Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
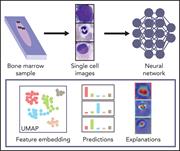
Highly accurate differentiation of bone marrow cell morphologies using deep neural networks on a large image data set
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms are changing many facets of our lives and have great potential for disease diagnosis. In this Plenary Paper, Matek et al describe training a convolutional neural network model using 171 374 bone marrow cytology images from 945 patients with various hematological diseases before validating its accuracy in classifying single cells in an independent set of 627 images. The system can automatically classify 22 classes of bone marrow leukocytes, and with further improvements, it may bring AI-aided diagnosis of bone marrow biopsy specimens closer to fruition.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Phase 2 study of danicopan in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria with an inadequate response to eculizumab
Clinical Trials & Observations
Some patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) remain persistently anemic despite treatment with eculizumab and may have significant extravascular hemolysis. Kulasekararaj and colleagues report a phase 2 trial of danicopan, a first-inclass oral complement factor D inhibitor, added to ongoing eculizumab therapy in PNH patients who still needed transfusions. This small study of 12 patients reveals that the combination has acceptable safety while substantially increasing the hemoglobin concentration, reducing extravascular hemolysis, and improving the fatigue score.
Control of hemolysis in patients with PNH
Clinical Trials & Observations
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
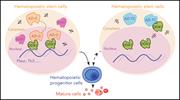
A comprehensive RNA editome reveals that edited Azin1 partners with DDX1 to enable hematopoietic stem cell differentiation
Wang et al provide insight into how epigenetic regulation of the transcriptome can rewire cell fate decisions by mapping the RNA-editing landscape during hematopoiesis. They report that adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing of antizyme inhibitor 1 (Azin1) is a novel regulator of hematopoietic cell fate, capable of influencing self-renewal and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells. This work sets the scene for developing RNA editing–targeted therapeutics for stem cell expansion and modulating AZIN1-induced cancer stem cell generation.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
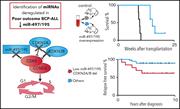
MicroRNA-497/195 is tumor suppressive and cooperates with CDKN2A/B in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Current improvements in treatment for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) are based on detailed molecular classification that influences prognosis and can guide therapy. Boldrin et al identified a novel biomarker of poor outcome in ALL, and, using cell and in vivo models, they delineated the biological link between microRNA-497/195 repression and more aggressive disease. Their research also points to exploring pharmacological cell cycle inhibition as a potential method for treating these high-risk leukemias.
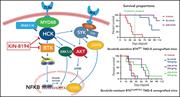
The HCK/BTK inhibitor KIN-8194 is active in MYD88-driven lymphomas and overcomes mutated BTKCys481 ibrutinib resistance
Activating mutations in MYD88 are highly prevalent in Waldenström macroglobulinemia, primary central nervous system lymphoma, and several other lymphomas. Inhibitors of Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) have clinical activity, but over time resistance emerges. Yang and colleagues report the preclinical efficacy of a novel inhibitor that targets both BTK and hematopoietic cell kinase (HCK) and has activity against ibrutinib-resistant tumors.
IgM-MM is predominantly a pre–germinal center disorder and has a distinct genomic and transcriptomic signature from WM
CME
Brief Report
In this month’s CME article, Bazarbachi et al describe the genomic characterization of immunoglobulin M (IgM) multiple myeloma (MM) and contrast this rare entity with the far more common non-IgM MM and Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Their results help explain why IgM-MM is a distinct clinical and biological entity and highlight specific genetic abnormalities and transcriptomic features. These findings provide a rational basis for the future exploration of additional targeted therapies beyond those typically prescribed for MM in general.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
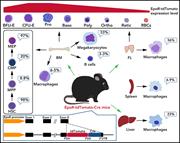
EpoR-tdTomato-Cre mice enable identification of EpoR expression in subsets of tissue macrophages and hematopoietic cells
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Effect of ibrutinib treatment on hemolytic anemia and acrocyanosis in cold agglutinin disease/cold agglutinin syndrome
Clinical Trials & Observations
Cold antibody-mediated autoimmune hemolytic anemia (cAIHA) is a rare disease, usually related to an underlying indolent clonal B-cell lymphoproliferative disorder. Jalink and colleagues describe an international retrospective analysis of Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibition in patients with cAIHA. The data indicate a rapid and notable improvement in both the hemolytic anemia as well as acrocyanosis, suggesting that this may be an effective approach, regardless of underlying pathology or MYD88 mutational status.
BLOOD WORK
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Edited AZI protein (green) translocates from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, enabling its interaction with DDX1 (red) in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. This nuclear binding enables DDX1 to regulate the expression of hematopoietic regulators to sustain normal hematopoietic differentiation. See the article by Wang et al on page 1939.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals




Can the computer see what the human sees?