Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
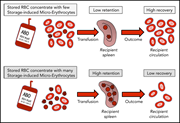
Rapid clearance of storage-induced microerythrocytes alters transfusion recovery
Refrigerated storage is known to affect the morphology of red cells. In a Plenary Paper, Roussel et al examine the relationship between storage-induced microerythrocytes (SMEs) and transfusion recovery. Using a mouse model, they demonstrate that SMEs after long-term storage are rapidly cleared by the splenic macrophages. Abundance of SMEs is inversely correlated with red cell recovery after transfusion in human volunteers. Quantifying SMEs may allow assessment of the quality of red cell concentrates for transfusion.
PERSPECTIVE
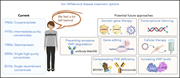
von Willebrand disease: what does the future hold?
While great strides have been achieved in treating hemophilia, the therapy for von Willebrand disease (VWD) has been virtually unchanged over the past 30 years. In a Perspective article, Denis and colleagues discuss the impact of VWD on health and quality of life, as well as potential innovative therapies for improving VWD care.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
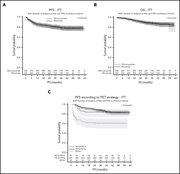
Obinutuzumab vs rituximab for advanced DLBCL: a PET-guided and randomized phase 3 study by LYSA
Clinical Trials & Observations
Le Gouill and colleagues present results of the phase 3 GAINED trial of obinutuzumab vs rituximab in untreated, high-risk, transplant-eligible patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using positron emission tomography (PET)–guided consolidation therapy. Obinutuzumab is not superior to rituximab. PET-guided stratification of further therapy identifies patients who do well with completion of 6 cycles of therapy vs those who benefit from autologous transplantation and others who would benefit from novel intensification approaches.
DLBCL outcomes: much ventured, much GAINED
Clinical Trials & Observations
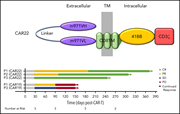
CD22-directed CAR T-cell therapy induces complete remissions in CD19-directed CAR–refractory large B-cell lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
GENE THERAPY
A combination of cyclophosphamide and interleukin-2 allows CD4+ T cells converted to Tregs to control scurfy syndrome
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
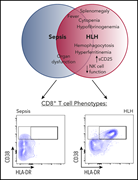
T-cell activation profiles distinguish hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and early sepsis
Chaturvedi et al investigated T-cell profiles in patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) and sepsis, 2 contrasting cytokine storm syndromes that are often difficult to distinguish. They identified a population of CD38high/HLA-DR+ activated T cells that are abundant in severe HLH and absent in sepsis. Identification of over 7% CD38high/HLA-DR+ activated T cells has excellent predictive value in distinguishing HLH from sepsis and provides an important diagnostic tool.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Integrative genomic analysis of pediatric T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma reveals candidates of clinical significance
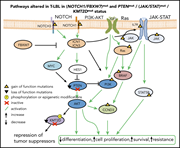
T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma (T-LBL) is a malignancy seen primarily in children and adolescents and is morphologically similar to T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). As relapsed T-LBL has a dismal prognosis, Khanam and colleagues sought to define the genomic landscape of T-LBL to identify predictors of relapse. As in T-ALL, NOTCH1 is a driver for T-LBL, and mutated KMT2D is an important negative prognostic marker, providing potential targets for improved therapy.
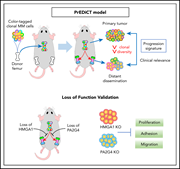
Progression signature underlies clonal evolution and dissemination of multiple myeloma
The progression of multiple myeloma reflects a complex interaction between tumor cells and the bone marrow (BM) microenvironment. Shen and colleagues developed an elegant model of multiple myeloma progression using mouse xenografts and DNA barcoding to track myeloma interaction with the BM microenvironment. Only a subset of myeloma clones can circulate and colonize outside the BM, and RNA sequencing identifies master regulators of this process, identifying potential therapeutic targets.
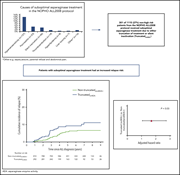
Relapse risk following truncation of pegylated asparaginase in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Clinical Trials & Observations
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
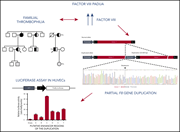
Partial F8 gene duplication (factor VIII Padua) associated with high factor VIII levels and familial thrombophilia
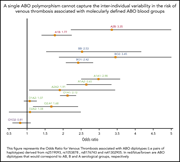
Association between ABO haplotypes and the risk of venous thrombosis: impact on disease risk estimation
TRANSPLANTATION
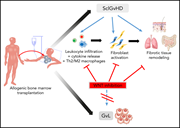
Targeting of canonical WNT signaling ameliorates experimental sclerodermatous chronic graft-versus-host disease
Zhang et al report that canonical WNT signaling is central to the pathogenesis of sclerodermatous chronic graft-versus-host-disease (sclGVHD). Activation of WNT signaling was documented in gene expression signatures of human sclGVHD lesions, and the WNT inhibitors prevented the development of sclGVHD in mouse models. As the WNT inhibitor pyrvinium is already in clinical use and other WNT inhibitors are in clinical trials for other indications, these studies have important clinical implications.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Trichrome-stained skin tissue of mice with sclerodermatous chronic graft-versus-host disease. Treatment with the WNT inhibitor G007-LK ameliorates fibrotic tissue remodeling with reduced leukocyte infiltration and reduced collagen accumulation compared to vehicle treatment. See the article by Zhang et al on page 2403.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals




In vivo clearance of stored red blood cells