Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
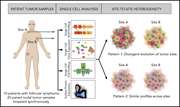
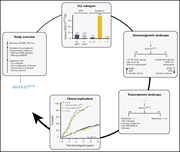
Single-cell analysis can define distinct evolution of tumor sites in follicular lymphoma
In a Plenary Paper, Haebe and colleagues demonstrate the heterogeneity of follicular lymphoma between divergent sites in the same patient. Using single-cell RNA sequencing, B-cell and T-cell receptor sequencing, and multiparameter flow cytometry, they show that many tumors display independent site-specific clonal evolution. With increasing use of targeted therapies, this study highlights the limitations of single-site biopsies for the diagnosis of follicular lymphoma.
REVIEW ARTICLE
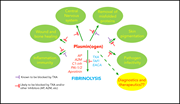
Plasminogen: an enigmatic zymogen
While plasminogen is best recognized as the precursor to plasmin, which plays a critical role in fibrinolysis, plasminogen plays many other important roles unrelated to fibrin removal. Keragala and Medcalf review the wide-ranging roles of plasmin and plasminogen in the unfolded protein response, in inflammatory and immune responses, and potentially as an antiviral protein.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
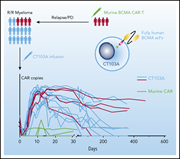
A phase 1 study of a novel fully human BCMA-targeting CAR (CT103A) in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma
Clinical Trials & Observations
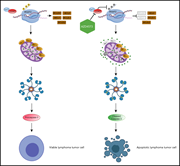
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells targeting B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) are effective in relapsed, refractory multiple myeloma (R/RMM), but remissions tend to be short-lived. In a phase 1 study, Wang et al found preliminary evidence of impressive efficacy and safety with a fully human BCMA-specific CAR in patients with R/RMM, reporting 100% response and median transgene persistence of 307 days, including in patients previously receiving murine CAR T-cell therapy.
GENE THERAPY
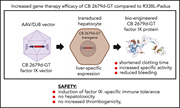
Gene therapy for hemophilia B using CB 2679d-GT: a novel factor IX variant with higher potency than factor IX Padua
Brief Report
Gene therapy for factor IX (FIX) deficiency is effective, but it is hampered by low transgene persistence and dose-dependent liver toxicity. Vectors incorporating FIX Padua, a naturally occurring mutation that increases procoagulant activity, improve outcomes. Nair et al used rational protein design to further modify FIX Padua with 2 mutations that increase resistance to antithrombin inhibition and improve affinity for factor VIII. In mice, this vector produces similar FIX protein levels but markedly increased functional FIX activity, suggesting potential for improved FIX gene therapy.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
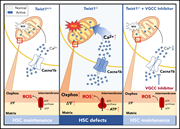
TWIST1 preserves hematopoietic stem cell function via the CACNA1B/Ca2+/mitochondria axis
Wang et al highlight the importance of mitochondria in maintaining hematopoietic stem cells. They demonstrate that TWIST1 contributes to stem cell maintenance by regulating mitochondrial calcium metabolism. TWIST1 deletion increases mitochondrial calcium and production of reactive oxygen species, resulting in reduced stem cell quiescence and self-renewal and also reduced resistance to genotoxic stress.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
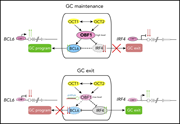
OBF1 and Oct factors control the germinal center transcriptional program
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
IGLV3-21R110 identifies an aggressive biological subtype of chronic lymphocytic leukemia with intermediate epigenetics
Mutation of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable (IGHV) region separates mutated (good-prognosis) from unmutated (poor-prognosis) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Epigenetic profiling can independently define leukemia cell maturation, distinguishing naïve, intermediate, and mature immunogenetic subtypes. Nadeu et al demonstrate that the presence or absence of a single mutation in the splice site between the variable and constant sequences in the λ light chain segregates the phenotype and prognosis of intermediate CLL into groups resembling naïve or mature CLL, respectively.
PHAGOCYTES, GRANULOCYTES, AND MYELOPOIESIS
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
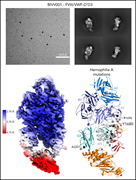
Molecular determinants of the factor VIII/von Willebrand factor complex revealed by BIVV001 cryo-electron microscopy
Two studies elucidate the molecular details of factor VIII interactions with other proteins. In one, the investigators used a bioengineered factor VIII molecule with increased affinity for von Willebrand factor (VWF) to perform cryo-electron microscopy to elucidate the 3-dimensional structure of the factor VIII–VWF interaction. In the others, the authors crystallized factor VIII bound to an inhibitor from a patient with a factor VIII inhibitor to define their interaction, with the hope that better understanding of factor VIII structural interactions may offer clues to the unique immunogenicity of factor VIII.
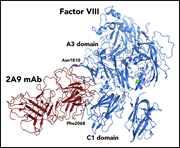
Structure of blood coagulation factor VIII in complex with an anti–C1 domain pathogenic antibody inhibitor
Brief Report
Two studies elucidate the molecular details of factor VIII interactions with other proteins. In one, the investigators used a bioengineered factor VIII molecule with increased affinity for von Willebrand factor (VWF) to perform cryo-electron microscopy to elucidate the 3-dimensional structure of the factor VIII–VWF interaction. In the others, the authors crystallized factor VIII bound to an inhibitor from a patient with a factor VIII inhibitor to define their interaction, with the hope that better understanding of factor VIII structural interactions may offer clues to the unique immunogenicity of factor VIII.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Incidence of skin hyperpigmentation in Black patients receiving treatment with immunomodulatory drugs
Clinical Trials & Observations
In a retrospective single-center review of patients with myeloma treated with the immunomodulatory drug thalidomide, lenalidomide, or pomalidomide, the authors report that marked hyperpigmentation occurred in 40% of Black patients, compared with 3.5% of White patients. Since only 2% of the participants in the original pivotal trial of lenalidomide were Black, this unexpectedly high rate was not previously recognized.
Markers of complement activation in plasma during quiescent phases in patients with catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome
Accumulating evidence suggests that complement activation is a critical contributor to catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome (CAPS). While complement activation and C5b-9 levels have been documented in acute CAPS, Ruffati et al report that patients with a history of CAPS have higher levels of C5a and C5b-9 even in the quiescent phase, suggesting an underlying defect in complement regulation.
Clonal hematopoiesis and therapy-related myeloid neoplasms following neuroblastoma treatment
Clinical Trials & Observations
Decreased activity and stability of pyruvate kinase in sickle cell disease: a novel target for mitapivat therapy
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
van der Waals sphere representation of the factor VIII C1 domain, highlighting surface‐exposed hemophilia A–associated mutations that cause impaired von Willebrand factor binding and overlap with a pathogenic anti‐C1 domain inhibitor epitope. See the article by Gish et al on page 2981.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals



Discordant solutions to discordant problems