Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PERSPECTIVE
Refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: a new working definition beyond corticosteroid refractoriness
With the recent approval of ruxolitinib as a treatment for steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease, there is now a need to refine the definition of treatment failure in this still highly challenging clinical setting. In this Perspective, the authors put forward a provisional proposal for consideration by the transplant community and cooperative groups.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
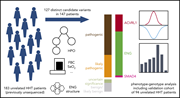
Mutational and phenotypic characterization of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
Clinical Trials & Observations
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is a vascular dysplasia inherited as an autosomal dominant trait, but families have often been left without a firm diagnosis because of imprecision in clinical criteria and an incomplete mutational database. Shovlin et al identify more than 100 new likely pathogenic variants in the 4 known HHT genes and provide justification for a systematic approach to the diagnosis of HHT incorporating mutation analysis, modeling, and detailed clinical information.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
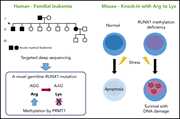
Hematopoietic stem cells acquire survival advantage by loss of RUNX1 methylation identified in familial leukemia
Clinical Trials & Observations
In an elegant investigation of a familial predisposition to acute leukemia, Matsumura and colleagues implicated mutation of a specific methylation site in the RUNX1 gene. They went on to reveal how altered methylation of this regulatory gene in mice confers on hematopoietic stem cells the hallmark leukemic features of resistance to apoptosis and survival advantage under stress.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
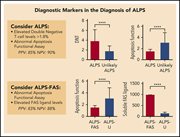
Key diagnostic markers for autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome with molecular genetic diagnosis
Clinical Trials & Observations
Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS) is a rare immunodeficiency caused by mutations in genes affecting the extrinsic apoptotic pathway (FAS, FASL, and CASP10). Through analysis of 215 patients with suspected ALPS, Molnár and colleagues report improved diagnostic accuracy through measurement of double-negative T-cell number, soluble FAS ligand, and apoptotic function.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
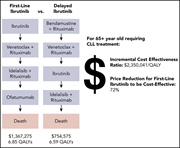
Cost-effectiveness of first-line vs third-line ibrutinib in patients with untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Clinical Trials & Observations
Using data from a randomized trial of ibrutinib vs chemoimmunotherapy for patients needing first treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia, the authors calculated that the incremental cost per quality-adjusted life year gained of using ibrutinib as a first treatment rather than as a later treatment exceeds $2 million. They explore scenarios that influence the cost-effectiveness of ibrutinib and price reductions necessary to meet willingness-to-pay thresholds.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
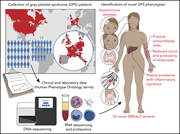
Novel manifestations of immune dysregulation and granule defects in gray platelet syndrome
Clinical Trials & Observations
Sims et al comprehensively studied 47 patients with gray platelet syndrome, expanding both the palette of causal mutations in the NBEAL2 gene and the spectrum of clinical manifestations to include immune dysregulation and autoimmunity. They describe granule defects in multiple leukocyte lineages as well as the classical α-granule defects in platelets, potentially explaining the broader clinical phenotypes.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
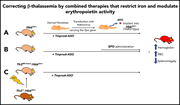
Correcting β-thalassemia by combined therapies that restrict iron and modulate erythropoietin activity
Thalassemias are characterized by anemia, ineffective erythropoiesis, splenomegaly, and systemic iron overload. In this preclinical murine study, the authors provide data indicating that the impact on anemia of iron restriction therapies, such as hepcidin activators, increases when these therapies are used in combination with erythroid stimulators like erythropoietin.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Transdifferentiation of lymphoma into sarcoma associated with profound reprogramming of the epigenome
Novel inhibitors of the histone methyltransferase DOT1L show potent antileukemic activity in patient-derived xenografts
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Megakaryocytes in the bone marrow from a patient with gray platelet syndrome (GPS). Intact neutrophils are present within the megakaryocytes (emperipolesis), a common feature in GPS (CD61 alkaline phosphatase immunostain with fast red substrate and hematoxylin counterstain; magnification ×1000). See the article by Sims et al on page 1956.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals



ALPS or not?