Issue Archive
Table of Contents
EDITORIAL
Introduction to a How I Treat series on acquired hemolytic anemia
Diagnosis and treatment of acquired hemolytic anemia can be challenging. In this How I Treat series, edited by Mario Cazzola, clinical experts discuss their approaches to the treatment of patients with 4 different classes of acquired hemolytic anemia.
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
HOW I TREAT SERIES
Acquired Hemolytic Anemia
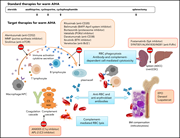
How I treat warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Diagnosis and treatment of acquired hemolytic anemia can be challenging. In this How I Treat series, edited by Mario Cazzola, clinical experts discuss their approaches to the treatment of patients with 4 different classes of acquired hemolytic anemia.
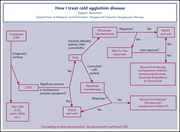
How I treat cold agglutinin disease
Diagnosis and treatment of acquired hemolytic anemia can be challenging. In this How I Treat series, edited by Mario Cazzola, clinical experts discuss their approaches to the treatment of patients with 4 different classes of acquired hemolytic anemia.
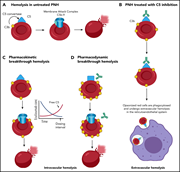
How I treat paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Diagnosis and treatment of acquired hemolytic anemia can be challenging. In this How I Treat series, edited by Mario Cazzola, clinical experts discuss their approaches to the treatment of patients with 4 different classes of acquired hemolytic anemia.
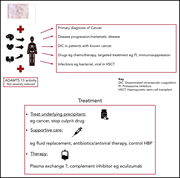
How I treat microangiopathic hemolytic anemia in patients with cancer
Diagnosis and treatment of acquired hemolytic anemia can be challenging. In this How I Treat series, edited by Mario Cazzola, clinical experts discuss their approaches to the treatment of patients with 4 different classes of acquired hemolytic anemia.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
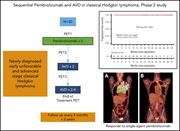
Pembrolizumab followed by AVD in untreated early unfavorable and advanced-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Blockade of programmed death 1 (PD-1) is now established as a standard treatment for relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma, and how this approach can be incorporated into first line therapies is an important question. Allen et al report an early-phase trial of single agent pembrolizumab for an initial 3 cycles followed by 4 to 6 cycles of chemotherapy. They demonstrate encouraging single-agent activity and excellent efficacy and tolerability for the sequential therapy in previously untreated patients with either unfavorable early-stage or advanced-stage disease.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
SRP54 mutations induce congenital neutropenia via dominant-negative effects on XBP1 splicing
Congenital neutropenias (CNs) are characterized by defective neutrophil maturation caused by mutations in any one of more than 20 different genes, including the signal recognition particle 54 gene (SRP54). Schürch et al show that SRP54 mutations found in CN act in a dominant negative manner in zebrafish models, causing neutropenia due to impaired splicing of the transcription factor Xbox-binding protein 1 (XBP1).
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Spatial signatures identify immune escape via PD-1 as a defining feature of T-cell/histiocyte-rich large B-cell lymphoma
T-cell/histiocyte-rich large B-cell lymphoma has a unique tumor microenvironment with an extensive infiltrate of T cells and histiocytes. Using multiparameter immunophenotyping studies with sophisticated spatial image analyses, Griffin and colleagues report that the unique cellular architecture of this lymphoma’s microenvironment appears to be an important contributor to immune escape of the lymphoma cells.
Higher-order connections between stereotyped subsets: implications for improved patient classification in CLL
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Plasmacytoid dendritic cell expansion defines a distinct subset of RUNX1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia
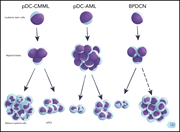
Xiao et al describe a subset of acute myeloid leukemias (AMLs) that displays expansion of mature plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs). This subset is enriched for RUNX1 mutations and has a poor prognosis. The authors also show that AML blasts with RUNX1 mutations have a propensity to make pDCs, suggesting unappreciated leukemia biology and a possible therapeutic target for further exploration.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
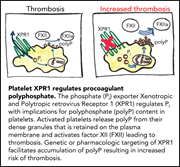
Xenotropic and polytropic retrovirus receptor 1 regulates procoagulant platelet polyphosphate
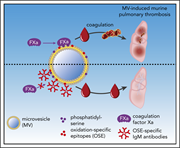
Natural IgM antibodies inhibit microvesicle-driven coagulation and thrombosis
Plasma microvesicles are a heterogeneous collection of membranous cell-derived microparticles that are released in response to various insults and are typically prothrombotic. Obermayer and colleagues report the discovery of naturally occurring immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies that bind to microvesicles and inhibit their contribution to the propagation of coagulation. Their work reveals a specific endogenous means to counter the prothrombotic effect of microvesicles and an anticoagulant role for innate immunity.
TRANSPLANTATION
LETTERS TO BLOOD
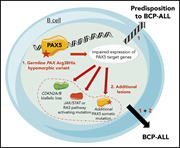
Germline PAX5 mutation predisposes to familial B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Fluorescent microscopy image of platelet-rich thrombi in the lung of a mouse with microvesicle-induced pulmonary thrombosis. Visualized are platelets (CD41, orange), pancreatic cancer cell–derived (HPAF-II) microvesicles (CMFDA, green), and nuclei (DAPI, blue). See the article by Obermayer et al on page 1406.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals




PD-1 blockade for untreated Hodgkin lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations