia efficacy of CC-90009 was determined in vivo using xenografting of 35 primary AML samples in NOD.SCID mice (Figure 6B). GSPT1 was quickly degraded in most AML xenografts within 24 hours after treatment of recipient mice with CC-90009 (Figure 6C). All the mice were healthy and tolerant to CC-90009 during the 4-week period of treatment. In 24 samples, CC-90009 significantly reduced CD45+33+ AML cells by 52% to 100% in injected femur (RF) and 62% to 99% in noninjected bones (BM), compared with vehicle-treated mice (Figure 6D; Table 1). These samples were termed “responders” in keeping with the classification scheme we previously developed.45 Eight “partial responders” had a less robust response to CC-90009, with 20% to 60% relative reduction. Three “nonresponders” had very little or negligible response to CC-90009, with <20% relative reduction (Table 1). The CC-90009-induced AML graft reduction was accompanied by increased cell death in both RF and BM (supplemental Figure 7D); this effect was greater in responders and partial responders compared with nonresponders.
Classification of AML responses to CC-90009
| Patient ID . | LSC17 classification . | RF mean engraftment (%) . | RR (%) . | BM mean engraftment (%) . | RR (%) . | In vivo response . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC-90009 . | Vehicle . | P . | CC-90009 . | Vehicle . | P . | |||||
| 12 | LSC17hi | 0.0 | 32.2 | <.05 | 100 | 0.0 | 2.2 | <.05 | 99 | R |
| 20 | LSC17hi | 0.1 | 86.6 | <.0001 | 100 | 0.0 | 14.1 | <.0001 | 100 | R |
| 8 | LSC17hi | 0.1 | 75.0 | <.0001 | 100 | 0.0 | 4.5 | NS | 100 | R |
| 37 | LSC17hi | 0.1 | 65.3 | <.01 | 100 | 0.0 | 48.6 | <.0001 | 100 | R |
| 38 | LSC17hi | 0.3 | 85.0 | <.0001 | 100 | 0.1 | 67.7 | <.0001 | 100 | R |
| 15 | LSC17lo | 0.6 | 88.2 | <.0001 | 99 | 0.2 | 57.2 | <.0001 | 100 | R |
| 34 | LSC17hi | 0.7 | 44.5 | <.0001 | 99 | 0.1 | 7.1 | <.05 | 98 | R |
| 5 | LSC17hi | 3.7 | 96.9 | <.0001 | 96 | 6.7 | 76.1 | <.0001 | 91 | R |
| 11 | LSC17lo | 3.2 | 81.8 | <.0001 | 96 | 1.4 | 81.9 | <.0001 | 98 | R |
| 21 | LSC17hi | 3.0 | 77.3 | <.0001 | 96 | 0.5 | 64.6 | <.0001 | 99 | R |
| 10 | LSC17hi | 2.6 | 54.5 | <.05 | 95 | 0.6 | 45.5 | <.0001 | 99 | R |
| 9 | LSC17hi | 3.6 | 72.0 | <.0001 | 95 | 0.32 | 16.7 | <.01 | 98 | R |
| 1 | LSC17hi | 4.6 | 79.0 | <.0001 | 94 | 2.0 | 66.5 | <.0001 | 97 | R |
| 26 | LSC17hi | 3.6 | 41.2 | <.001 | 91 | 0.4 | 30.6 | <.01 | 99 | R |
| 7 | LSC17lo | 8.8 | 91.8 | <.0001 | 91 | 4.4 | 38.3 | <.001 | 89 | R |
| 36 | LSC17lo | 7.4 | 52.3 | <.05 | 86 | 2.7 | 25.8 | <.01 | 96 | R |
| 18 | LSC17hi | 24.2 | 91.3 | NS | 74 | 3.1 | 78.5 | <.01 | 96 | R |
