Issue Archive
BLOOD COMMENTARY
PLENARY PAPER
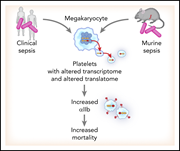
Sepsis alters the transcriptional and translational landscape of human and murine platelets
In a Plenary Paper, Middleton and colleagues describe important transcriptional and translational changes in murine and human platelets during sepsis, elucidating the emerging role of platelets in the complications of systemic inflammatory illness.
SPECIAL REPORT
Selection of unrelated donors and cord blood units for hematopoietic cell transplantation: guidelines from the NMDP/CIBMTR
CME
This Special Report, this month’s CME article, details evidence-based guidelines for the selection of optimal unrelated donors and cord blood units for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
GIMEMA AML1310 trial of risk-adapted, MRD-directed therapy for young adults with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia
Clinical Trials & Observations
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
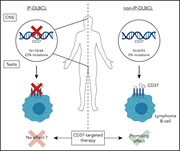
High frequency of inactivating tetraspanin CD37 mutations in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma at immune-privileged sites
Brief Report
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Combining gene mutation with gene expression analysis improves outcome prediction in acute promyelocytic leukemia
Luceno-Araujo et al use assays of mutations associated with myeloid malignancy to propose an integrative prognostic score for acute promyelocytic leukemia (ISAPL) in patients treated with all-trans retinoic acid and anthracycline-based therapy. They demonstrate that the ISAPL is superior for predicting outcomes and identifying patients who may benefit from alternative therapies to maximize their chance of a cure.
Analysis of 153 115 patients with hematological malignancies refines the spectrum of familial risk
Sud and colleagues interrogated the familial risk of hematological malignancy in association with over 150 000 patients. The majority of hematological malignancies showed increased familial relative risk, most prominently in association with B-cell malignancies.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
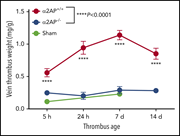
Venous stasis-induced fibrinolysis prevents thrombosis in mice: role of α2-antiplasmin
Singh et al investigated the relationship among stasis, fibrinolysis, and venous thromboembolism (VTE), demonstrating a complex interaction by which venous stasis activates both thrombosis and fibrinolysis. Blocking the effects of α2-antiplasmin abolishes VTE, suggesting a potential novel approach to preventing thrombosis.
VASCULAR BIOLOGY
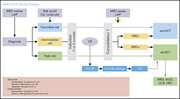
Proximity proteomics of endothelial Weibel-Palade bodies identifies novel regulator of von Willebrand factor secretion
Brief Report
Weibel-Palade (WPB) bodies are endothelial cell organelles that store von Willebrand factor (VWF) and other proteins important for vascular hemostasis. Holthenrich and colleagues used an elegant proximity proteomics approach to compile a complete catalog of WPB-associated proteins and identify Munc13-2 as a novel factor mediating VWF secretion via WPB exocytosis.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Confocal image of human umbilical vein endothelial cells expressing a Rab27a-APEX2 construct that localizes to Weibel-Palade bodies (WPBs). APEX2 activation leads to the biotinylation of proximal proteins that constitute the WPB-associated proteome. See the article by Holthenrich et al on page 979.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon AdvertisingAdvertising
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals




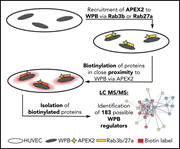

Proximity proteomics of endothelial Weibel-Palade bodies identifies novel regulator of von Willebrand factor secretion
Brief Report
Weibel-Palade (WPB) bodies are endothelial cell organelles that store von Willebrand factor (VWF) and other proteins important for vascular hemostasis. Holthenrich and colleagues used an elegant proximity proteomics approach to compile a complete catalog of WPB-associated proteins and identify Munc13-2 as a novel factor mediating VWF secretion via WPB exocytosis.