Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
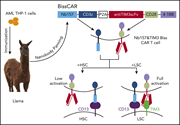
Bispecific and split CAR T cells targeting CD13 and TIM3 eradicate acute myeloid leukemia
The use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML) has been hampered by the difficulty of identifying target antigens specific to AML that spare normal hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), and the availability of monoclonal antibodies that increase T-cell cytotoxicity against AML. In a Plenary Paper, He and colleagues describe the use of a novel selection system to isolate heavy chain–only antibodies, also known as nanobodies, yielding bispecific CAR T cells that selectively target AML cells with limited HSC toxicity.
HOW I TREAT
How I assess and manage the risk of bleeding in patients treated for venous thromboembolism
Clinical Trials & Observations
Klok and Huisman discuss management of bleeding risk in patients with venous thromboembolism through a discussion of 2 relevant cases.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
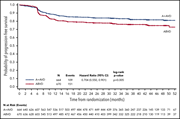
Brentuximab vedotin with chemotherapy for stage III/IV classical Hodgkin lymphoma: 3-year update of the ECHELON-1 study
Clinical Trials & Observations
The authors present a 3-year update of a phase 3 trial of brentuximab vedotin with doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (A + AVD) for frontline treatment of advanced-stage Hodgkin lymphoma. They confirm that A + AVD provides superior progression-free survival over doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (ABVD) without treatment intensification and avoiding the toxicity of bleomycin.
PHAGOCYTES, GRANULOCYTES, AND MYELOPOIESIS
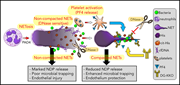
Fc-modified HIT-like monoclonal antibody as a novel treatment for sepsis
During sepsis, neutrophils release neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) composed of DNA, histones, and antimicrobial proteins that sequester pathogens but also damage tissue through toxic degradation products. The authors demonstrate that platelet factor 4 (PF4) binds to, compacts, and prevents degradation of NETs, and that an anti-PF4 antibody modified to block immune activation through its Fc portion improves survival in a murine sepsis model.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
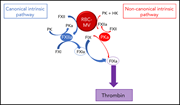
Red blood cell microvesicles activate the contact system, leading to factor IX activation via 2 independent pathways
Stored red blood cells release microvesicles (RBC-MVs) that are thought to contribute to coagulation. Noubouossie and colleagues demonstrate that RBC-MVs activate factor IX by 2 distinct pathways and may contribute to transfusion-associated complications.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Outcomes of rare patients with a primary cutaneous CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorder developing extracutaneous disease
Clinical Trials & Observations
Multiple BCL2 mutations cooccurring with Gly101Val emerge in chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression on venetoclax
The BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax has complete response rates of up to 50% in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients, but secondary resistance reflecting acquired mutations in BCL2 can lead to treatment failure. Blombery et al report that an unexpectedly large number of patients carry multiple BCL2 mutations with subclonal variation in their occurrence.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells with labeled nuclei (blue) and cytoplasm (green) were grown to confluence in a microfluidic channel. Cells were exposed to neutrophil extracellular traps compacted with platelet factor 4 and demonstrate minimal change in morphology. See the article by Gollomp et al on page 743.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals




A bispecific approach to improving CAR T cells in AML