Issue Archive
Table of Contents
EDITORIAL
Introduction to a How I Treat series on hematologic complications in pregnancy
Clinical Trials & Observations
The hematologic complications of pregnancy may impact both the mother and the fetus and are invariably challenging. In this How I Treat series, edited by Editor-in-Chief Nancy Berliner and Associate Editor Catherine Bollard, clinical experts discuss their approach to 4 scenarios where the standard approach to diagnosis and care has to be adapted to optimize outcomes for both the pregnant mother and her fetus.
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
SPECIAL REPORT
Management of thrombotic microangiopathy in pregnancy and postpartum: report from an international working group
HOW I TREAT SERIES
Hematologic Complications in Pregnancy
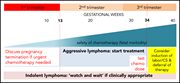
How I treat lymphoma in pregnancy
The hematologic complications of pregnancy may impact both the mother and the fetus and are invariably challenging. In this How I Treat series, edited by Editor-in-Chief Nancy Berliner and Associate Editor Catherine Bollard, clinical experts discuss their approach to 4 scenarios where the standard approach to diagnosis and care has to be adapted to optimize outcomes for both the pregnant mother and her fetus.
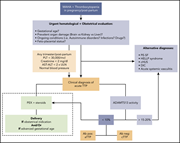
How I treat thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in pregnancy
The hematologic complications of pregnancy may impact both the mother and the fetus and are invariably challenging. In this How I Treat series, edited by Editor-in-Chief Nancy Berliner and Associate Editor Catherine Bollard, clinical experts discuss their approach to 4 scenarios where the standard approach to diagnosis and care has to be adapted to optimize outcomes for both the pregnant mother and her fetus.
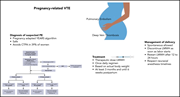
How I treat venous thromboembolism in pregnancy
The hematologic complications of pregnancy may impact both the mother and the fetus and are invariably challenging. In this How I Treat series, edited by Editor-in-Chief Nancy Berliner and Associate Editor Catherine Bollard, clinical experts discuss their approach to 4 scenarios where the standard approach to diagnosis and care has to be adapted to optimize outcomes for both the pregnant mother and her fetus.
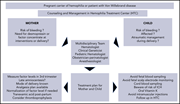
How I manage pregnancy in carriers of hemophilia and patients with von Willebrand disease
The hematologic complications of pregnancy may impact both the mother and the fetus and are invariably challenging. In this How I Treat series, edited by Editor-in-Chief Nancy Berliner and Associate Editor Catherine Bollard, clinical experts discuss their approach to 4 scenarios where the standard approach to diagnosis and care has to be adapted to optimize outcomes for both the pregnant mother and her fetus.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
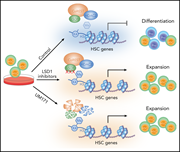
Lysine-specific demethylase 1A restricts ex vivo propagation of human HSCs and is a target of UM171
The complexity of regulation of hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) proliferation and differentiation has proved to be a barrier to HSC expansion for clinical application. Subramaniam et al reveal the mechanism by which the clinically tested pyrimidoindole derivative UM171 affects HSC expansion, propagation, fate, and engraftment by inducing rapid proteasome-mediated degradation of lysine-specific demethylase 1A (LSD1) and the the LSD1-containing chromatin remodeling complex.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
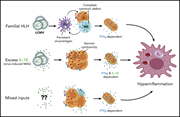
Interleukin-18 and cytotoxic impairment are independent and synergistic causes of murine virus-induced hyperinflammation
Using a viral infection model, Tsoukas et al investigated how elevated interleukin-18 (IL-18) triggers hyperinflammation. They demonstrate that IL-18 can induce autoinflammatory amplification of CD8 T-cell responses and interferon-γ overproduction and that hyperinflammation can be exacerbated by even minor defects in impaired cytotoxic responses to a virus.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Developing new ceramide analogs and identifying novel sphingolipid-controlled genes against a virus-associated lymphoma
Primary effusion lymphoma is an aggressive, poor-prognosis malignancy driven by infection with Kaposi sarcoma–associated herpesvirus (KSHV). Chen and colleagues identified ceramide analog compounds that effectively inhibit KSHV-associated lymphoma growth and progression in vitro and in vivo, providing a novel path to potential future treatments.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
PHAGOCYTES, GRANULOCYTES, AND MYELOPOIESIS
The integrin-linked kinase is required for chemokine-triggered high-affinity conformation of the neutrophil β2-integrin LFA-1
Brief Report
Margraf et al selectively deleted integrin-linked kinase in myeloid cells of mice to show that this integrin-binding protein suppresses chemokine-induced neutrophil extravasation and ischemia-induced reperfusion injury.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
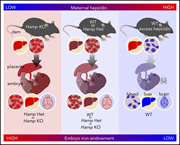
Maternal hepcidin determines embryo iron homeostasis in mice
Sangkhae and colleagues used murine model systems and hepcidin analogs to investigate the central role of maternal hepcidin in determining fetal iron status, the deleterious consequences of its elevation during pregnancy, and its potential relevance in the setting of inflammation. They demonstrate that suppression of maternal hepcidin during pregnancy is essential for maternal and embryo iron homeostasis and health.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
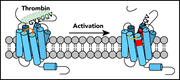
PAR4 activation involves extracellular loop 3 and transmembrane residue Thr153
Protease-activated receptor 4 (PAR4) is one of four thrombin receptors mediating sustained thrombin signaling in platelets and enabling formation of a stable thrombus. Han et al demonstrate for the first time the structural underpinnings for PAR4 activation in platelets and the role of PAR4 activation in venous thromboembolism.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Treatment of HIV-associated primary CNS lymphoma with antiretroviral therapy, rituximab, and high-dose methotrexate
Clinical Trials & Observations
Increased tumor burden in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia after 36 months of imatinib discontinuation
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
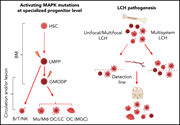
Mutant BRAFV600E protein detection by immunohistochemistry in the lesion of a unifocal bone patient with Langerhans cell histiocytosis. The presence of the mutation in multiple myeloid cell types supports the idea that it originated in an oligopotent hematopoietic progenitor. See the article by Xiao et al on page 2188.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals



“Breaking down” the mechanisms of expansion