Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
Mice expressing nonpolymerizable fibrinogen have reduced arterial and venous thrombosis with preserved hemostasis
Fibrin clots form through thrombin-mediated conversion of fibrinogen into monomeric fibrin, which then polymerizes. Lack of fibrinogen leads to severe bleeding, lack of platelet aggregation, and delayed wound healing. However, in this Plenary Paper, Hur and colleagues show that fibrin polymerization is not required for these functions in vivo in mice expressing nonpolymerizable fibrinogen. Further, these mice were protected against venous thrombosis and had suppressed arterial thrombosis, revealing new avenues to reducing thrombosis without increasing bleeding.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
CD19/CD22 targeting with cotransduced CAR T cells to prevent antigen-negative relapse after CAR T-cell therapy for B-cell ALL
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Emergence of CD19-negative disease and limited chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell persistence have emerged as the major limitations of current CD19 CAR T-cell approaches for pediatric relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). In a phase 1 clinical trial investigating a novel CD19/CD22-bispecific CAR T-cell product, Ghorashian et al report no antigen-negative relapses among a cohort of 12 patients with relapsed ALL. Although requiring more mature follow-up and confirmation in larger studies, these data suggest progress toward reducing a major mechanism of treatment failure.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
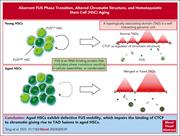
Aging-disturbed FUS phase transition impairs hematopoietic stem cells by altering chromatin structure
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) alter their function during aging. B. Tang and colleagues newly identify the RNA-binding protein FUS as an effector of HSC aging, with its protein levels increasing in HSCs with age and aberrant FUS condensates forming. These aberrant FUS condensates induce a global 3-dimensional chromatin reorganization by blurring the boundaries of topology-associating domains, and this generates an aged HSC-like transcriptional signature.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
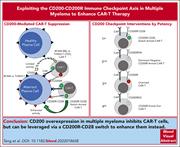
Exploiting the CD200-CD200R immune checkpoint axis in multiple myeloma to enhance CAR T-cell therapy
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies hold promise for the treatment of multiple myeloma, but expression of immune checkpoints such as CD200 by malignant plasma cells often drives CAR T-cell exhaustion. Y. Tang and colleagues engineered several CAR constructs to explore how to best overcome this barrier to successful therapy. By utilizing the CD200 expression to drive CD28 costimulation of their B-cell maturation antigen–targeting CAR T cells, the authors demonstrate promising in vitro and in vivo activity in preclinical models. Such an approach requires testing in clinical trials.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
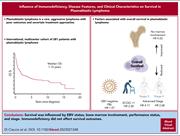
The influence of immunodeficiency, disease features, and patient characteristics on survival in plasmablastic lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Plasmablastic lymphoma is a rare and aggressive form of large B-cell lymphoma that has been associated with immunodeficiency and poor prognosis in small case series. Di Ciaccio et al more completely define this entity, reporting on a multinational series of 281 patients that confirms the strong association with immunodeficiency. While response rates exceeded 70%, outcomes were poor despite intensive regimens, with Epstein-Barr virus–negative lymphoma, poor performance status, and advanced stage being negative prognostic features. New therapeutic strategies, especially for the highest risk forms, are clearly needed.
TRANSPLANTATION
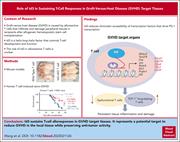
Tissue-infiltrating alloreactive T cells require Id3 to deflect PD-1–mediated immune suppression during GVHD
Inhibitor of DNA-binding 3 (Id3) is a helix-loop-helix transcription factor that plays a key role in T-cell biology, being involved in both T-cell development and emergence of T-cell memory. Wang and colleagues report that genetic ablation of Id3 attenuates graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) through upregulation of PD-1 expression in alloreactive donor T cells but does not diminish antileukemic activity in murine transplant models. This work suggests that targeting Id3 may provide a new avenue for GVHD prevention and treatment.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Outcomes and characteristics of nonmelanoma skin cancers in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms on ruxolitinib
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Immunostaining of a venous thrombus isolated from an
FgaWT/EK mouse 24 hours after induction of inferior vena cava (IVC) stasis, highlighting fibrin(ogen) (green) and platelets (CD41, red) with nuclei counterstained with DAPI (blue). Platelets and nucleated cells (neutrophils) colocalize within the IVC thrombus in heterogenous patches, while fibrin(ogen) is distributed throughout the clot. See the article by Hur et al on page 105. - PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






Better with poorly performing fibrin(ogen)