Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PERSPECTIVE
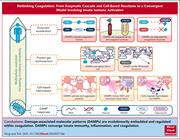
Rethinking coagulation: from enzymatic cascade and cell-based reactions to a convergent model involving innate immune activation
In this Perspective, Yong and Toh present a novel model of coagulation that integrates recent insights into the close connection between coagulation and innate immunity. The authors integrate traditional models of the coagulation cascade and the cellular schema supporting and activating coagulation with newer concepts of an intersection between clotting and the inflammatory and immune response to injury.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Natural history study of patients with familial platelet disorder with associated myeloid malignancy
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
Familial platelet disorder with associated myeloid malignancy (FPDMM), a rare syndrome of thrombocytopenia, abnormal platelet function, and predisposition to myeloid malignancy, is caused by mutations in the RUNX1 gene. In this month’s CME article, Cunningham et al report on the first 111 patients derived from 45 unrelated families enrolled in the National Institutes of Health–initiated FPDMM natural history study between 2019 and 2021. The authors confirm the major features of the disease and add allergic and gastrointestinal symptoms to the catalog. This longitudinal study offers a valuable resource for further study of this rare disease.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
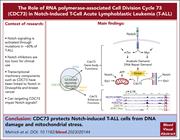
Cdc73 protects Notch-induced T-cell leukemia cells from DNA damage and mitochondrial stress
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) has a high prevalence of activated Notch signaling, but Notch-1 inhibitors have proven excessively toxic in clinical studies. Melnick et al investigate cell division cycle 73 (Cdc73), a Notch cofactor and component of RNA polymerase-associated transcription, as a possible indirect target to inhibit Notch-deregulated T-ALL. The authors demonstrate that Cdc73 interacts with Notch and enhances transcription of genes facilitating DNA repair and oxidative phosphorylation, suggesting it likely is a candidate target for treating Notch-deregulated T-ALL.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
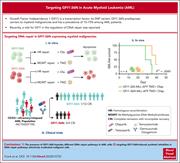
Germ line variant GFI1-36N affects DNA repair and sensitizes AML cells to DNA damage and repair therapy
Growth factor independence 1 (GFI1) is a key transcriptional regulator of hematopoiesis. A germ line GFI1 variant, GFI1-36N, is present in 5-7% of Caucasians but is enriched to 10-15% in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Frank and colleagues delineate that GFI1-36N cells have increased mutational burden and chromosomal aberrations and also evince impaired DNA repair. The authors identify O6-methylguaninine-DNA-methyltransferase (MGMT) as a downstream target of GFI1-36N. Combination of the MGMT inhibitor temozolomide and a PARP inhibitor kills GIF1-36N–associated AML cells, suggesting a potential novel therapy for GFI1-36N–associated AML.
Lineage-specific detection of residual disease predicts relapse in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia stopping therapy
Brief Report
The success of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) as treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) has fueled an ambition to establish criteria for treatment-free remission (TFR). Pagani and colleagues used sensitive measurable residual disease (MRD) detection methods to predict relapse after TKI discontinuation. Median BCR::ABL1 DNA detected in granulocytes was predictive of relapse (100%). Patients with CML with undetectable granulocyte MRD were further stratified by detection of MRD in T cells with T-cell positivity predicting 67% relapse; among patients with negative MRD in both granulocytes and T cells, relapse was only 25%. These results lay a groundwork for safer choice of patients for TFR.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
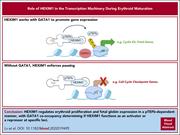
HEXIM1 is an essential transcription regulator during human erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesis relies on transcriptional regulation through modulation of the level and activity of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII). Lv et al elucidate a key role of HEXIM1 in these transcriptional pathways. HEXIM1 interacts with positive transcription factor β, which regulates RNAPII progression and pausing during transcription. HEXIM1 has been recognized as a negative regulator of RNAPII. Here, the authors demonstrate that HEXIM1 has a dual role in erythropoiesis, in that it also positively regulates RNAPII localization and differential transcriptional activity at the γ-globin and β-globin loci, suggesting modulation of HEXIM1 could be a therapeutic target to increase fetal hemoglobin.
LETTER TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
A confocal microscopy image of fluorescent staining with the mitochondrial tracker Deep Red shows mitochondrial localization in OCI-Ly10 cells. Blue indicates cell nuclear staining with DAPI.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





Seeding the future: the natural history of RUNX1 deficiency
Clinical Trials & Observations