Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
REVIEW ARTICLE
Dysregulation of the TET family of epigenetic regulators in lymphoid and myeloid malignancies
TET2 is frequently mutated in lymphoid and myeloid malignancy. Lio et al review the current understanding of the role of TET enzymes in lymphoid and myeloid malignancy, highlighting that loss of TET protein function can occur either by mutation or as a result of metabolic alteration.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Pegylated interferon alfa-2a for polycythemia vera or essential thrombocythemia resistant or intolerant to hydroxyurea
Clinical Trials & Observations
Yacoub et al report excellent responses to pegylated interferon alfa-2a in patients with hydroxyurea-resistant/intolerant polycythemia vera or essential thrombocythemia.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
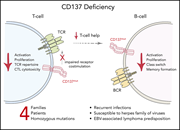
CD137 deficiency causes immune dysregulation with predisposition to lymphomagenesis
Brief Report
Somekh and colleagues identify CD137, a member of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily, as a novel cause of immunodeficiency associated with a risk of autoimmunity and lymphoid malignancy.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
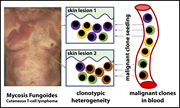
Skin colonization by circulating neoplastic clones in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Iyer and colleagues used deep sequencing of T-cell receptor genes to demonstrate clonal heterogeneity of mycosis fungoides, with repeated seeding of disparate clones from the blood.
The double-hit signature identifies double-hit diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with genetic events cryptic to FISH
Brief Report
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
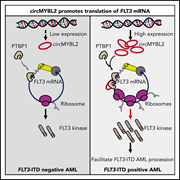
circMYBL2, a circRNA from MYBL2, regulates FLT3 translation by recruiting PTBP1 to promote FLT3-ITD AML progression
Sun et al identify a circular RNA, circMYBL2, that upregulates FLT3 translation to promote FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia (AML) progression, suggesting a novel therapeutic target for FLT3-ITD AML.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
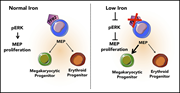
Low iron promotes megakaryocytic commitment of megakaryocytic-erythroid progenitors in humans and mice
Xavier-Ferrucio and colleagues elucidate the mechanism of thrombocytosis in iron deficiency anemia, using murine and human cell models to demonstrate that iron deficiency attenuates ERK signaling and biases the commitment of megakaryocyte-erythrocyte progenitors toward the megakaryocytic lineage.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Improved survival of men 50 to 75 years old with acute myeloid leukemia over a 20-year period
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Wright-Giemsa staining of bone marrow from mice engrafted with FLT3-ITD–positive cells, cells with large nuclei. Knocking down circMYBL2 specifically inhibits the proliferation and promotes differentiation in FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia. See the article by Sun et al on page 1533.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





Pegylated interferon alfa-2a for polycythemia vera or essential thrombocythemia resistant or intolerant to hydroxyurea
Clinical Trials & Observations
Yacoub et al report excellent responses to pegylated interferon alfa-2a in patients with hydroxyurea-resistant/intolerant polycythemia vera or essential thrombocythemia.