Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
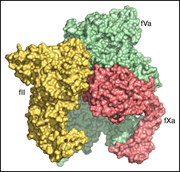
Cryo-EM structure of the prothrombin-prothrombinase complex
In this Plenary Paper, Ruben et al determine structures of the prothrombinase complex that are responsible for the proteolytic conversion of prothrombin to thrombin, the penultimate step in the coagulation cascade. This landmark study illustrates how factors Va and Xa associate on a membrane surface and how prothrombin binds in a conformation that leads to the generation of thrombin through a catalytically active intermediate form.
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT
Asciminib: a new therapeutic option in chronic-phase CML with treatment failure
Clinical Trials & Observations
In this Blood Spotlight, Hughes and colleagues discuss asciminib, a first-in-class allosteric inhibitor of BCR::ABL1 kinase activity, and its recent approval for use in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) who have failed 2 lines of therapy or whose leukemia bears the T315I mutation. The authors review its mechanism of action and the clinical data underpinning its approval, and they provide guidance on its use, particularly in the context of ABL mutations.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Molecular mechanisms of leukocyte β2 integrin activation
Leukocytes depend on integrin activation, conformational change, and dramatic changes in ligand affinity to enable rapid exit from the vasculature at sites of inflammation. Wen and colleagues review the latest data on this critical molecular change, formulating an integrated model of β2 integrin activation that will both inform understanding and drive future research.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
A study of ruxolitinib response–based stratified treatment for pediatric hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
Clinical Trials & Observations
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a rare, life-threatening systemic illness that is characterized by unrestrained T-cell activation and cytokine-mediated hyperinflammation. Zhang and colleagues report on the largest prospective study to date of a first-line targeted therapy for children with HLH. Their data indicate that the JAK inhibitor ruxolitinib can induce rapid, complete, and durable responses in approximately 40% of patients, encouraging further clinical trials of this therapy as an initial approach.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Concurrent CDX2 cis-deregulation and UBTF::ATXN7L3 fusion define a novel high-risk subtype of B-cell ALL
These 2 independently performed studies by Passet et al and Kimura et al describe a novel genetic subtype of B-progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) characterized by 2 separate focal genomic deletions leading to upregulation of CDX2 on chromosome 13 and to the formation of a chimeric gene fusion (UBTF::ATXN7L3) on chromosome 17. This novel subtype confers high clinical risk and is found in 1-2% of patients with B-ALL, with higher representation in adolescents and young adults.
Enhancer retargeting of CDX2 and UBTF::ATXN7L3 define a subtype of high-risk B-progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia
These 2 independently performed studies by Passet et al and Kimura et al describe a novel genetic subtype of B-progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) characterized by 2 separate focal genomic deletions leading to upregulation of CDX2 on chromosome 13 and to the formation of a chimeric gene fusion (UBTF::ATXN7L3) on chromosome 17. This novel subtype confers high clinical risk and is found in 1-2% of patients with B-ALL, with higher representation in adolescents and young adults.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
TRANSPLANTATION
Impact of diagnostic genetics on remission MRD and transplantation outcomes in older patients with AML
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
Murdock and colleagues applied extensive diagnostic molecular profiling and measurable residual disease detection of persistent mutations in a 295-patient multicenter cohort of older adults (age ≥60 years) with acute myeloid leukemia to identify the most useful predictors of relapse-free survival after allogeneic transplantation in first remission. Their results, published in this month's CME article, indicate that while molecular persistence in remission is frequent in older adults, it does not retain prognostic value for posttransplant outcomes after adjusting for specific baseline molecular and clinical variables.
BLOOD WORK
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Membrane-binding module of prothrombinase, comprising the Gla domain (raspberry red) of factor Xa and the C1 (green) and C2 (greenish yellow) domains of factor Va. Residues likely to interact with the membrane are highlighted (blue). See the article by Ruben et al on page 3463.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals







Shining a light on thrombin activation