| 25 | LSC17hi | 18.5 | 66.7 | <.001 | 72 | 12.8 | 38.2 | <.0001 | 67 | R |
| 30 | LSC17hi | 11.1 | 37.1 | >.05 | 70 | 5.0 | 34.5 | <.05 | 86 | R |
| 17 | LSC17lo | 12.7 | 40.9 | <.001 | 69 | 8.4 | 22.3 | <.05 | 62 | R |
| 14 | LSC17lo | 23.1 | 74.0 | <.001 | 69 | 1.6 | 64.6 | <.01 | 98 | R |
| 13 | LSC17lo | 27.4 | 78.0 | <.0001 | 65 | 19.0 | 82.6 | <.0001 | 77 | R |
| 3 | LSC17hi | 16.4 | 42.0 | <.05 | 61 | 8.0 | 29.6 | <.05 | 73 | R |
| 27 | LSC17hi | 31.6 | 65.0 | <.01 | 52 | 3.3 | 23.6 | <.001 | 86 | R |
| 6 | LSC17hi | 49.8 | 92.0 | <.01 | 46 | 2.9 | 57.0 | <.0001 | 95 | PR |
| 24 | LSC17hi | 6.2 | 7.0 | NS | 9 | 1.7 | 48.4 | <.05 | 97 | PR |
| 4 | LSC17hi | 56.8 | 99.0 | <.01 | 42 | 46.5 | 97.6 | <.01 | 52 | PR |
| 28 | LSC17hi | 76 | 91.0 | NS | 17 | 35.8 | 81.5 | <.0001 | 56 | PR |
| 2 | LSC17hi | 84.4 | 97.2 | NS | 13 | 27.6 | 84.5 | <.01 | 67 | PR |
| 19 | LSC17hi | 80.6 | 88.3 | <.01 | 9 | 64.7 | 87.1 | <.05 | 26 | PR |
| 32 | LSC17hi | 84.2 | 88.0 | NS | 4 | 62.0 | 86.6 | <.05 | 28 | PR |
| 35 | LSC17lo | 93.2 | 94.3 | NS | 1 | 66.4 | 83.3 | <.05 | 20 | PR |
| 16 | LSC17hi | 96.6 | 96.2 | NS | 0 | 92.4 | 94.6 | NS | 2 | NR |
| 31 | LSC17hi | 98.0 | 97.5 | NS | 0 | 96.8 | 97.4 | NS | 1 | NR |
| 23 | LSC17hi | 76.8 | 63.5 | NS | 0 | 14.5 | 4.1 | NS | 0 | NR |
| Patient ID . | LSC17 classification . | RF mean engraftment (%) . | RR (%) . | BM mean engraftment (%) . | RR (%) . | In vivo response . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC-90009 . | Vehicle . | P . | CC-90009 . | Vehicle . | P . | |||||
| 12 | LSC17hi | 0.0 | 32.2 | <.05 | 100 | 0.0 | 2.2 | <.05 | 99 | R |
| 20 | LSC17hi | 0.1 | 86.6 | <.0001 | 100 | 0.0 | 14.1 | <.0001 | 100 | R |
| 8 | LSC17hi | 0.1 | 75.0 | <.0001 | 100 | 0.0 | 4.5 | NS | 100 | R |
| 37 | LSC17hi | 0.1 | 65.3 | <.01 | 100 | 0.0 | 48.6 | <.0001 | 100 | R |
| 38 | LSC17hi | 0.3 | 85.0 | <.0001 | 100 | 0.1 | 67.7 | <.0001 | 100 | R |
| 15 | LSC17lo | 0.6 | 88.2 | <.0001 | 99 | 0.2 | 57.2 | <.0001 | 100 | R |
| 34 | LSC17hi | 0.7 | 44.5 | <.0001 | 99 | 0.1 | 7.1 | <.05 | 98 | R |
| 5 | LSC17hi | 3.7 | 96.9 | <.0001 | 96 | 6.7 | 76.1 | <.0001 | 91 | R |
| 11 | LSC17lo | 3.2 | 81.8 | <.0001 | 96 | 1.4 | 81.9 | <.0001 | 98 | R |
| 21 | LSC17hi | 3.0 | 77.3 | <.0001 | 96 | 0.5 | 64.6 | <.0001 | 99 | R |
| 10 | LSC17hi | 2.6 | 54.5 | <.05 | 95 | 0.6 | 45.5 | <.0001 | 99 | R |
| 9 | LSC17hi | 3.6 | 72.0 | <.0001 | 95 | 0.32 | 16.7 | <.01 | 98 | R |
| 1 | LSC17hi | 4.6 | 79.0 | <.0001 | 94 | 2.0 | 66.5 | <.0001 | 97 | R |
| 26 | LSC17hi | 3.6 | 41.2 | <.001 | 91 | 0.4 | 30.6 | <.01 | 99 | R |
| 7 | LSC17lo | 8.8 | 91.8 | <.0001 | 91 | 4.4 | 38.3 | <.001 | 89 | R |
