Issue Archive
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
Pembrolizumab: living up to expectations
Clinical Trials & Observations
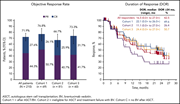
Pembrolizumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: 2-year follow-up of KEYNOTE-087
Clinical Trials & Observations
Chen and colleagues report excellent durability of response at 2 years for patients responding to pembrolizumab for relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma.
PLENARY PAPER
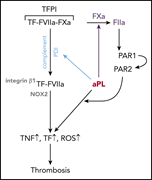
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor primes monocytes for antiphospholipid antibody-induced thrombosis
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome is caused by antiphospholipid antibodies (aPLs) that cause thrombosis and pregnancy loss. In a Plenary Paper, Müller-Calleja et al dissect the complex and multifaceted mechanism by which aPLs induce thrombosis through priming of monocytes and disruption of the balance of tissue factor activation and inhibition.
SPECIAL REPORT
Consensus criteria for diagnosis, staging, and treatment response assessment of T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia
In a Special Report, the T-PLL International Study group presents consensus criteria for the diagnosis, staging, and treatment response assessment of patients with T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Pembrolizumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: 2-year follow-up of KEYNOTE-087
Clinical Trials & Observations
Chen and colleagues report excellent durability of response at 2 years for patients responding to pembrolizumab for relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
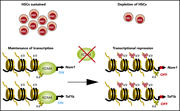
The KDM4/JMJD2 histone demethylases are required for hematopoietic stem cell maintenance
Brief Report
KDM4 and JMJD2 are histone demethylases that are considered promising targets for treatment of MLL translocation–bearing acute myeloid leukemia. Agger and colleagues demonstrate an important role of KDM4 activity in long-term normal hematopoiesis that should be considered when contemplating the clinical use of long-term inhibition of KDM4 demethylase activity.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
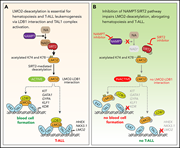
LMO2 activation by deacetylation is indispensable for hematopoiesis and T-ALL leukemogenesis
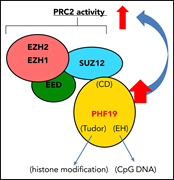
PHF19 promotes multiple myeloma tumorigenicity through PRC2 activation and broad H3K27me3 domain formation
Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) dysregulation is associated with proliferation of hematological malignancies. Ren et al elucidate the mechanisms of PRC2 in multiple myeloma (MM), demonstrating that malignant progression of MM is associated with overexpression of PHF19, a PRC2-associated factor that enhances its gene-regulatory function.
LETTER TO BLOOD
A method for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of monogenic autosomal recessive disorders
Using sickle cell disease as a model, Cutts et al describe a highly sensitive method for prenatal diagnosis of known single-gene defects using next-generation sequencing of maternal plasma cell-free DNA.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Bone marrow infiltration by T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia (T-PLL) cells depicted by immunohistologic double staining with CD5 (red) and TCL1 (brown). Notice the cytoplasmatic expression of the TCL1 oncogene that is characteristic for T-PLL. See the article by Staber et al on page 1132.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon AdvertisingAdvertising
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals



Consensus criteria for diagnosis, staging, and treatment response assessment of T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia
In a Special Report, the T-PLL International Study group presents consensus criteria for the diagnosis, staging, and treatment response assessment of patients with T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia.