Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PERSPECTIVE
REVIEW SERIES
Predisposition to myeloid malignancies in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome: biological insights and clinical advances
Routine use of next-generation sequencing of hematologic malignancies has greatly expanded the representation of hereditary predisposition syndromes among patients with leukemia. Introduced by Associate Editor Mario Cazzola, this Review Series highlights 4 such genetic predisposition syndromes and provides strong support for the need to include germ line genetic testing for patients with myelodysplasia and myeloid leukemia.
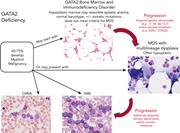
The spectrum of GATA2 deficiency syndrome
Routine use of next-generation sequencing of hematologic malignancies has greatly expanded the representation of hereditary predisposition syndromes among patients with leukemia. Introduced by Associate Editor Mario Cazzola, this Review Series highlights 4 such genetic predisposition syndromes and provides strong support for the need to include germ line genetic testing for patients with myelodysplasia and myeloid leukemia.
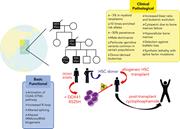
Hereditary platelet disorders associated with germ line variants in RUNX1, ETV6, and ANKRD26
Routine use of next-generation sequencing of hematologic malignancies has greatly expanded the representation of hereditary predisposition syndromes among patients with leukemia. Introduced by Associate Editor Mario Cazzola, this Review Series highlights 4 such genetic predisposition syndromes and provides strong support for the need to include germ line genetic testing for patients with myelodysplasia and myeloid leukemia.
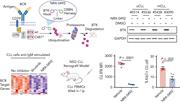
DDX41-associated susceptibility to myeloid neoplasms
Routine use of next-generation sequencing of hematologic malignancies has greatly expanded the representation of hereditary predisposition syndromes among patients with leukemia. Introduced by Associate Editor Mario Cazzola, this Review Series highlights 4 such genetic predisposition syndromes and provides strong support for the need to include germ line genetic testing for patients with myelodysplasia and myeloid leukemia.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as a targeted therapy for bone marrow failure in Ghosal hematodiaphyseal dysplasia
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Ghosal hematodiaphyseal dysplasia (GHDD) is an extremely rare disorder associated with normocytic anemia and cortical bone thickening, caused by mutations in thromboxane A synthase 1 (TBXAS1). Marrow failure is thought to result from loss of thromboxane and a consequent increase in proinflammatory prostaglandin synthesis and is treated with corticosteroids. Brown and colleagues report on the treatment of 2 patients with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, leading to cyclooxygenase inhibition and complete hematologic response, suggesting this should be first-line therapy for this rare disorder.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
HLA-E–restricted immune responses are crucial for the control of EBV infections and the prevention of PTLD
Over 95% of the population has been infected by Epstein-Barr virus, but why only some patients develop symptomatic infectious mononucleosis (IM) and why only a small subset of patients develop posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) after stem cell transplantation are unknown. Vietzen et al describe an interplay of genetic determinants in host and virus involving variants in host HLA-E that interact with specific latent membrane protein 1 peptide variants to modulate T-cell and natural killer cell responses that predict for IM and PTLD.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
The location of the t(4;14) translocation breakpoint within the NSD2 gene identifies a subset of patients with high-risk NDMM
Clinical Trials & Observations
Translocation t(4;14) between the NSD2 gene and the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus defines a high-risk subset of patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM). Stong et al present a whole genome and transcriptome analysis of 258 t(4;14) patients compared to 183 non-t(4;14) patients with NDMM. The authors demonstrate that 3 different breakpoints within the NSD2 gene subdivide these patients prognostically, with only 1 subgroup demonstrating high risk, establishing a role for targeted sequencing in further defining prognosis.
NRX-0492 degrades wild-type and C481 mutant BTK and demonstrates in vivo activity in CLL patient-derived xenografts
Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a driver of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and covalent inhibitors of BTK like ibrutinib have become central to CLL therapy. Resistance to ibrutinib is often associated with mutations that block binding. Zhang and colleagues report on excellent activity in patient-derived xenografts of a targeted protein degrader that links a noncovalent BTK-binding domain to cereblon, catalyzing ubiquitylation of BTK and targeting it for proteosomal degradation. Ongoing clinical studies may establish this as a strategy for overcoming BTK-inhibitor resistance.
Noncanonical β-catenin interactions promote leukemia-initiating activity in early T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
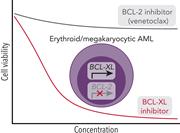
Erythroid/megakaryocytic differentiation confers BCL-XL dependency and venetoclax resistance in acute myeloid leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with erythroid or megakaryocytic differentiation (pure erythroid leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome with erythroid features, and acute megakaryocytic leukemia) has a poor response to therapy and a poor prognosis. Kuusanmäki and colleagues report on a high-throughput screen to identify potential drugs with improved efficacy. The authors show that these subtypes depend on BCL-XL and not on BCL2 or MCL; consequently, BCL-XL inhibition was effective in cell lines and primary cells that were resistant to venetoclax.
TRANSPLANTATION
Oxidative DNA damage in reconstituting T cells is associated with relapse and inferior survival after allo-SCT
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) is potentially curative for hematologic malignancies, depending on a graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) effect; however, many patients go on to relapse. Karl et al investigated the role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in abrogating GVL. The authors report elevated levels of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine, a biomarker of oxidant stress, in patients after allo-SCT. Continued high levels were associated with T-cell activation, markers of T-cell exhaustion, and shorter overall survival, highlighting ROS as an important contributor to relapse.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Somatic TP53 mutations are preleukemic events in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Bone marrow aspirate showing dysplastic erythrocyte precursors and multiple dysplastic megakaryocytes with separated nuclear lobes in the marrow of a 17-year-old male with GATA2 deficiency and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia with monosomy 7 and mutations in ASXL1, SETBP1, and U2AF1. See the article by Calvo and Hickstein on page 1524.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals



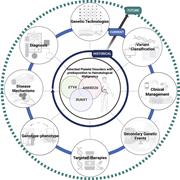



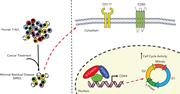


Introduction to a review series on germ line predisposition to hematologic malignancies: time to consider germ line testing