Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
EPCR deficiency or function-blocking antibody protects against joint bleeding–induced pathology in hemophilia mice
Hemophilic arthropathy reflects the impact of repeated joint bleeding, synovitis, and inflammation. The authors dissected the important role of the endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR) in both hemostasis and inflammation within joints, demonstrating that blocking EPCR signaling through knockout studies or blocking antibodies reduces inflammation, macrophage infiltration, and neoangiogenesis following intraarticular injury.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
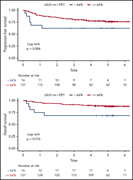
Prognostic value of interim FDG-PET in diffuse large cell lymphoma: results from the CALGB 50303 Clinical Trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Schöder and colleagues report the results of an imaging substudy within a randomized trial of R-CHOP or dose-adjusted-EPOCH-R for de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. In this carefully conducted study, interim positron emission tomography after 2 cycles of treatment had predictive value only when the percent change in tracer uptake was calculated, not when the standard visual 5-point scale was used.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
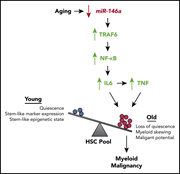
Altered microRNA expression links IL6 and TNF-induced inflammaging with myeloid malignancy in humans and mice
During aging, inflammatory changes accumulate and there is a loss of stem cell function. The microRNA miR-146a is known to be anti-inflammatory. Grants and colleagues identified low miR-146a as a poor prognostic marker in acute myeloid leukemia and used knockout mice to define how loss of this microRNA promotes “inflammaging” and predilection to myeloid malignancy.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
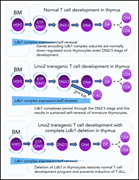
Ldb1 is required for Lmo2 oncogene–induced thymocyte self-renewal and T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Early T-progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia is associated with Lmo2-driven inappropriate self-renewal of immature thymocytes. Using conditional knockout mice, Li et al demonstrated a key requirement for the cofactor Ldb1 in Lmo2-induced leukemic transformation of thymocytes.
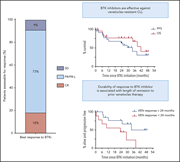
BTK inhibitor therapy is effective in patients with CLL resistant to venetoclax
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Ibrutinib became a standard therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) before venetoclax received registration. Consequently, data on the use of ibrutinib and other Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors only after venetoclax are sparse. Lin and colleagues report durable efficacy of BTK inhibitors in CLL after progression on venetoclax, including BCL2 G101V–mutant CLL.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
SETD2 deficiency accelerates MDS-associated leukemogenesis via S100a9 in NHD13 mice and predicts poor prognosis in MDS
CME
In this month’s CME article, Chen and colleagues reveal that low levels of expression of SETD2, which encodes a histone methyltransferase frequently mutated in certain leukemias, is associated with poor prognosis in myelodysplasia. They go on to demonstrate that loss of Setd2 impairs stem cell differentiation and promotes leukemogenesis in a murine model of myelodysplasia.
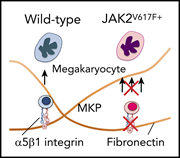
Adhesion to fibronectin via α5β1 integrin supports expansion of the megakaryocyte lineage in primary myelofibrosis
Brief Report
Matsuura et al describe mechanistic connections between megakaryocyte physiology, integrin biology, and myeloid neoplasia in revealing a novel contribution of fibronectin to megakaryocytosis in JAK2-mutant primary myelofibrosis.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
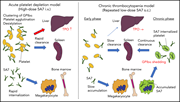
Mechanisms of anti-GPIbα antibody–induced thrombocytopenia in mice
Morodomi et al investigated 2 murine models of immune thrombocytopenia, finding that the mechanisms of anti-GPIbα antibody–induced thrombocytopenia and thrombopoietin response differ in relation to antibody concentration.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
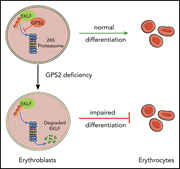
GPS2 promotes erythroid differentiation by control of the stability of EKLF protein
Ma and colleagues investigated the contribution of GPS2 to erythropoiesis using CD34+ cells and knockout mice, revealing that GPS2 is critical for erythroid differentiation and that GPS2 acts by increasing the availability of EKLF to activate transcription.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Tocilizumab in patients with symptomatic Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus–associated multicentric Castleman disease
Clinical Trials & Observations
Combination dose-escalated hydroxyurea and transfusion: an approach to conserve blood during the COVID-19 pandemic
Nickel et al describe a single-arm trial using dose-escalated hydroxyurea and regular transfusions to prevent complications of sickle cell anemia. Preliminary results suggest that a reduction in volume of red cell requirements may be achievable.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Liver cryosection from a mouse with acute thrombocytopenia induced by anti-GPIbα antibody. Opsonized platelets stained with anti-rat immunoglobulin G (green) tended to form aggregates and were detected adjacent to hepatocytes stained with anti-ASGPR1 antibody (red). See the article by Morodomi et al on page 2292.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals



EPCR knockout: inflaming the discussion