Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
REVIEW ARTICLE
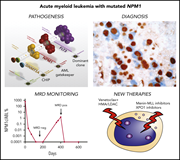
NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia: from bench to bedside
In a comprehensive and timely review from the pioneers of the field, Falini and colleagues discuss the latest research on nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1)–mutant acute myeloid leukemia and place it in the context of contemporary clinical practice.
GENE THERAPY
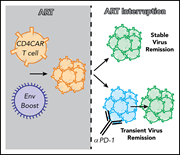
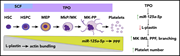
Robust expansion of HIV CAR T cells following antigen boosting in ART-suppressed nonhuman primates
The success of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells in hematological malignancies is leading to exploration of their potential to cure other incurable diseases, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Rust et al describe new innovations in CAR T-cell immunotherapy to treat HIV that enable profound expansion and improved function of CAR T cells in vivo.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
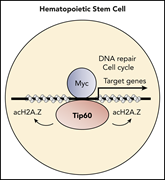
Lysine acetyltransferase Tip60 is required for hematopoietic stem cell maintenance
Numata and colleagues add new knowledge about the intricate regulation of hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) self-renewal and differentiation by the epigenetic machinery. Using conditional knockout models, they demonstrate a critical requirement of lysine acetyltransferase 5 (Kat5, also known as Tip60) for murine HSC maintenance through the regulation of Myc target gene expression.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
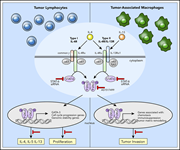
Genome-wide transcriptome analysis of the STAT6-regulated genes in advanced-stage cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
To dissect the role of STAT6 in advanced cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, Gaydosik et al combined gene expression analyses and functional studies with a specific STAT6 inhibitor. They reveal key roles of STAT6 both in proliferation of the malignant T cells and in shaping the tumor microenvironment, suggesting future therapeutic possibilities for this difficult-to-treat disease.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
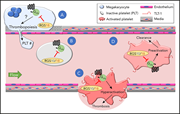
miR-125a-5p regulates megakaryocyte proplatelet formation via the actin-bundling protein L-plastin
The process of proplatelet formation requires extreme changes to megakaryocyte structure and cytoplasmic organization. Bhatlekar and colleagues identify the microRNA miR-125-5p as a regulator of the actin-bundling protein L-plastin and show how L-plastin levels control platelet formation by human megakaryocytes.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
RGS10 and RGS18 differentially limit platelet activation, promote platelet production, and prolong platelet survival
Much is known about how platelet activation is triggered, but less is understood about its negative regulation and how this is molecularly controlled. Using knockout mice, DeHelian et al reveal that 2 members of the regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) family, RGS10 and RGS18, play important roles in dampening agonist-induced platelet activation and thrombus growth at sites of vascular injury.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Impact of TKIs post–allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in Philadelphia chromosome–positive ALL
Clinical Trials & Observations
How to best use tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) of BCR-ABL after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for Philadelphia chromosome–positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is unknown but will almost certainly not be addressed by a definitive randomized trial. Saini and colleagues provide a large body of observational data to reinforce earlier circumstantial evidence favoring prophylactic use of TKIs for at least 2 years posttransplant.
A new gene associated with a β-thalassemia phenotype: the observation of variants in SUPT5H
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Skin involvement by leukemic cells with aberrant cytoplasmic expression of nucleophosmin (red) in NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. See the article by Falini et al on page 1707.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals



Antigenic cells augment CAR T cells