Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
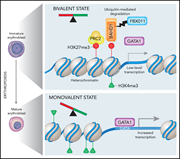
FBXO11-mediated proteolysis of BAHD1 relieves PRC2-dependent transcriptional repression in erythropoiesis
The mechanisms that regulate specific histone marks and consequent transcriptional repression are critical for hematopoietic development but poorly understood. In a Plenary Paper, Xu and colleagues describe a new mechanism that drives terminal human erythroid differentiation, identifying the heterochromatin-associated protein BAHD1 as a major target of the E3 ubiquitin ligase FBXO11 and showing that degradation of BAHD1 relieves transcriptional repression. This allows GATA1-mediated activation of a large number of erythroid genes.
PERSPECTIVES
Optimizing therapy in the modern age: differences in length of maintenance therapy in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Teachey et al review the data on duration of maintenance therapy for children and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and the differences in practice across cooperative groups. They provide their perspective regarding the length of maintenance therapy and the Children’s Oncology Group’s change to use the same duration of treatment for girls and boys in current trials.
HOW I TREAT
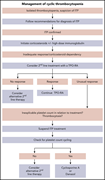
How I manage cyclic thrombocytopenia
Clinical Trials & Observations
Cyclic thrombocytopenia (CTP) is a rare disease, with most patients initially misdiagnosed as having immune thrombocytopenia. Kyrle and Eichinger provide their view on how to diagnose and manage CTP, anticipating that early accurate diagnosis will prevent affected patients from being exposed to possibly harmful therapies.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
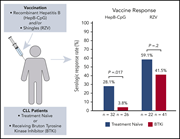
Effect of Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor on efficacy of adjuvanted recombinant hepatitis B and zoster vaccines
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
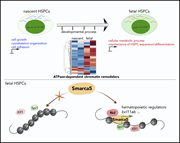
Smarca5-mediated epigenetic programming facilitates fetal HSPC development in vertebrates
Ding and colleagues used zebrafish and murine models to decipher how functional hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) develop in the embryo.They provide novel insight into the role of Smarca5 in the maintenance of chromatin accessibility at promoters of hematopoiesis-related genes in fetal HSPCs through interaction with nucleolin to promote chromatin remodeling.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
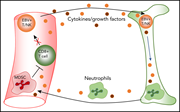
Characterizing EBV-associated lymphoproliferative diseases and the role of myeloid-derived suppressor cells
Collins and colleagues report novel methods for the identification, phenotyping, and functional comparison of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–infected and noninfected lymphocytes in a cohort of 5 patients with chronic active EBV infection and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, revealing the presence of large numbers of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) which inhibit T-cell growth and responses. The authors postulate that these MDSCs may explain the lack of clearance of EBV-infected cells.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
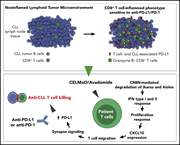
Triggering interferon signaling in T cells with avadomide sensitizes CLL to anti-PD-L1/PD-1 immunotherapy
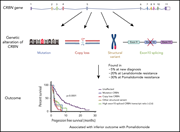
Multiple cereblon genetic changes are associated with acquired resistance to lenalidomide or pomalidomide in multiple myeloma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Cereblon binding is essential to the function of lenalidomide and pomalidomide as antimyeloma agents. In this first comprehensive analysis of cereblon alterations in myeloma as patients sequence through lines of therapy, Gooding et al found that genetic alterations in cereblon identified after progression on lenalidomide predict for early pomalidomide failure and occur in myeloma in one-third of patients with pomalidomide-refractory disease.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
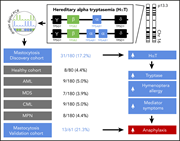
Hereditary α tryptasemia is a valid genetic biomarker for severe mediator-related symptoms in mastocytosis
Clinical Trials & Observations
The diverse clinical presentations of systemic mastocytosis (SM) reflect neoplastic mast cell (MC)–related mediator release and organ damage, but the most severe mediator symptoms are often found in patients with indolent SM, including those with minimal MC burden. Greiner et al shine new light on this conundrum by revealing that hereditary α tryptasemia occurs in high prevalence among patients with SM associated with an increased risk of severe mediator-related symptoms.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
TRANSFUSION MEDICINE
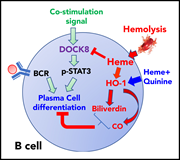
Hemolysis inhibits humoral B-cell responses and modulates alloimmunization risk in patients with sickle cell disease
Pal and colleagues report differences in heme response pathways in B cells between alloimmunized and nonalloimmunized patients with sickle cell disease (SCD). These data suggest the potential for identifying biomarkers of alloimmunization and the development of strategies for targeting these pathways for prevention of alloimmunization in patients with SCD.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Microscopy reveals the ability of avadomide to induce type I/II interferon-inducible CXCL10 (red) and CXCR3 (white) on CD8 T cells (colocalization: yellow) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) xenografts. The promotion of a T-cell–inflamed microenvironment sensitizes CLL to anti–programmed death 1. See the article by Ioannou et al on page 216.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals




A ubiquitin ligase toggles red cell differentiation