Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
REVIEW ARTICLE
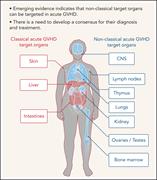
Nonclassical manifestations of acute GVHD
Zeiser and Teshima provide a comprehensive review illustrating the breadth of how acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) manifests after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Highlighting organ involvement beyond the standard triad of skin, gut and liver, they review the evidence in humans and in murine models for acute GVHD damaging multiple other organs, including the brain, lungs, kidneys, bone marrow, and gonads.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
The contact activation inhibitor AB023 in heparin-free hemodialysis: results of a randomized phase 2 clinical trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Prevention of clotting in extracorporeal circuits during hemodialysis by unfractionated heparin is standard, but not always tolerated. AB023 is a monoclonal antibody that blocks contact activation of blood clotting by inhibiting factor XI activation by factor XIIa but not by thrombin. Lorentz et al report on a randomized phase 2 placebo-controlled trial with patients undergoing heparin-free chronic hemodialysis, demonstrating reduced dialyzer clotting and thrombin-antithrombin complex formation and setting the stage for phase 3 trials.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
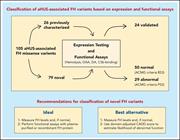
Functional characterization of 105 factor H variants associated with aHUS: lessons for variant classification
Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) is a life-threatening thrombotic microangiopathy, and complement dysregulation due to pathogenic variants in factor H (FH) is a recognized cause. The clinical utility of genetic testing in aHUS is limited by the large number of variants reported as “variants of uncertain significance” for the FH gene. Martin Merinero and colleagues functionally characterized 105 FH variants and provide critical data that improve understanding of their clinical significance and should better informclinical practice.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
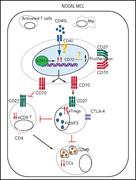
SOX11, CD70, and Treg cells configure the tumor immune microenvironment of aggressive mantle cell lymphoma
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) remains a treatment challenge, and allogeneic stem cell transplantation and emerging T cell-based therapies are key options for relapsed disease. In seeking to understand how SOX11 oncogenic expression contributes to the aggressiveness of MCL, Balsas et al reveal that SOX11+ MCLs have a tumor microenvironment with reduced immune infiltrates and downmodulation of antitumor response genes, but with overexpression of CD70, which can promote immune evasion. CD70 expression is associated with increased Treg infiltration, high proliferation, and aggressive clinical course and may represent a new target for therapy.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Inferring the dynamics of mutated hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells induced by IFNα in myeloproliferative neoplasms
Interferon-α (IFNα) is a reconized therapy for polycythemia vera and essential thrombocytosis, but its efficacy is heterogeneous. Mosca and colleagues report a detailed analysis of JAK2- and CALR-mutant stem cells and progenitors obtained from patients treated with IFNα. They found that the exhaustion of the malignant stem cell pool varies by genotype, with homozygous JAK2- mutant cells being more sensitive than heterozygous cells, and that distinct CALR mutations also show differing kinetics of response. Their data may inform future personalization of IFNα-based therapy.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
Insights in ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia
Greinacher et al report a detailed characterization of a potential mechanism underlying the pathogenesis of vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT). They propose that the pathogenesis of VITT involves a 2-step mechanism, initiated by binding of platelet factor 4 to components of the ChadOX1 nCov-19 adenoviral vaccine followed by a prothrombotic antibody response similar to autoimmune heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. This work helps explain the clinical observations and also suggests modifications to future vaccine production to reduce the risk of VITT.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
TRANSPLANTATION
Belumosudil for chronic graft-versus-host disease after 2 or more prior lines of therapy: the ROCKstar Study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) is a major cause of morbidity and late mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cutler and colleagues report on a randomized phase 2 clinical trial of belumosudil, an oral ROCK2 inhibitor, in 132 patients with cGVHD requiring third- or later-line therapy. They found that treatment with 200 mg of belumosudil daily induces responses in 74% of patients, including those with cGVHD refractory to steroids, ruxolitinib, and ibrutinib. These data form the basis for this agent’s recent approval by the US Food and Drug Administration.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Host immune system modulation in Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients treated with dasatinib and blinatumomab
Childhood acute myeloid leukemia shows a high level of germline predisposition
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Cover art by Brian Cannon, American Society of Hematology.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






Iron metabolism as a novel therapeutic target