Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PERSPECTIVE
The United Kingdom Infected Blood Inquiry: its findings and lessons for the future of transfusion
Over 30 000 people in the United Kingdom were infected with HIV and hepatitis C after receiving contaminated blood products in the 1970s and 1980s. Established in 2017, the UK Infected Blood Inquiry collected evidence from people that were infected as well as from clinicians and government and blood service officials. In this Perspective, Murphy and colleagues describe the key findings of the report and the recommendations that followed, with significant implications for blood banking practices in the United Kingdom and worldwide.
HOW I TREAT
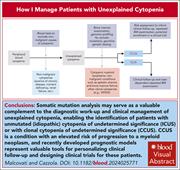
How I manage patients with unexplained cytopenia
Unexplained cytopenia describes a condition usually seen after the age of 50 which is characterized by peripheral blood cytopenia that cannot be attributed to any concomitant diseases or other identifiable causes using conventional tests. Malcovati and Cazzola provide diagnostic and management guidance through discussion of 4 illustrative cases, underscoring the importance of identifying individuals at risk of hematological malignancies within this population of patients.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Epcoritamab plus GemOx in transplant-ineligible relapsed/refractory DLBCL: results from the EPCORE NHL-2 trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
The treatment landscape for relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) has improved significantly with novel immunotherapy strategies. However, patients who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant have dismal outcomes. Brody and colleagues report the results of the phase 1b/2 EPCORE non-Hodgkin lymphoma-2 (NHL-2) trial of the CD3×CD20 bispecific antibody epcoritamab in combination with 4 cycles of gemcitabine plus oxaliplatin (GemOx), finding an impressive complete remission rate of 61%. While the data are preliminary, many remissions appear durable, highlighting the potential of this combination therapy.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
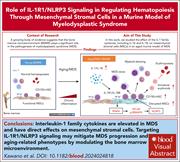
IL-1R1 and IL-18 signals regulate mesenchymal stromal cells in an aged murine model of myelodysplastic syndromes
The bone marrow (BM) microenvironment may play a significant role in the initiation and progression of myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Kawano and colleagues show that interleukin-1b (IL-1) and IL-18 are upregulated in BM samples from patients with MDS and that these cytokines regulate the BM niche by disrupting the capacity of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to support hematopoietic stem cells. Using an aged mouse model of MDS, the authors showed that inhibitors of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) and NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) reverse the proliferation of dysfunctional MSCs, suggesting that the IL-1 signaling pathway constitutes a promising target for new therapies for MDS.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
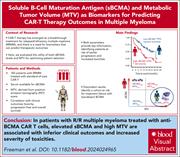
Tumor burden quantified by soluble B-cell maturation antigen and metabolic tumor volume determines myeloma CAR-T outcomes
In recent years, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has emerged as a treatment option for patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. However, response rates and toxicity profiles remain highly variable and unpredictable. Freeman and colleagues investigated the use of cleaved soluble B-cell maturation antigen (sBCMA) and metabolic tumor volume (MTV) as biomarkers for treatment outcomes, finding that elevated levels of sBCMA and high MTV predict inferior outcomes and increased toxicity. If further validated, these findings have the potential to establish robust predictive biomarkers for CAR T-cell therapy.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Efficacy and safety of daratumumab in intermediate/high-risk smoldering multiple myeloma: final analysis of CENTAURUS
Clinical Trials & Observations
Some patients with smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM) have high rates of progression to symptomatic MM. Early intervention strategies are being explored, but mature data are needed. Landgren and colleagues present the final analyses of an open label phase 2 study of 3 daratumumab regimens of varying intensity and duration. After a median follow up of 7 years, approximately only 40% had experienced progressive disease, and the majority of patients tolerated 20 cycles of therapy, enhancing the evidence base for early intervention in patients with high risk SMM.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
High-throughput drug screening identifies SMAC mimetics as enhancers of NK-cell cytotoxicity in chronic myeloid leukemia
The presence of functional natural killer (NK) cells has been linked with protection from relapse in tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) cessation trials in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), suggesting a functional role in CML control. Nygrén and colleagues report that second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases (SMAC) mimetic compounds enhance NK-cell cytotoxicity in CML cells. The authors’ findings suggest that combining these compounds with TKIs could offer a novel approach for treating CML blast crisis or sensitizing CML cells to TKIs by enhancing in vivo NK-cell activity.
TRANSPLANTATION
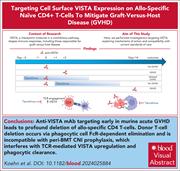
Targeting cell-surface VISTA expression on allospecific naïve T cells promotes tolerance
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) remains 1 of the most serious complications of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). Koehn and colleagues demonstrate that the immune checkpoint molecule V-domain immunoglobulin-containing suppressor of T-cell activation (VISTA) is briefly upregulated on donor T cells after allo-HSCT, and that an anti-VISTA monoclonal antibody selectively depletes alloreactive donor T cells, suppressing GVHD while preserving bystander T cells without affecting the graft-versus-leukemia effect in mice. These findings suggest that targeting VISTA could serve as a promising therapeutic strategy for GVHD.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Immunohistochemical staining for B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) demonstrating strong membranous and cytoplasmic expression in neoplastic plasma cells. The study highlights serum BCMA as a marker for tumor burden and predictor of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy outcomes. See the article by Freeman et al on page 1645.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






CD3×CD20 bispecifics + chemotherapy: good news for R/R DLBCL
Clinical Trials & Observations