Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
A multicenter, open-label phase 3 study of emicizumab prophylaxis in children with hemophilia A with inhibitors
Clinical Trials & Observations
In a Plenary Paper, Young et al describe impressive favorable outcomes of emicizumab prophylaxis in children with hemophilia A and factor VIII inhibitors, reporting a 99% reduction in annualized bleeding, with 77% of patients having no treated bleeding events.
REVIEW ARTICLE
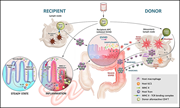
The primacy of gastrointestinal tract antigen-presenting cells in lethal graft-versus-host disease
Koyama and Hill review the role of the gut microbiome interaction with pretransplant conditioning injury in stimulating graft-versus-host disease.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
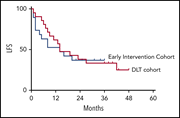
Preemptive mitigation of CD19 CAR T-cell cytokine release syndrome without attenuation of antileukemic efficacy
Gardner et al report that early intervention with tocilizumab and steroids at the first signs of mild cytokine release syndrome (CRS) following CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell infusion for B-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia reduces the development of life-threatening severe CRS without having a negative impact on antileukemic effect.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
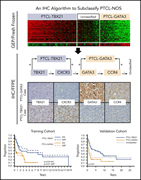
Reproducing the molecular subclassification of peripheral T-cell lymphoma–NOS by immunohistochemistry
One-third of peripheral T-cell lymphomas are “not otherwise specified” (PTCL-NOS), but they have been subdivided into 2 subgroups based on gene expression profiling. Amador and colleagues generated an immunohistochemical algorithm that parallels the molecular separation of PTCL-NOS and provides useful prognostic information.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
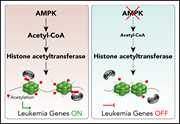
AMP-activated protein kinase links acetyl-CoA homeostasis to BRD4 recruitment in acute myeloid leukemia
There is increasing evidence that the metabolic regulation of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell growth interacts with epigenetic pathways of gene expression and differentiation. Jiang et al link inhibition of glucose metabolism to epigenetic changes and altered transcriptional pathways in leukemic cells and demonstrate synergy between simultaneously targeting metabolism and chromatin modifiers in suppression of AML.
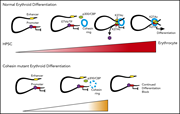
Cohesin-dependent regulation of gene expression during differentiation is lost in cohesin-mutated myeloid malignancies
Cohesin mutations are common in myeloid malignancy. Sasca et al elucidate the potential role of cohesin loss in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia (MDS/AML). They demonstrate that cohesin binding is critical for erythroid-specific gene expression and that reduction in cohesin impairs terminal erythroid maturation and promotes myeloid malignancy.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
Immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in older patients: prognosis and long-term survival
Prevel and colleagues examined the natural history of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) in older adults, reporting that the geriatric TTP population experiences delayed diagnosis and more severe neurologic and renal impairment. Older patients also have greater short- and long-term mortality.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Blood monitoring of circulating tumor plasma cells by next generation flow in multiple myeloma after therapy
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Giemsa-stained AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)–deficient acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells from mouse bone marrow. AMPK-deficient AML cells have an increased cytoplasm-to-nucleus ratio and lobulated nucleus that are characteristics of myeloid differentiation. See the article by Jiang et al on page 2183.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon AdvertisingAdvertising
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





The earlier the better: timely mitigation of CRS