| 36 | LSC17lo | 7.4 | 52.3 | <.05 | 86 | 2.7 | 25.8 | <.01 | 96 | R |
| 18 | LSC17hi | 24.2 | 91.3 | NS | 74 | 3.1 | 78.5 | <.01 | 96 | R |
| 25 | LSC17hi | 18.5 | 66.7 | <.001 | 72 | 12.8 | 38.2 | <.0001 | 67 | R |
| 30 | LSC17hi | 11.1 | 37.1 | >.05 | 70 | 5.0 | 34.5 | <.05 | 86 | R |
| 17 | LSC17lo | 12.7 | 40.9 | <.001 | 69 | 8.4 | 22.3 | <.05 | 62 | R |
| 14 | LSC17lo | 23.1 | 74.0 | <.001 | 69 | 1.6 | 64.6 | <.01 | 98 | R |
| 13 | LSC17lo | 27.4 | 78.0 | <.0001 | 65 | 19.0 | 82.6 | <.0001 | 77 | R |
| 3 | LSC17hi | 16.4 | 42.0 | <.05 | 61 | 8.0 | 29.6 | <.05 | 73 | R |
| 27 | LSC17hi | 31.6 | 65.0 | <.01 | 52 | 3.3 | 23.6 | <.001 | 86 | R |
| 6 | LSC17hi | 49.8 | 92.0 | <.01 | 46 | 2.9 | 57.0 | <.0001 | 95 | PR |
| 24 | LSC17hi | 6.2 | 7.0 | NS | 9 | 1.7 | 48.4 | <.05 | 97 | PR |
| 4 | LSC17hi | 56.8 | 99.0 | <.01 | 42 | 46.5 | 97.6 | <.01 | 52 | PR |
| 28 | LSC17hi | 76 | 91.0 | NS | 17 | 35.8 | 81.5 | <.0001 | 56 | PR |
| 2 | LSC17hi | 84.4 | 97.2 | NS | 13 | 27.6 | 84.5 | <.01 | 67 | PR |
| 19 | LSC17hi | 80.6 | 88.3 | <.01 | 9 | 64.7 | 87.1 | <.05 | 26 | PR |
| 32 | LSC17hi | 84.2 | 88.0 | NS | 4 | 62.0 | 86.6 | <.05 | 28 | PR |
| 35 | LSC17lo | 93.2 | 94.3 | NS | 1 | 66.4 | 83.3 | <.05 | 20 | PR |
| 16 | LSC17hi | 96.6 | 96.2 | NS | 0 | 92.4 | 94.6 | NS | 2 | NR |
| 31 | LSC17hi | 98.0 | 97.5 | NS | 0 | 96.8 | 97.4 | NS | 1 | NR |
| 23 | LSC17hi | 76.8 | 63.5 | NS | 0 | 14.5 | 4.1 | NS | 0 | NR |
LSC17hi, high LSC17 score; LSC17lo, low LSC17 score; NS, no significant difference between CC-90009- and vehicle-treated mice or <20% relative reduction in both RF and BM; PR, 20% to 50% RR in RF or >20% RR in BM only; R, >50% RR in RF; RF, injected right femur; RR, relative reduction.
The majority of xenografts derived from patients with high risk features (secondary and relapsed AML, MRC cytogenetic risk, and abnormal cytogenetics) responded to CC-90009 as well as those derived from relatively more favorable (de novo, intermediate risk, and normal cytogenetics) cases (Figure 6E; Table 2). We previously reported a 17-gene stemness cell score (LSC17) that is highly predictive of survival and treatment response in newly diagnosed AML patients.46 In our cohort, 7 of 8 samples with low LSC17 scores and 17 of 27 samples with high LSC17 scores were good responders to CC-90009, with >50% relative reduction of leukemic engraftment in RF and BM (Figure 6E; Table 2). Of potential therapeutic importance, 12 of 27 high-LSC17 score cases showed >90% depletion of the leukemic graft. Together, these data indicate that CC-90009 has potent growth inhibitory effects on AML cells from patients with adverse prognostic features.
