Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
HOW I TREAT
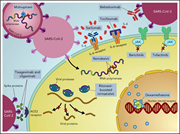
How I treat and prevent COVID-19 in patients with hematologic malignancies and recipients of cellular therapies
Clinical Trials & Observations
Using 3 illustrative cases, Chaer et al discuss the options for the prevention and therapy of COVID-19 infection in patients with hematologic malignancies and recipients of cellular therapies. The authors provide useful practical recommendations and algorithms for current treatment.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
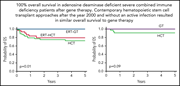
Outcomes following treatment for ADA-deficient severe combined immunodeficiency: a report from the PIDTC
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
In this month’s CME article, Cuvelier and colleagues report on outcomes over a 35-year period for patients with adenosine deaminase (ADA)-deficient severe combined immune deficiency who were enrolled in the Primary Immune Deficiency Treatment Consortium (PIDTC). Event-free survival prior to 2020 favored gene therapy (GT) over hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT); however, for patients treated after the year 2000 without infection, there was no difference between HCT and GT. This finding suggests that patients undergoing definitive therapy early in life before infectious complications may be considered for HCT, especially when GT is not available.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
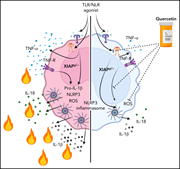
Quercetin ameliorates XIAP deficiency–associated hyperinflammation
XIAP deficiency causes hyperinflammatory disease (X-linked lymphoproliferative disease) and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis related to dysregulated TNF-receptor signaling and increased NFRP3 inflammasome activity. Chiang et al demonstrated that downregulation of inflammasome activity with quercetin reduces cytokine levels in XIAP mice, supporting a trial of the agent for the treatment of XIAP deficiency.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
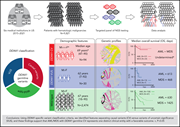
The genetic landscape of germline DDX41 variants predisposing to myeloid neoplasms
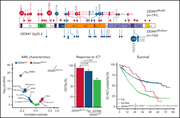
DDX41 germline mutations define the most common genetic syndrome predisposing to myeloid neoplasms (MN). Two papers highlight the genetic landscape and prognostic implications of germline DDX41-related MN. Li et al analyzed DDX41 variants and demonstrated that germline causal variants identify a population with a distinct AML subtype. The group, characterized by male predominance, late onset, and favorable prognosis, develop concurrent somatic DDX41 variants but rarely show the usual MN-associated somatic mutations. This contrasts to patients with variants of uncertain significance who develop MN with canonical MN-associated mutations, suggesting they define distinct entities. In the second article, Duployez et al confirmed the prognostic significance in 191 patients with DDX41 germline mutation, reporting higher remission rates and longer overall survival than patients without DDX41 germline mutation. Transplantation in first remission prolonged relapse-free survival but not overall survival.
Prognostic impact of DDX41 germline mutations in intensively treated acute myeloid leukemia patients: an ALFA-FILO study
Clinical Trials & Observations
DDX41 germline mutations define the most common genetic syndrome predisposing to myeloid neoplasms (MN). Two papers highlight the genetic landscape and prognostic implications of germline DDX41-related MN. Li et al analyzed DDX41 variants and demonstrated that germline causal variants identify a population with a distinct AML subtype. The group, characterized by male predominance, late onset, and favorable prognosis, develop concurrent somatic DDX41 variants but rarely show the usual MN-associated somatic mutations. This contrasts to patients with variants of uncertain significance who develop MN with canonical MN-associated mutations, suggesting they define distinct entities. In the second article, Duployez et al confirmed the prognostic significance in 191 patients with DDX41 germline mutation, reporting higher remission rates and longer overall survival than patients without DDX41 germline mutation. Transplantation in first remission prolonged relapse-free survival but not overall survival.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
The oral ferroportin inhibitor vamifeport improves hemodynamics in a mouse model of sickle cell disease
Nyffenegger and colleagues report that blocking ferriportin with vamifeport reduces hemolysis in a murine model of sickle cell disease (SCD). Vamifeport reduces intracellular iron and induces iron-limited hematopoiesis. Since a small decrease in the intracellular sickle hemoglobin concentration has a marked impact on the delay time for sickling, reducing sickle hemoglobin decreases sickling and hemolysis. In addition, vamifeport also reduces adhesion molecule expression, decreasing inflammation. This supports further development of vamifeport as a novel therapy for SCD.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Prevalence of neuropsychiatric symptoms and stroke in patients with hereditary thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Clinical Trials & Observations
In this article, Borogovac et al emphasized the burden of stroke and neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with hereditary thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (hTTP) based on an analysis of the International hTTP Registry. Given the rarity of hTTP, patient numbers were small; nevertheless, the prevalence of stroke reached 100% in patients over the age of 50. Nearly all patients also had evidence of neuropsychiatric symptoms. These data confirm the need to diagnose hTTP as early as possible and support the use of prophylaxis to prevent future events.
Thrombopoietin receptor agonists in adult Evans syndrome: an international multicenter experience
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Scanning electron microscopy image of red blood cells (RBCs) from a mouse with sickle cell disease (SCD) treated with the oral ferroportin inhibitor vamifeport. The elongated cell in the center shows a sickle RBC which appears rounder with a biconcave shape, as compared to more fibrous and rigid RBCs in control mice with SCD. See the article by Nyffenegger et al on page 769.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals



Four decades of progress
Clinical Trials & Observations