Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT
FDA-approved therapies for chronic GVHD
In this Blood Spotlight, Lee and Zeiser succinctly review the new targeted therapies that are available for the treatment of chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). The authors explain how ruxolitinib, belumosudil, ibrutinib, and axatilimab each inhibit various cytokine and other receptor signaling, and they critically evaluate the clinical data underpinning the registrations. They also identify gaps in knowledge, especially about the optimal use of these drugs, alone and in combination.
HOW I TREAT
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Long-term efficacy and safety of danicopan as add-on therapy to ravulizumab or eculizumab in PNH with significant EVH
Clinical Trials & Observations
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), a genetic disorder of complement regulation on red cell membranes that causes thrombosis and hemolysis, is effectively controlled by the use of terminal complement inhibitors (eculizumab and ravulizumab), but some patients experience significant extravascular hemolysis (EVH). Kulasekararaj and colleagues report long-term clinical data from the ALPHA trial showing that the addition of the oral complement factor D inhibitor danicopan improves hemoglobin ≥2 g/dL in patients with PNH experiencing clinically significant EVH despite standard therapy. These data suggest that combination therapy may be optimal management for a subset of people.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
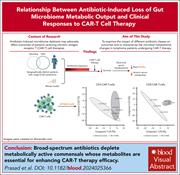
Antibiotic-induced loss of gut microbiome metabolic output correlates with clinical responses to CAR T-cell therapy
Clinical Trials & Observations
Associations between exposure to broad spectrum antibiotics and inferior outcomes from chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy are emerging. In a large international cohort of patients with lymphoma who received anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, Prasad and colleagues found that survival was reduced in patients receiving commonly prescribed extended spectrum antibiotics and that this was associated with dysbiosis of the gut and altered circulating microbial metabolites. In mechanistic murine studies, antibiotics depleted metabolically active commensals whose metabolites were essential for enhancing CAR T-cell efficacy, collectively arguing for increased caution when selecting antibiotics for use prior to CAR T-cell therapy.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Serum free light chains in a racially diverse population including African Americans and populations from South Africa
Diagnosis of asymptomatic conditions such as light chain–only monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (LC-MGUS) requires that the appropriate reference range is applied. Recently, racial differences in ratios between κ and λ light chains have been found in healthy people. Bertamini and colleagues report improved precision for identifying individuals with African ancestry harboring LC-MGUS and related gammopathies after establishing a new reference interval for the serum-free light chain test based on a racially diverse population.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
BRAFV600E induces key features of LCH in iPSCs with cell type–specific phenotypes and drug responses
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is a rare inflammatory myeloid neoplasm of histiocytes, clinically characterized by bone pain, skin lesions, lung cysts, diabetes insipidus, central nervous system involvement, and activating mutation of the BRAF gene in half of the cases. Abagnale et al developed an induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) model, revealing that the BRAFV600E mutation induced the differentiation of CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells into LCH cells and that BRAFV600E iPSC-derived microglia-like cells induced neurodegeneration, a feature of the disease. As well as providing insight into pathogenesis, the model should enable more faithful preclinical evaluation of small molecule therapies.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
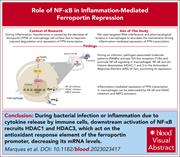
Inflammation-driven NF-κB signaling represses ferroportin transcription in macrophages via HDAC1 and HDAC3
Macrophages play a central role in the regulation of iron homeostasis, exporting iron collected through clearance of aged red cells. Marques et al unravel how inflammation reduces the production in macrophages of the iron exporter ferroportin, implicating repression of transcription following NF-κB signaling–induced histone deacetylase recruitment to a regulatory element of Slc40a1, the gene which encodes ferroportin. This finding may enable the development of selective treatments that reverse the anemia of inflammation.
TRANSPLANTATION
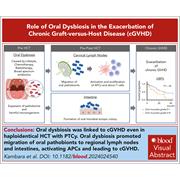
Oral inflammation and microbiome dysbiosis exacerbate chronic graft-versus-host disease
CME
The gut microbiome is recognized as a factor influencing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. In this month’s CME article, Kambara et al explore for the first time the role of oral dysbiosis in exacerbating GVHD in clinical association studies and mechanistic preclinical studies, including in vivo intervention studies in mice. The authors found that oral dysbiosis exacerbated GVHD and that targeted interventions mitigated these effects, clearly pointing to oral microbiome modulation as a potential avenue for GVHD prevention and treatment.
BLOOD WORK
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Immunofluorescence image of wild-type induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)–derived mature forebrain neurons stained with neuronal markers class 3 β-tubulin (yellow) and synapsin (red); nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). In a model of Langerhans cell histiocytosis, the presence of BRAFV600E iPSC-derived hematopoietic progenitor origin microglia-like cells induce neurodegeneration, a feature of the disease. See the article by Abagnale et al on page 850.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals








A belt-and-suspenders approach to PNH
Clinical Trials & Observations