Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
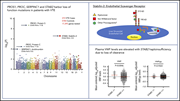
Whole-exome sequencing identifies rare variants in STAB2 associated with venous thromboembolic disease
In this Plenary Paper, Desch and colleagues describe whole-exome sequencing of patients with venous thromboembolic disease (VTE) vs controls and novel analytic techniques to identify rare STAB2 variants associated with VTE, each of which reduces the surface expression of the gene product stabilin-2. Stabilin-2 enhances clearance of von Willebrand factor (VWF), and elevated levels of VWF are observed in patients with STAB2 variants, suggesting a mechanism for the elevated VTE risk. This work establishes STAB2 as a thrombophilia gene.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Functional and genetic testing in adults with HLH reveals an inflammatory profile rather than a cytotoxicity defect
Clinical Trials & Observations
While primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is explained by genetic deficiencies in lymphocyte cytotoxicity, the role of intrinsic cytotoxicity defects in the more common secondary HLH has not been defined. Carvelli and colleagues reveal that no major intrinsic cytotoxicity dysfunction is seen in secondary HLH when appropriate comparisons are made with patients having the same precipitating diseases but without HLH.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
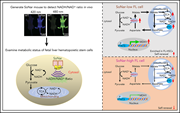
MDH1-mediated malate-aspartate NADH shuttle maintains the activity levels of fetal liver hematopoietic stem cells
Gu et al used a transgenic mouse model that reports mitochondrial respiration to explore how energy metabolism and stemness interrelate between different stages of developmental hematopoiesis. Their work reveals that fetal liver stem cells principally use mitochondrial respiration as their main energy source and demonstrates how this is tightly regulated.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
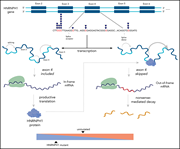
Coding and noncoding drivers of mantle cell lymphoma identified through exome and genome sequencing
Pararajalingam and colleagues performed large-scale genomic analysis for discovery and resequencing of 191 mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) samples with clinical follow-up, confirming the prognostic significance of TP53 and NOTCH1 mutations and revealing evidence for aberrant regulation of messenger RNA processing in MCL pathobiology.
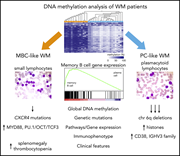
Identification of 2 DNA methylation subtypes of Waldenström macroglobulinemia with plasma and memory B-cell features
The B cells of 35 patients with MYD88-mutated Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) were studied by Roos-Weil et al, using integrated genome-wide DNA methylation, transcriptome, and mutation profiling. Their data suggest that WM can be subdivided into 2 major groups (memory B-cell–like and plasma cell–like) based on patterns of DNA methylation, each associating with different genetic and phenotypic features.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
The miR-185/PAK6 axis predicts therapy response and regulates survival of drug-resistant leukemic stem cells in CML
Lin and colleagues explored the issue of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibition in chronic myeloid leukemia, implicating an important regulatory function of the microRNA miR-185, acting through PAK6, in determining the drug sensitivity of leukemic stem cells.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
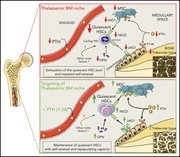
Hematopoietic stem cell function in β-thalassemia is impaired and is rescued by targeting the bone marrow niche
Aprile et al report bone marrow niche defects in a well-established murine model of β-thalassemia and suggest that the niche renders stem cells more proliferative due to reduced parathormone (PTH) expression and impaired osteolineage niche regulation. Importantly, the stem cell defect can be corrected by PTH treatment, suggesting possibilities for targeting this niche in clinical care.
TRANSPLANTATION
Risk score to predict event-free survival after hematopoietic cell transplant for sickle cell disease
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Deciding whether to recommend allogeneic transplantation for sickle cell disease is not straightforward. To assist, Brazauskas and colleagues propose a simple risk score comprising age and donor type based on their retrospective analyses of outcomes in 1425 patients.
VASCULAR BIOLOGY
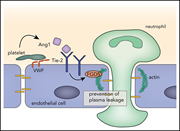
Platelets docking to VWF prevent leaks during leukocyte extravasation by stimulating Tie-2
Braun et al provide insights into a new regulatory pathway preventing vascular leakage during neutrophil diapedesis. Using murine models, they demonstrated that platelets prevent plasma leaks by binding to endothelium via VWF and releasing angiopoietin-1, which stimulates endothelial Tie-2 to trigger diapedesis pore closure.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Racial variation in ITP prevalence and chronic disease phenotype suggests biological differences
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
PECAM-1–labeled blood vessel of the murine cremaster muscle in an interleukin-1β–treated mouse. Upon interference with the Tie-2 signaling pathway, fluorescent microspheres (white) leak out as MRP14-labeled neutrophils are extravasated from the vessel, thus marking sites of neutrophil-induced vascular leaks. See the article by Braun et al on page 627.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






A collapse for venous thromboembolism