Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
HOW I TREAT
How I treat the toxicities of pegasparaginase in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Pegasparaginase is a key drug in curative regimens for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), but has unique toxicities that may be unfamiliar to adult hemato-oncologists. Using 5 cases of adults with ALL who were treated with pediatrically inspired regimens, Aldoss and Douer illustrate the management of several pegasparaginase-associated adverse effects and guide whether and how to continue the drug.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
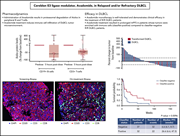
Avadomide monotherapy in relapsed/refractory DLBCL: safety, efficacy, and a predictive gene classifier
Clinical Trials & Observations
Avadomide is a novel cereblon-modulating drug that both kills lymphoma cells directly and stimulates T cells and natural killer cells. Carpio et al describe the safety and preliminary efficacy of avadomide in relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and how immune cell composition is associated with differential responses. The companion article by Risueño et al details a new gene expression classifier that discriminates DLBCL based on tumor and immune-cell composition and that may assist in identifying patients most likely to respond to immunomodulatory therapy, such as avadomide.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
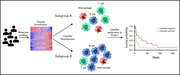
Leveraging gene expression subgroups to classify DLBCL patients and select for clinical benefit from a novel agent
Avadomide is a novel cereblon-modulating drug that both kills lymphoma cells directly and stimulates T cells and natural killer cells. Carpio et al describe the safety and preliminary efficacy of avadomide in relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and how immune cell composition is associated with differential responses. The companion article by Risueño et al details a new gene expression classifier that discriminates DLBCL based on tumor and immune-cell composition and that may assist in identifying patients most likely to respond to immunomodulatory therapy, such as avadomide.
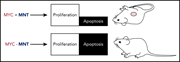
Development and survival of MYC-driven lymphomas require the MYC antagonist MNT to curb MYC-induced apoptosis
Aberrant MYC activity is a major driver of B-cell lymphomagenesis. However, if it is left unchecked, this oncogenic signal also drives cells to apoptosis. Nguyen et al reveal the important role of MNT, another component in the MYC transcription factor network, in the establishment and maintenance of MYC-driven lymphomas, and point to it as a future target for therapy.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
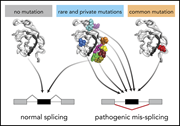
Rare and private spliceosomal gene mutations drive partial, complete, and dual phenocopies of hotspot alterations
Mutations in the RNA splicing factors SF3B1, SRSF2, and U2AF1 are common in myeloid neoplasms and usually occur at specific hotspots. Pangallo et al studied rare and private mutations in these genes and demonstrated that most of them are also pathogenic, frequently phenocopying hotspot mutations.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
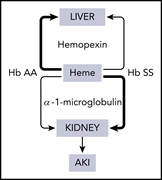
Hemopexin deficiency promotes acute kidney injury in sickle cell disease
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Ofori-Acquah et al report findings that are important to understanding the pathophysiology of sickle cell disease (SCD)–related kidney injury. Using both human samples and murine models, they identified acquired hemopexin deficiency as a risk factor for acute kidney injury in SCD and hemopexin replacement as a potential therapy.
TRANSPLANTATION
Complement blockade for TA-TMA: lessons learned from a large pediatric cohort treated with eculizumab
Clinical Trials & Observations
Jodele et al detail their experience with 64 pediatric patients with stem cell transplant–associated thrombotic microangiopathy (TA-TMA) and end organ damage treated with the complement blocker eculizumab. They report improved outcomes with brief, intensive therapy in comparison with historical controls.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
HAVCR2 mutations are associated with severe hemophagocytic syndrome in subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma
Ruxolitinib can cause weight gain by blocking leptin signaling in the brain via JAK2/STAT3
Clinical Trials & Observations
Mollé et al investigated the patterns of weight gain associated with ruxolitinib therapy in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms, defined high-risk groups for treatment-acquired obesity, and defined a plausible mechanism in mouse models.
Hemoglobin concentration of young men at residential altitudes between 200 and 2000 m mirrors Switzerland's topography
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Multiplex immunofluorescence of a biopsy specimen from a patient with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma after 2 weeks of avadomide treatment. Avadomide has immunomodulatory activity; treatment results in infiltration of CD3+ T cells (light blue) and CD8+ T cells (green) in CD20+ B-cell (red) tumors. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (dark blue). See the article by Carpio et al on page 996.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





MYC needs MNT to drive B cells over the edge