Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
One hundred thirty-four germ line PU.1 variants and the agammaglobulinemic patients carrying them
Inborn errors of immunity can reveal nonredundant molecular requirements for the generation, maintenance, and function of human immune cells. In this Plenary Paper, Knox and colleagues report on a large functional complement of 134 variants in SPI1, the gene encoding the transcription factor PU.1, present in molecularly undiagnosed patients with agammaglobulinemia. The authors found 25 variants causing haploinsufficiency in 21 kindreds, each clinically manifested as severe B- and dendritic-cell deficiency with propensity for sinopulmonary bacterial infections. These data greatly expand our knowledge of the recently discovered PU.1-mutated agammaglobulinemia syndrome and provide a reminder that in silico prediction of novel variant pathogenicity is insufficient without functional studies.
SPECIAL REPORT
Role of allo-HCT in “nonclassical” MPNs and MDS/MPNs: recommendations from the PH&G Committee and the CMWP of the EBMT
Among myeloid neoplasms (MNs), there are a large number of rare disease entities, collectively “nonclassical” myeloproliferative and myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative disorders, defined by prominent clinical and/or genetic features, for which high quality data on definitive management, including allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HCT), are lacking. In this Special Report, Polverelli and colleagues from 2 international working groups synthesize the available data and provide guidance on the role of allo-HCT in 8 “nonclassical” entities. Where the evidence allows, the authors make recommendations about prognostication and timing of transplant, and they suggest alignment with preparatory regimens and transplant policies used routinely for more common “classical” MNs.
REVIEW ARTICLE
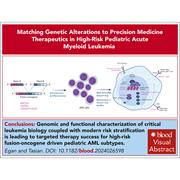
Precision medicine for high-risk gene fusions in pediatric AML: a focus on KMT2A, NUP98, and GLIS2 rearrangements
New molecular techniques and the use of sophisticated bioinformatic pipelines have uncovered many new fusion oncogenes driving acute myeloid leukemia (AML), especially in pediatric disease. Beyond allowing for better classification and understanding of biology, does this new knowledge change therapeutic options and improve outcomes? Egan and Tasian review the evidence, focusing on emerging new targeted therapies for 3 high-risk subtypes of AML with oncogenic gene fusions that pediatric physicians regularly encounter.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Ibrutinib lead-in followed by venetoclax plus ibrutinib for relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: the SAKK 34/17 trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
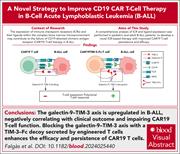
A TIM-3–Fc decoy secreted by engineered T cells improves CD19 CAR T-cell therapy in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
After CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, most relapses of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) still express CD19, suggesting exhaustion of the response rather than a loss of antigen as the mechanism of failure. Falgàs et al examined samples at diagnosis and relapse and identified parallel upregulation of the checkpoint receptor TIM-3 on CD8+ T cells and its ligand galectin-9 (Gal-9) on relapsed B-ALL. The authors show that incubating T cells with Gal-9 led to impaired CAR T-cell survival and cytotoxicity, and they describe a novel CAR T-cell armor strategy via secretion of a TIM-3–Fc decoy to overcome TIM-3-Gal-9–mediated CAR T-cell exhaustion. These promising preclinical data portend further evolution of clinical CAR T-cell products.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
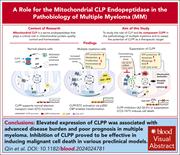
Targeting caseinolytic mitochondrial matrix peptidase, a novel contributor to the pathobiology of high-risk multiple myeloma
Evaluating the impact of CRBN mutations on response to immunomodulatory drugs and novel cereblon E3 ligase modulators in myeloma
Cereblon (CRBN) is the molecular target of thalidomide and its analogs, and mutations in the protein can mediate resistance in this class of drug. Chrisochoidou et al systematically evaluated the structural and functional consequences of CRBN missense mutations observed in patients with immunomodulatory drug–resistant myeloma, identifying 3 categories that render cells resistant to all such drugs, or have no effect, or have selective effects depending on the specific drug tested. These data will help refine development of CRBN E3 ligase modulators.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Venetoclax and decitabine vs intensive chemotherapy as induction for young patients with newly diagnosed AML
Clinical Trials & Observations
Preliminary evidence suggests that venetoclax–hypomethylating agent regimens approved for older, unfit patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) may perform well in younger adults. Lu et al report results of the first randomized clinical trial comparing outcomes in newly diagnosed younger patients with AML treated with venetoclax-decitabine (VEN-DEC) vs idarubicin-cytarabine as induction, prior to conventional consolidation therapy for all. The study found similar rates of complete remission, measurable residual disease negativity, and event-free survival, while demonstrating superior safety with VEN-DEC. While overall survival data remain immature, the study potentially identifies differential efficacy according to AML subtype. This pioneering trial points one way forward as we wrestle with how to incorporate venetoclax-based regimens into the care for young, fit adults with AML.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
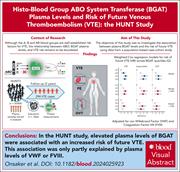
Histo–blood group ABO system transferase plasma levels and risk of future venous thromboembolism: the HUNT study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Meta-analyses of epidemiological studies teach us that people with non-O blood groups (A, AB, and B) have a 2 to 3-fold higher risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) than those from the O blood group. Onsaker and colleagues analyzed plasma proteome data from a large population-based case-control study of healthy people who develop VTE and provide evidence that links histo–blood group ABO system transferase (BGAT) with this elevated risk, especially for unprovoked VTE. The authors found that the effects of higher BGAT levels in non-O blood groups likely go beyond influencing von Willebrand factor and factor VIII levels, but future mechanistic studies are needed to define the precise biological explanation for the association.
LETTER TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Precision medicine targets for
KMT2A -rearranged,NUP98 -rearranged, andGLIS2 -rearranged acute myeloid leukemia. See the article by Egan and Tasian on page 2574. - PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals








SPI-ing on human B-cell development