Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARY
PLENARY PAPER
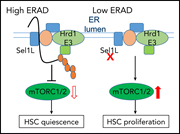
ER-associated degradation preserves hematopoietic stem cell quiescence and self-renewal by restricting mTOR activity
Life-long persistence of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) depends upon maintaining their quiescence. In a Plenary Paper, Liu and colleagues demonstrate that HSC quiescence depends on protein quality control through the unfolded protein response. Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) of misfolded proteins maintains HSC quiescence; loss of ERAD causes increased mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) activity, HSC proliferation, and stem cell depletion.
HOW I TREAT
How I treat nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
Eichenauer and Engert present their approach to the treatment of nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL), a rare variant with an overall excellent prognosis. Using 2 illustrative cases, the authors discuss treatment options and choices for low-grade, high-risk, and advanced-stage NLPHL.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
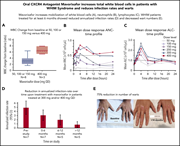
Results of a phase 2 trial of an oral CXCR4 antagonist, mavorixafor, for treatment of WHIM syndrome
Clinical Trials & Observations
Warts, hypogammaglobulinemia, infections, and myelokathexis (WHIM) syndrome is a rare disorder attributable to gain-of-function mutations in the CXCR4 gene. Dale and colleagues report that mavorixafor, an oral CXCR4 receptor antagonist, improves neutrophil and lymphocyte counts, decreases infections, and reduces warts in patients with WHIM syndrome. Although similar responses have been seen with plerixafor, a parenteral CXCR4 inhibitor administered twice daily, mavorixafor is the first oral inhibitor for the treatment of WHIM syndrome and should transform therapy.
Novel drug for WHIM
Clinical Trials & Observations
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
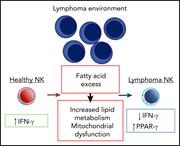
Increased lipid metabolism impairs NK cell function and mediates adaptation to the lymphoma environment
Natural killer (NK) cells are important for protection against malignancy. The authors demonstrate that exposure to increased fatty acids in the tumor microenvironment suppresses NK cell function in the setting of lymphoma.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
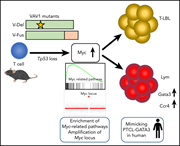
VAV1 mutations contribute to development of T-cell neoplasms in mice
Activating mutations in VAV1 are seen in mature T-cell neoplasms (TCNs), and Fukumoto et al illuminate their oncogenic role in tumorigenesis in transgenic mice. Transgenic expression of mutant VAV1 on a p53-null background promotes accelerated death from TCNs associated with myc pathway activation.
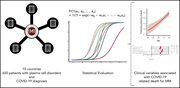
Clinical features associated with COVID-19 outcome in multiple myeloma: first results from the International Myeloma Society data set
Clinical Trials & Observations
Chari et al present a large cooperative retrospective study of 650 patients with multiple myeloma with COVID-19 infection. Mortality in hospitalized patients was 33%. Older age, high-risk disease, active or progressive disease, and comorbidities were risk factors for death.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Impact of gemtuzumab ozogamicin on MRD and relapse risk in patients with NPM1-mutated AML: results from the AMLSG 09-09 trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Kapp-Schwoerer and colleagues report that minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity following therapy of NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is associated with significantly lower relapse rate following chemotherapy. They show that addition of gemtuzumab ozogamicin to intensive chemotherapy results in an increased rate of MRD negativity and a reduction in relapse.
PHAGOCYTES, GRANULOCYTES, AND MYELOPOIESIS
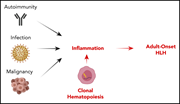
Contribution of clonal hematopoiesis to adult-onset hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
Brief Report
Miller et al examined clonal hematopoiesis (CH) in an annotated cohort of adult patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), reporting that CH is more prevalent in HLH patients than in controls. Furthermore, in a mouse model of adult HLH, Tet2 mutation leads to an exaggerated inflammatory response and more striking HLH findings.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
Use of thrombopoietin receptor agonists for immune thrombocytopenia in pregnancy: results from a multicenter study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Treatment of immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) in pregnancy is usually restricted to steroids and IV immunoglobulin because thrombopoietin receptor agonists (Tpo-RAs) cross the placenta and are not recommended. In a preliminary study of 15 women with severe refractory ITP, the authors report responses to Tpo-RAs in 77% of patients with no serious adverse events and only 1 case of neonatal thrombocytosis.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
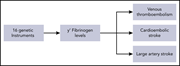
A Mendelian randomization of γ′ and total fibrinogen levels in relation to venous thromboembolism and ischemic stroke
γ′ fibrinogen is an isoform that has anticoagulant properties. The authors performed a Mendelian randomization to elucidate the role of genetically determined levels of γ′ fibrinogen in venous thromboembolism (VTE) and stroke. They demonstrate that higher γ′ fibrinogen levels are protective against VTE, cardioembolic events, and large artery stroke.
TRANSPLANTATION
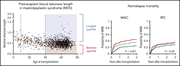
Short telomere length predicts nonrelapse mortality after stem cell transplantation for myelodysplastic syndrome
Clinical Trials & Observations
Myllymäki and colleagues studied the relationship between pretransplant telomere length and survival following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Inherited or acquired shortened telomere length in patients with MDS is associated with increased nonrelapse mortality, especially with patients with intensive myeloablative regimens. This suggests that patients with short telomeres pre-HSCT should be considered for less toxic preparative regimens.
LETTER TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Mature T-cell lymphoma showing high-level expression of Myc. The lymphoma, resembling human GATA3-type peripheral T-cell lymphoma, developed in a Trp53−/− VAV1-Tg mouse. Imaging was done via laser fluorescent confocal microscopy. CD3, red; Myc, green; 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI), blue. See the article by Fukumoto et al on page 3018.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






Blood stem cells SELect quiescence