Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
An intact gut microbiome protects genetically predisposed mice against leukemia
Despite strong evidence of genetic predisposition to childhood precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (pB-ALL), fewer than 1% of genetically predisposed carriers develop disease, and infectious exposures are thought to provide a “second hit” for leukemia development. In a Plenary Paper, Vicente-Dueñas and colleagues, using mouse models of pB-ALL, make the remarkable observation that mutation carriers have an distinct gut microbiome and that its disruption through antibiotics or changing environment is sufficient to promote ALL without infection.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma: a rare but challenging entity
The authors provide an up-to-date review of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma, including new insights into its genetic landscape and therapeutic approaches to this rare poor-prognosis malignancy.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Zanubrutinib for the treatment of patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia: 3 years of follow-up
Clinical Trials & Observations
Two papers in this issue report on the efficacy of zanubrutinib, a novel selective BTK inhibitor, in Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM). The first reports the 3-year follow-up of patients with WM treated with zanubrutinib, demonstrating deep and durable responses, albeit very few complete responses; progression-free survival was over 80%. The second decribes a phase 3 trial comparing ibrutinib to zanubrutinib in WM and reports excellent responses to both drugs; there was no significant difference in response rates, but zanubrutinib was associated with less toxicity, especially cardiac toxicity.
A randomized phase 3 trial of zanubrutinib vs ibrutinib in symptomatic Waldenström macroglobulinemia: the ASPEN study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Two papers in this issue report on the efficacy of zanubrutinib, a novel selective BTK inhibitor, in Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM). The first reports the 3-year follow-up of patients with WM treated with zanubrutinib, demonstrating deep and durable responses, albeit very few complete responses; progression-free survival was over 80%. The second decribes a phase 3 trial comparing ibrutinib to zanubrutinib in WM and reports excellent responses to both drugs; there was no significant difference in response rates, but zanubrutinib was associated with less toxicity, especially cardiac toxicity.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
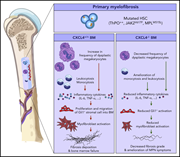
Increased CXCL4 expression in hematopoietic cells links inflammation and progression of bone marrow fibrosis in MPN
In primary myelofibrosis (PMF), bone marrow fibrosis is driven by normal stromal cells in the context of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) that carry myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN)–related mutations. The authors investigated the cross talk between mutant stem cells and normal stromal cells that drives fibrosis in several mouse models of PMF. They demonstrate that CXCL4 is markedly upregulated in MPN stem cells and increased expression in both stem cells and stromal cells is associated with increasing fibrosis; furthermore, they show that knockout of CXCL4 ameliorates fibrosis.
PHAGOCYTES, GRANULOCYTES, AND MYELOPOIESIS
Macrophage hypophagia as a mechanism of innate immune exhaustion in mAb-induced cell clearance
Clearance of monoclonal antibody (mAb)–opsonized cells by macrophages, or macrophage antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP), is the cytotoxic mechanism mediating tumor lysis in response to rituximab and other therapeutic antibodies. The authors demonstrate that rapid uptake of opsonized cells is followed by a period of markedly reduced phagocytosis (hypophagia) that may limit therapeutic effect.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
Direct activation of the alternative complement pathway by SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins is blocked by factor D inhibition
Yu et al demonstrate that SARS-CoV-2 spike protein subunits activate the alternative pathway of complement in vitro, suggesting that many clinical manifestations of COVID-19, such as microangiopathy, renal injury, and thrombophilia may be driven by complement activation.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Confocal microscopy of primary murine Gli1+ stromal cells stimulated with recombinant interleukin-6 (IL-6), an upregulated cytokine in primary myelofibrosis. IL-6 stimulation of Gli1+ bone marrow stromal cells (red) for 72 hours leads to the increase in α smooth muscle actin–positive fibers (green) and to their transformation into myofibroblasts. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; dark blue). See the article by Gleitz et al on page 2051.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals








A “gut feeling” about precursor B-ALL