Issue Archive
Table of Contents
EDITORIAL
Introduction to a review series on COVID-19 and the hematologist
Since the COVID-19 pandemic began over 2 years ago, its global impact has been enormous. Our growing understanding of the pathophysiology of this disease has particular links to hematology. Introduced by Ortel and Berliner, this Review Series provides up-to-date overviews of the many areas in which COVID-19 has implications for hematology practice.
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
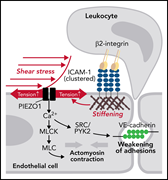
Mechanosensation by endothelial PIEZO1 is required for leukocyte diapedesis
CME
Neutrophils must penetrate the endothelial barrier to diapedese into sites of infection or inflammation. Though well recognized to be initiated by neutrophil adherence through adhesion molecules, the process by which the endothelial barrier is breached is not established. In this month’s CME article, Wang and colleagues demonstrate that adhesion cooperates with blood flow–induced shear stress and increased endothelial membrane tension to activate PIEZO1, the mechanosensitive cation channel that activates downstream signaling events that open the endothelial barrier.
REVIEW SERIES
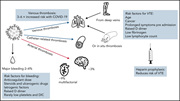
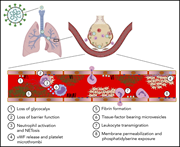
Clinical features of thrombosis and bleeding in COVID-19
Since the COVID-19 pandemic began over 2 years ago, its global impact has been enormous. Our growing understanding of the pathophysiology of this disease has particular links to hematology. Introduced by Ortel and Berliner, this Review Series provides up-to-date overviews of the many areas in which COVID-19 has implications for hematology practice.
COVID-19 convalescent plasma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Since the COVID-19 pandemic began over 2 years ago, its global impact has been enormous. Our growing understanding of the pathophysiology of this disease has particular links to hematology. Introduced by Ortel and Berliner, this Review Series provides up-to-date overviews of the many areas in which COVID-19 has implications for hematology practice.
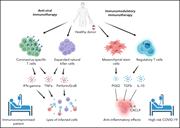
Cellular therapies for the treatment and prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection
Since the COVID-19 pandemic began over 2 years ago, its global impact has been enormous. Our growing understanding of the pathophysiology of this disease has particular links to hematology. Introduced by Ortel and Berliner, this Review Series provides up-to-date overviews of the many areas in which COVID-19 has implications for hematology practice.
Vasculopathy in COVID-19
Since the COVID-19 pandemic began over 2 years ago, its global impact has been enormous. Our growing understanding of the pathophysiology of this disease has particular links to hematology. Introduced by Ortel and Berliner, this Review Series provides up-to-date overviews of the many areas in which COVID-19 has implications for hematology practice.
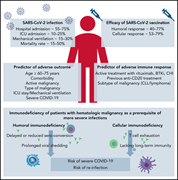
COVID-19 in patients with hematologic malignancy
Since the COVID-19 pandemic began over 2 years ago, its global impact has been enormous. Our growing understanding of the pathophysiology of this disease has particular links to hematology. Introduced by Ortel and Berliner, this Review Series provides up-to-date overviews of the many areas in which COVID-19 has implications for hematology practice.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
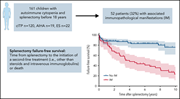
Determinants of long-term outcomes of splenectomy in pediatric autoimmune cytopenias
Clinical Trials & Observations
Pincez et al examined splenectomy outcomes in 161 pediatric patients with autoimmune cytopenia. Failure-free survival is markedly decreased in patients with associated immunopathologic disease, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.39 in those with a diagnosed systemic autoimmune disease before splenectomy, and an HR of 0.21 in those with a diagnosis subsequent to splenectomy.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
Expansion of CD4dimCD8+ T cells characterizes macrophage activation syndrome and other secondary HLH
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a rare hyperinflammatory state that can occur as a primary inherited disorder or secondary to other triggers. CD8+ T-cell activation is seen in both primary and infection-associated HLH, and this activation distinguishes these disorders from sepsis. De Matteis et al report that T-cell activation profiles of pediatric patients with macrophage activation syndrome (MAS), a form of HLH associated with systemic autoimmune disease, is highly similar to that seen in HLH. They further identify a subset of activated T cells highly correlated with severity of MAS.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
ABO O blood group as a risk factor for platelet reactivity in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
Karnes and colleagues report on the results of a genome-wide association study to find predictors of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, comparing patients with a positive functional assay for platelet activation, patients with anti-PF4 antibodies, and antibody-negative controls. A positive functional assay is highly associated with ABO O blood group, and a single nucleotide polymorphism is identified for future exploration of clinical utility in risk prediction.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Prospective comparison of outcomes with azacitidine and decitabine in patients with AML ineligible for intensive chemotherapy
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Image of the cremaster 3 hours after intrascrotal injection of 50 ng of interleukin-1β. Shown is the reduced extravasation of leukocytes (green, MRP14) in endothelium-specific Piezo1 deficient mice. Microvascular endothelial cells are stained in red (PECAM-1). See the article by Wang et al on page 171.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





The tension rises in leukocyte extravasation