Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
HNRNPC and m6A RNA methylation control oncogenic transcription and metabolism in T-cell leukemia
The RNA methylation landscape and its downstream influences on disease biology remain poorly understood in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). In this Plenary Paper, De Kesel et al use a comprehensive multiomics approach and describe widespread alterations in N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation in T-ALL, identifying heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (HNRNPC) and fat mass and obesity-associated protein as putative therapeutic targets. The study strengthens the rationale for targeting RNA modifications in this disease, and it will be important to establish which molecular T-ALL subtypes are most susceptible to epitranscriptomic intervention.
SPECIAL REPORT
International consensus statement on diagnosis, evaluation, and research of Richter transformation: the ERIC recommendations
Richter transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a rare but aggressive complication with persistently poor outcomes. In this Special Report, Kittai and colleagues discuss an international group of experts coordinated by the European Research Initiative on CLL (ERIC) who reported consensus recommendations on the diagnosis, workup, and evaluation of treatment responses in Richter transformation of CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma. The group provides guidance for clinicians, pathologists, and researchers and aims to harmonize clinical and translational research with a goal of improving patient outcomes.
PERSPECTIVE
Proteostasis disruption in inherited bone marrow failure syndromes
There is increasing evidence that disruption of proteostasis is a hallmark of several inherited bone marrow failure syndromes (IBMFS). In this Perspective, Yu and Signer discuss how disruptions of protein synthesis, folding, processing, and proteotoxic stress response pathways may contribute to IBMFS pathogenesis. The authors further highlight how investigating proteostasis regulation and the consequences of proteostasis disruption in IBMFS could inform the development of new biomarkers, therapeutic agents, and preventative approaches.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Ruxolitinib combined with dexamethasone for adult patients with newly diagnosed hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in China
Clinical Trials & Observations
The treatment for adult hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) remains challenging, with poor overall survival. In a phase 2 trial evaluating a novel frontline combination of ruxolitinib and dexamethasone, Zhou et al demonstrated that this regimen was both feasible and effective as induction therapy, particularly in nonmalignancy-associated HLH. These findings support further investigation of early ruxolitinib use in adult HLH, although head-to-head comparisons with other new agents such as anakinra are needed.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
An unbiased genomewide screen uncovers 7 genes that drive hematopoietic stem cell fate from mouse embryonic stem cells
Developing strategies for the in vitro generation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) remains a major objective in regenerative medicine. Palma and colleagues used a CRISPR activation screen during embryonic stem cell (ESC) differentiation to identify a novel gene set capable of endowing ESC-derived mesodermal populations with multilineage, serially engraftable hematopoietic repopulating capacity. These findings provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms governing HSC fate during embryogenesis and stimulate further studies that delineate the precise mechanism by which this gene set enhances HSC fate.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
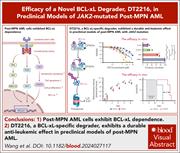
Efficacy of a novel BCL-xL degrader, DT2216, in preclinical models of JAK2-mutated post-MPN AML
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
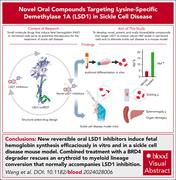
Novel, potent, and orally bioavailable LSD1 inhibitors induce fetal hemoglobin synthesis in a sickle cell disease mouse model
Small molecule drugs that induce fetal hemoglobin (HbF) in red blood cells serve as a promising therapeutic strategy for the treatment of sickle cell disease (SCD). Wang and colleagues employed a structure-aided drug design to develop potent new reversible lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) inhibitors that robustly increase HbF by inducing γ-globin expression both in vitro and in an SCD mouse model. Notably, combined treatment with a BRD4 degrader rescued the erythroid-to-myeloid lineage conversion that accompanies LSD1 inhibition. These findings support the clinical evaluation of these agents as a novel therapeutic approach for SCD.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
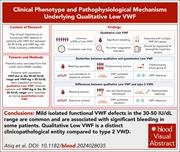
Clinical phenotype and pathophysiological mechanisms underlying qualitative low VWF
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
The clinical importance of functional von Willebrand factor (VWF) defects in patients with VWF activity levels between 30 to 50 IU/dL has been well recognized, but VWF antigen levels >50 IU/dL is poorly understood. In this month’s CME article, Atiq et al leveraged 2 wellcharacterized cohorts and show that mild isolated functional VWF defects in the 30 to 50 IU/dL range were common and were associated with significant bleeding in some patients. This study makes a case for low VWF activity levels with a positive bleeding assessment tool score to be included as diagnostic criteria for mild type 1 von Willebrand disease.
VASCULAR BIOLOGY
Platelet NLRP6 protects against microvascular thrombosis in sepsis
Platelets play a central role in linking inflammation and thrombosis, while nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)–like receptors regulate host defense during microbial infections through both pro- and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Jiang et al demonstrate that deletion of NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 6 protein (NLRP6) in platelets enhances NF-κB signaling and granule secretion, leading to increased microthrombosis and reduced survival in a sepsis model. This study reveals a previously unrecognized protective role for platelet NLRP6 in regulating microvascular thrombosis during sepsis and suggests new opportunities for targeted therapeutic intervention.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
A confocal image showing the neutrophil extracellular traps formation in the lung tissues of sepsis mice with the deletion of platelet nucleotide-oligomerization domain–like receptor family pyrin domain containing 6 protein. Red: neutrophils; green: citrullinated histone H3; blue: nuclei. See the article by Jiang et al on page 382.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals








m6A meets T-ALL: HNRNPC and FTO as new therapeutic targets