Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
HOW I TREAT
How I prevent infections in patients receiving CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cells for B-cell malignancies
Hill and Seo use an illustrative clinical case to discuss issues of infection prophylaxis and therapy in patients prior to, during, and following chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for B-cell malignancies.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
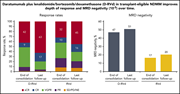
Daratumumab, lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone for transplant-eligible newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: the GRIFFIN trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Voorhees et al report results of a randomized trial of daratumumab added to standard frontline therapy with lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (RVd) in transplant-eligible patients with multiple myeloma. They demonstrated improved stringent complete response rates posttransplant that deepened over time.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
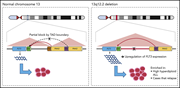
13q12.2 deletions in acute lymphoblastic leukemia lead to upregulation of FLT3 through enhancer hijacking
FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) somatic mutations are common driver mutations in acute leukemia. Yang et al used three-dimensional (3D) modeling to demonstrate that a subset of acute lymphoblastic leukemia harbors a small deletion in chromosome 13q12.2, leading to the overexpression of FLT3 in the absence a coding mutation. Lying 3’ of the FLT3 gene, the deletion alters the 3D interactions between a downstream enhancer and FLT3.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
The EMT modulator SNAI1 contributes to AML pathogenesis via its interaction with LSD1
The authors investigated the role of SNAI1 in leukemogenesis, demonstrating that SNAI1 overexpression impairs differentiation and increases self-renewal and proliferation of myeloid progenitors.They demonstrated that the mechanism involves interaction with the histone demethylase KDM1A/LSD1, suggesting a potential role for LSD1 inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) treatment.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
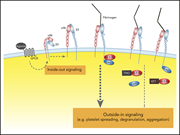
The 14-3-3ζ–c-Src–integrin-β3 complex is vital for platelet activation
Platelet binding to β-integrins is associated with bidirectional signaling. Inside-out signaling upon platelet activation facilitates platelet adhesion and aggregation; outside-in signaling amplifies platelet activation and thrombus extension. The authors demonstrated that modifying adaptor molecule binding to β-integrins can selectively inhibit thrombus extension without threatening primary hemostasis.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
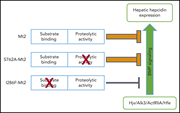
The ectodomain of matriptase-2 plays an important nonproteolytic role in suppressing hepcidin expression in mice
Matriptase-2 (MT2) suppresses hepcidin expression, a key regulator of iron metabolism. Though it is presumed to act by cleaving proteins in the BMP signaling pathway that upregulate hepcidin, the authors demonstrated that although MT2 does cleave key components in the hepcidin-induction pathway, its activity is dependent on substrate binding, and that proteolytic activity is dispensable for hepcidin regulation.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Somatic genetic rescue in hematopoietic cells in GATA2 deficiency
Haploinsufficiency of GATA2 caused by heterozygous loss-of-function mutations is associated with cytopenias and predisposition to myelodysplasia and AML with other variable extrahematopoietic manifestions, including lymphedema, pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, and hearing loss. The authors report on 2 siblings with the disorder whose father was asymptomatic because of an acquired missense mutation in the affected allele that was restricted to hematopoietic cells; surprisingly, he also had no extrahematopoietic complications.
Long-term outcomes for patients with limited-stage follicular lymphoma: update of a population-based study
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
With a median follow-up of 16.6 years, Lo and colleagues report excellent long-term outcomes with primary radiotherapy for limited-stage follicular lymphoma in this month’s CME article.
BLOOD WORK
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis and chronic lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate in a lung section from a patient with GATA2 deficiency. The alveoli are filled with an abnormal accumulation of surfactant. See the article by Catto et al on page 1002.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals



Daratumumab in transplant regimens for myeloma?
Clinical Trials & Observations