Clinical characteristics of CC-90009 responders and partial/nonresponders
| . | Responders (n = 24) . | Partial/nonresponders (n = 11) . |
|---|---|---|
| De novo vs secondary/relapsed AML (n) | n = 21 | n = 10 |
| De novo | 14 | 8 |
| Secondary/relapsed | 7 | 2 |
| MRC cytogenetic risk at diagnosis (n) | n = 23 | n = 11 |
| Intermediated | 15 | 9 |
| Adverse | 8 | 2 |
| Normal vs abnormal cytogenetic AML (n) | n = 24 | n = 11 |
| Normal | 13 | 7 |
| Abnormal | 11 | 4 |
| LSC17 score (n) | n = 24 | n = 11 |
| High score | 17 | 10 |
| Low score | 7 | 1 |
| . | Responders (n = 24) . | Partial/nonresponders (n = 11) . |
|---|---|---|
| De novo vs secondary/relapsed AML (n) | n = 21 | n = 10 |
| De novo | 14 | 8 |
| Secondary/relapsed | 7 | 2 |
| MRC cytogenetic risk at diagnosis (n) | n = 23 | n = 11 |
| Intermediated | 15 | 9 |
| Adverse | 8 | 2 |
| Normal vs abnormal cytogenetic AML (n) | n = 24 | n = 11 |
| Normal | 13 | 7 |
| Abnormal | 11 | 4 |
| LSC17 score (n) | n = 24 | n = 11 |
| High score | 17 | 10 |
| Low score | 7 | 1 |
Secondary includes therapy-related AML and after myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm AML.
MRC, Medical Research Council classification.
CC-90009 treatment eliminates LSCs
To prevent relapse, therapies must target the disease-driving LSCs. CC-90009 treatment reduced the proportion of primitive CD34+ AML blasts that are enriched for LSC in responding samples (Figure 7A-B), with lesser reduction or even enrichment of CD34+ cells in partial and nonresponders (Figure 7B). In some samples where the percentage of CD34+ cells in the AML graft was not reduced, the proportion of CD34+ cells in the mouse bone marrow was still significantly reduced owing to overall reduction of AML engraftment in treated mice (Figure 7C). In contrast, CC-90009 had lesser inhibitory effect on normal cord blood CD34+ primitive cells in the xenograft than AML CD34+ cells (supplemental Figure 7E).
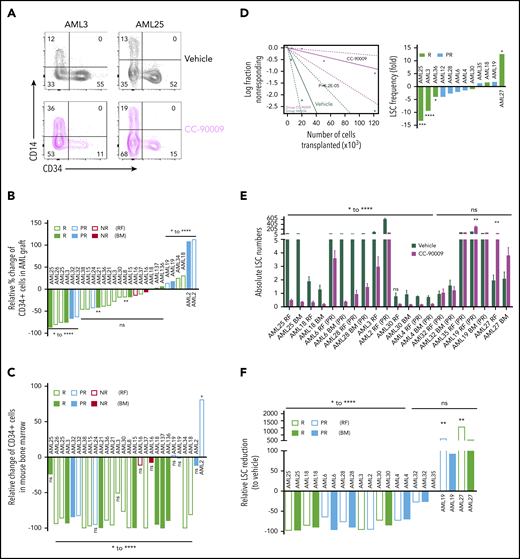
Self-renewal LSCs are targeted by CC-90009. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of 2 representative samples (AML3 and AML25) showing CD34+CD14− cells in the AML graft in mice treated with CC-90009 or vehicle control. (B-C) Relative change in %CD34+ population in AML graft (B) or in the mouse bone marrow (C) from CC-90009-treated mice compared with controls. (D) LSC frequency in CC-90009- or control-treated mice determined by secondary transplantation at limiting doses for representative sample AML3 (left) and summary graph showing fold change in LSC frequency for all samples tested by limiting dilution analysis (right). (E) Number of LSCs in the primary mouse bone marrow following treatment with CC-90009 (purple bars) or vehicle control (dark green bars) (5 mice per treatment group). Each bar indicates the mean ± SEM of an individual patient sample. (F) Relative reduction in LSC numbers in mice treated with CC-90009 compared with vehicle control. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, ****P < .0001. NR, nonresponder; ns, not significant.
Self-renewal LSCs are targeted by CC-90009. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of 2 representative samples (AML3 and AML25) showing CD34+CD14− cells in the AML graft in mice treated with CC-90009 or vehicle control. (B-C) Relative change in %CD34+ population in AML graft (B) or in the mouse bone marrow (C) from CC-90009-treated mice compared with controls. (D) LSC frequency in CC-90009- or control-treated mice determined by secondary transplantation at limiting doses for representative sample AML3 (left) and summary graph showing fold change in LSC frequency for all samples tested by limiting dilution analysis (right). (E) Number of LSCs in the primary mouse bone marrow following treatment with CC-90009 (purple bars) or vehicle control (dark green bars) (5 mice per treatment group). Each bar indicates the mean ± SEM of an individual patient sample. (F) Relative reduction in LSC numbers in mice treated with CC-90009 compared with vehicle control. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, ****P < .0001. NR, nonresponder; ns, not significant.
To determine whether CC-90009 decreased the frequency of LSCs in primary treated mice, we carried out serial limiting dilution assays in secondary recipients. A representative sample (AML3) is shown in Figure 7D (left), which showed a ninefold decrease in LSC frequency following CC-90009 treatment. Among the 6 responders and 6 partial responders tested, 3 samples demonstrated a statistically significant decrease in LSC frequency following CC-90009 treatment (Figure 7D, right). One responding sample, with regard to overall reduction in cellularity, had a significant increase in LSC frequency; the rest had either decrease or increase that were not statistically significant. Consistent with the observed decrease in LSC frequency, those samples also had reduced absolute LSC numbers in both injected RF and noninjected BM of primary treated mice; there was a >50% reduction in LSC numbers compared with controls in most samples (8 of 12) (Figure 7E-F). Two samples, 1 partial responder and 1 responder, showed an increase in LSC numbers following treatment (Figure 7E-F). Overall, these data indicate that CC-90009 can target LSCs in the AML xenograft model, albeit with heterogeneous responses among AML cases.
Discussion
Here, we present the identification and characterization of CC-90009, a new CELMoD agent that deploys CRL4CRBN to induce the selective degradation of GSPT1, ultimately evoking an antiproliferative and proapoptotic response. We show that CC-90009 displayed marked activity in AML xenograft assays across a wide spectrum of AML samples, including refractory/relapsed cases and those with adverse risk features who are at high risk of relapse. Importantly, disease-driving LSC can be eradicated in a subset of cases. Beyond CC-90009, selective degradation of just the intended target optimizes the therapeutic index and overcomes toxicities associated with earlier, more promiscuous, cereblon modulators and provides a roadmap for the design of the next-generation CELMoD agents.
Our CRISPR screening approach provides new insights into novel molecular machineries that modulate cereblon-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of GSPT1 that might be relevant for the design of future combination therapies if resistance appears with single-agent treatment. For example, the alternative splicing of CRBN mRNA transcripts controlled by the ILF2/ILF3 complex was detected in all tested cell lines regardless of cell type or tissue of origin (data not shown), suggesting that ILF2 or ILF3 loss should attenuate the response to all cereblon modulating agents. Indeed, ILF3 knockout was previously reported to reduce the lenalidomide sensitivity in primary effusion lymphoma through an unknown mechanism, which is likely associated with cereblon downregulation similar to what we observed in this work.33 Additionally, upregulation of mTORC1 signaling is a common pro-survival mechanism that promotes carcinogenesis and resistance to cancer therapies.47 We showed that mTORC1 hyperactivation owing to loss of TSC1 or TSC2 significantly blocked the CC-90009-induced GSPT1 recruitment to cereblon, and hence diminished GSPT1 degradation and CC-90009 sensitivity in AML. The mTORC1 signaling pathway was not previously reported to modulate the activity of other cereblon modulators. Consistently, we did not observe any effect of TSC1 or TSC2 loss on degradation of IKZF1/3 by lenalidomide or pomalidomide in AML and multiple myeloma cell lines, respectively (supplemental Figure 5D; data not shown). Because GSPT1 and IKZF1 share the same binding mode of engaging cereblon, we reasoned that the effect of mTORC1 activation on GSPT1 degradation is likely linked to the direct modulation of GSPT1 instead of cereblon, resulting in decrease of GSPT1 accessibility by cereblon.
