Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
REVIEW ARTICLE
Genetic and epigenetic insights into cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (CTCLs) are a heterogeneous group of non-Hodgkin T-cell lymphomas of the skin. In this state-of-the-art review, Tensin et al discuss the impact of next-generation sequencing, which has allowed a better characterization of the genetic and epigenetic landscape that defines the spectrum of CTCL, permitting better definition of distinct subgroups of CTCL.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
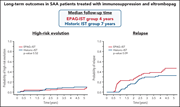
Long-term outcomes in patients with severe aplastic anemia treated with immunosuppression and eltrombopag: a phase 2 study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Patel et al report long-term outcomes of the phase 2 trial combining eltrombopag (EPAG) with immunosuppressive therapy (IST) for the treatment of newly diagnosed patients with severe aplastic anemia. As previously reported, adding EPAG improves responses in comparison to IST alone. However, there was no difference in the rate of relapse (29%) or the incidence of clonal evolution (15%), although events occur earlier in the EPAG group.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
IL-1 mediates microbiome-induced inflammaging of hematopoietic stem cells in mice
Aging is associated with impaired function and myeloid skewing of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) that has been attributed to age-associated inflammatory changes (“inflammaging”). Kovtonyuk et al demonstrate that the gut microbiome has a central role in this process by releasing microbial TLR4 and TLR8 ligands that increase marrow interleukin-1 (IL-1) production; IL-1 receptor knockout animals and germfree animals showed improved HSC function and decreased skewing. These data provide important insights into the process of HSC aging with potential important clinical implications.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
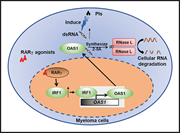
RARγ activation sensitizes human myeloma cells to carfilzomib treatment through the OAS-RNase L innate immune pathway
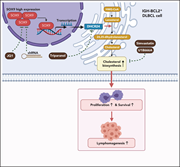
Oncogenic role of the SOX9-DHCR24-cholesterol biosynthesis axis in IGH-BCL2+ diffuse large B-cell lymphomas
Shen et al studied the stem cell regulatory protein SOX9 in the context of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), demonstrating that SOX9 positivity correlates with advanced-stage disease and SOX9 silencing decreases lymphoma cell proliferation. Transcriptome analysis identified DHCR24, a critical enzyme for cholesterol biosynthesis, as the target of SOX9, and inhibition of cholesterol synthesis also decreased growth of DLBCL xenografts. This suggests that statins may synergize with chemotherapy in the treatment of DLBCL.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
CEBPA mutations in 4708 patients with acute myeloid leukemia: differential impact of bZIP and TAD mutations on outcome
Clinical Trials & Observations
Mirroring recently reported observations in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (AML), Taube et al report in a study of over 4700 adult patients that both monoallelic and biallelic in-frame mutations of the CEBPA bZIP domain confer good prognosis, whereas point mutations and non-in-frame mutations do not confer the same overall good prognosis.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
The secreted tyrosine kinase VLK is essential for normal platelet activation and thrombus formation
Vertebrate lonesome kinase (VLK) is a widely expressed tyrosine kinase contained within platelet α -granules. Revollo and colleagues interrogated the role of VLK in platelet function through analysis of mice with a targeted VLK deletion in megakaryocytes and platelets. In the absence of VLK, platelets appeared normal but had in vitro and in vivo functional changes in platelet activation and thrombus formation, defining the first secreted protein kinase influencing normal platelet function.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
Factor VIIa suppresses inflammation and barrier disruption through the release of EEVs and transfer of microRNA 10a
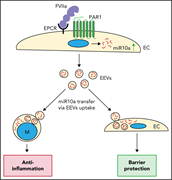
Factor VIIa (FVIIa) initiates coagulation by binding to tissue factor but also binds the endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR), where it induces anti-inflammatory responses and protective barrier responses that reduce fluid extravasation. Das et al report that FVIIa binding to the EPCR leads to release of endothelial extracellular vesicles (EEVs) containing anti-inflammatory microRNAs that confer an anti-inflammatory phenotype on monocytes; further, uptake of EEVs confers cytoprotection. This may explain the long-term protective effects of FVIIa prophylaxis in hemophilia with inhibitors.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Antibody response after 2 and 3 doses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant recipients
Clinical Trials & Observations
Three reports address the protection of the vulnerable population of patients with hematologic malignancies in the face of the ongoing COVID pandemic. The reports suggest that some patients who fail to mount a B-cell response to vaccine may nevertheless have protective T cell responses. As a group, these reports suggest that patients should continue to be immunized with additional doses to attempt to improve immune response but that they need to maintain the precautions recommended for the unvaccinated.
Severe impairment of T-cell responses to BNT162b2 immunization in patients with multiple myeloma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Three reports address the protection of the vulnerable population of patients with hematologic malignancies in the face of the ongoing COVID pandemic. The reports suggest that some patients who fail to mount a B-cell response to vaccine may nevertheless have protective T cell responses. As a group, these reports suggest that patients should continue to be immunized with additional doses to attempt to improve immune response but that they need to maintain the precautions recommended for the unvaccinated.
Humoral and cellular responses after COVID-19 vaccination in anti-CD20-treated lymphoma patients
Clinical Trials & Observations
Three reports address the protection of the vulnerable population of patients with hematologic malignancies in the face of the ongoing COVID pandemic. The reports suggest that some patients who fail to mount a B-cell response to vaccine may nevertheless have protective T cell responses. As a group, these reports suggest that patients should continue to be immunized with additional doses to attempt to improve immune response but that they need to maintain the precautions recommended for the unvaccinated.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Strong SOX9 expression by immunohistochemistry in a case of germinal center B-cell-type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with IGH-BCL2 translocation, diagnosed in a right arm mass biopsy specimen from a 55-year-old male patient. See the article by Shen et al on page 73.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





Eltrombopag: a springboard to early responses in SAA
Clinical Trials & Observations