Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
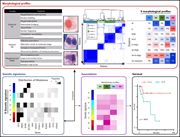
Machine learning demonstrates that somatic mutations imprint invariant morphologic features in myelodysplastic syndromes
Although genetic analysis is beginning to be incorporated into the assessment of myelodysplastic syndromes, the backbone of diagnosis remains assessment of bone marrow morphology. In this Plenary Paper, the authors describe the use of a machine-learning technique to integrate morphology with genomic events to develop distinct profiles with unique clinical profiles and prognosis.
PERSPECTIVE
The dangers of déjà vu: memory B cells as the cells of origin of ABC-DLBCLs
In a Perspective, Venturutti and Melnick propose a novel origin for activated B-cell–type diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (ABC-DLBCLs). They present evidence that ABC-DLBCLs arise from aberrant memory B cells that carry founder mutations that block plasmacytic maturation and, under the influence of recurrent antigen exposure, undergo cyclical reactivation that facilitates both extranodal localization and progressive transformation.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Mechanistic insights and potential therapeutic approaches for NUP98-rearranged hematologic malignancies
Nucleoporin 98 (NUP98) rearrangements are seen in many hematologic malignancies, especially in poor-risk pediatric leukemia. In this definitive review, the authors discuss the role of NUP98 fusion proteins in transcriptional regulation, their cooccurrence with additional mutations, and prospects for exploiting experimental systems to identify therapeutic entry points for improved treatment of these poor-prognosis malignancies.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
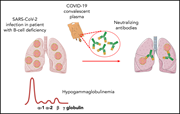
Convalescent plasma therapy for B-cell–depleted patients with protracted COVID-19
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
The authors report on the outcome of convalescent plasma infusion in 17 patients with persistent COVID-19 in the setting of rituximab-induced severe B-cell depletion. All but 1 patient had clinical improvement accompanied by clearance of the virus.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
Adult blood stem cell localization reflects the abundance of reported bone marrow niche cell types and their combinations
In a technical tour de force, the authors delineate the localization of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) within the bone marrow microenvironment through extensive examination of bone sections from HSC reporter lines. They elucidate the exact localization of HSCs and their association with heterogeneous niches within the marrow microenvironment.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
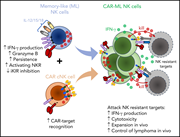
CAR-modified memory-like NK cells exhibit potent responses to NK-resistant lymphomas
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
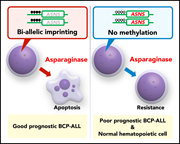
Association of aberrant ASNS imprinting with asparaginase sensitivity and chromosomal abnormality in childhood BCP-ALL
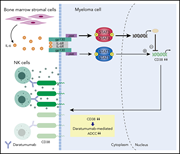
The JAK-STAT pathway regulates CD38 on myeloma cells in the bone marrow microenvironment: therapeutic implications
Monoclonal antibodies targeting CD38 are effective therapy for multiple myeloma. The authors demonstrate that the expression of CD38 is modulated by the bone marrow microenvironment, with interleukin-6 downregulating CD38 expression through JAK-STAT3 signaling and decreasing the cytotoxic effect of daratumumab. JAK-STAT inhibition with ruxolitinib restores daratumumab sensitivity.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
Phosphoproteomic quantitation and causal analysis reveal pathways in GPVI/ITAM-mediated platelet activation programs
Babur et al performed extensive phosphoproteomic analysis of the signaling events in platelet activation mediated by GPVI, cataloguing the extensive signaling relations in this highly regulated network relevant to thrombosis and vascular inflammation.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Immunofluorescence image of bone and bone marrow cellular architecture showing bone matrix (collagen-1 and osteopontin, white), vasculature (laminin, cyan), megakaryocytes (GP1bβ, magenta), nonmyelinated Schwann cells (GFAP, yellow), and hematopoietic stem cells (cKit, green) in a longitudinal section of murine sternum (objective magnification ×20). See the article by Kokkaliaris et al on page 2296.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






Human and artificial intelligence to illuminate MDS