GSPT1 degradation activates the GCN1/GCN2/eIF2α/ATF4 axis of the ISR, with concomitant induction of acute apoptosis in AML. The GCN2-mediated ISR is an adaptive signaling pathway that shuts down protein synthesis and turns on the ATF4 transcriptional program to cope with a range of physiological and pathological stresses. The nature, severity, and duration of stimuli determine whether GCN2 activation drives a pro-survival or pro-death signaling.48,49 In the context of dysregulated protein translation termination, the GCN2-mediated ISR upon GSPT1 degradation promotes acute apoptotic cell death in AML cell lines and patient blasts with minimal effect on normal PBMC, THLEs, or T-lymphocytes indicative of an exclusive vulnerability to GSPT1 loss in AML. Ablation of DDIT4(REDD1) significantly reduced the response to CC-90009 and largely mimicked the gene knockout effect of GCN1, GCN2, and ATF4, strongly suggesting that the GCN2-mediated anti-AML activity of CC-90009 is mainly exerted by REDD1 among all the target genes transactivated by ATF4. It has been demonstrated that REDD1 is a rapidly upregulated gene that inhibits mTORC1 signaling via the TSC1 complex under multiple cellular stresses.50 Although REDD1 upregulation is evident following CC-90009-induced GSPT1 degradation, we did not observe significant mTORC1 inhibition, based on the phosphorylation status of S6K1 (data not shown). Moreover, elimination of REDD1 or its upstream regulators GCN1, GCN2, and ATF4 did not affect the degradation of GSPT1 by CC-90009 (Figure 5E-G, and data not shown), a consequence of mTOR hyperactivation established in this work. The mTOR-independent function of REDD1 in mediating CC-90009-induced apoptosis remains to be elucidated.
Therapy resistance and disease relapse in AML are tied to LSC properties including self-renewal and quiescence.51-54 Our recent studies have shown that LSCs possess a distinct pro-survival ISR50 that mirrors that of normal hematopoietic stem cells.55,56 In both hematopoietic stem cell and LSC, specific translation dynamics lead to activation of the ISR.55 Our findings that persistent ISR activation by CC-90009 induces apoptosis substantiate the concept that the ISR wired into LSC can be modulated between prosurvival and prodeath, thereby providing a novel therapeutic approach to eradicate disease-driving LSC. We observed variability among samples in the degree of apoptosis and induction of differentiation and retention of primitive CD34+ cells following treatment. Additionally, although the majority of samples showed a reduction in LSC frequency, a few samples showed an increase in LSC frequency with CC-90009 treatment. These differences in response among patient samples may be related to distinct GSPT1 levels that exist between patients or even between LSC subclones within individual patients. Whether CC-90009 effectively targets genetically diverse LSC subclones will require clonal tracking studies in future clinical trials of patients treated with CC-90009.57,58 However, that we observed activity across a spectrum of high-risk samples gives some confidence that it will target intrasample genetic diversity. Such effective targeting of leukemic blasts and LSCs in AML samples with poorer prognosis supports further development of CC-90009 in clinical trials as a novel agent for patients with refractory/relapsed AML.
RNAseq data are available at the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) under access number GSE154257.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank members of the drug discovery and early development team at Bristol-Myers Squibb, including Stephanie Weng, Derek Nguyen, Nai-Yu Wang, Svetlana Gaidarova, Irit Rappley, Jinyi Zhu, Scott Wood, Mihul Dhanani, and Barbra Pagarigan for helpful discussion and/or technical assistance. They also thank Vivia Biotech for assessing the anti-AML activity of CC-90009 in patient samples under a research service agreement. Portions of the crystallographic structural studies were conducted at the Advanced Light Source. The authors thank the Orsino Leukemia Tissue Bank at Princess Margaret Cancer Center/University Health Network for providing primary AML samples. They also thank O. Gan, M. Anders, and L.Garcia-Prat from the J.E.D. laboratory for critical feedback.
Beamline 5.0.1 of the Advanced Light Source, a US Department of Energy, Office of Science User Facility under contract DE-AC02-05CH11231, is supported, in part, by the ALS-ENABLE program funded by the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of General Medical Sciences (grant P30 GM124169-01). This work received financial support by Sponsored Research Agreements from Bristol-Myers Squibb. Work in J.E.D.’s laboratory is supported by funds from the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre Foundation; the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (foundation 154293, operating grants 154293 and 89932); International Development Research Centre; Canadian Cancer Society (grant 703212); Terry Fox Research Institute Program Project Grant; Ontario Institute for Cancer Research through funding provided by the Government of Ontario, a Canadian Research Chair; and funding from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long Term Care to Princess Margaret Cancer Centre.
Authorship
Contribution: A.L.-G. and J.H. designed the phenotypic screen to identify novel cereblon modulators that possess anti-AML activity and analyzed the result; A.L.-G., E.R., and D.M. designed and performed the cell biology experiments to characterize the activity of CC-90009 in AML cell lines, PBMC, THLE, and patient blasts; A.L.-G. and C.F. designed and performed the tandem mass tag proteomics experiment; G.L., C.-C.L., and C.S. designed and performed the molecular biology experiments exploring the mechanism of action of CC-90009; P.C., M.M., T.C., and E.T. designed and performed biochemical and crystallographic structural studies; G.L. and C.S. designed the genome-wide CRISPR screen; C.S. performed the genome CRISPR-Cas9 screen; G.L., C.S., I.S.J., and K.W. analyzed the CRISPR screen result; C.S., C.-C.L., C.H., and A.C. performed the molecular and cellular biology experiments to validate genes and pathways that modulate the response to CC-90009 identified in the CRISPR screen; G.L., C.S., and E.T. designed and performed the RNA sequencing experiment and analyzed the results; L.J., J.F., D.W.P., M.P., and J.E.D. designed and discussed the in vitro and in vivo studies of CC-90009 efficacy in AML patient samples; L.J. and N.M. performed the experiments and analyzed the data; J.C.Y.W. supervised the work; M.D.M. provided primary AML patient samples; S.W.K.N. analyzed the LSC17 NanoString gene expression data; G.L., J.E.D., A.L.-G., D.W.P., M.P., J.F., J.H., K.W., P.C., B.C., J.C., and M.R. conceived and planned the work; G.L., J.E.D., and A.L.-G. supervised the project; G.L. and L.J. wrote the first draft; and all authors reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: C.S., C.-C.L., I.S.J., E.R., D.M., T.C., E.T., C.F., A.C., M.M., K.W., P.C., B.C., J.C., J.H., J.F., D.W.P., M.P., M.R., A.L.-G., and G.L. are, or have been, employees and equity holders at BMS. J.E.D. served on the Science Advisory Board (SAB) at Trillium Therapeutics, and has ownership interest (including patents) in Trillium Therapeutics Inc.There is an existing license agreement between TTI and University Health Network, and L.J., J.C.Y.W., and J.E.D. may be entitled to receive financial benefits further to this license and in accordance with their institution’s intellectual property policies. M.D.M. serves on the SAB at Astellas Pharma Inc. J.E.D. received financial support by sponsored research agreements from Bristol-Myers Squibb. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Gang Lu, Bristol-Myers Squibb, 10300 Campus Point Dr, Suite 100, San Diego, CA 92121; e-mail: gang.lu@bms.com; John E. Dick, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, 101 College St, PMCRT, Toronto, M5G 1L7, ON, Canada; e-mail: john.dick@uhnresearch.ca; or Antonia Lopez-Girona, Bristol-Myers Squibb, 10300 Campus Point Dr, Suite 100, San Diego, CA 92121; e-mail: antonia.lopez-girona@bms.com.
REFERENCES
Author notes
C.S. and L.J. are joint first authors.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal