Issue Archive
Table of Contents
EDITORIAL
Introduction to a review series on rare systemic hematologic disorders
We feature a series of authoritative reviews on a collection of rare systemic hematologic disorders that are frequently difficult to recognize, diagnose, and treat. The series highlights new genomic and proteomic insights that inform our understanding of their pathophysiology and treatment.
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
Something old, something new…
Clinical Trials & Observations
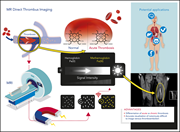
Recurrent ipsilateral deep vein thrombosis has major clinical ramifications, but is often difficult to distinguish from residual clot by ultrasound. van Dam et al demonstrated that magnetic resonance direct thrombus imaging can accurately distinguish the two, with a low risk of venous thromboembolism recurrence after a negative study.
Predicting the future for DLBCL
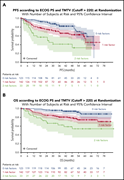
In this month’s CME article, Vercellino and colleagues report results of a secondary analysis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients in the REMARC trial who had baseline positron emission tomography scans, thereby demonstrating that metabolic tumor volume combined with performance status allowed risk stratification of patients before treatment and predicted survival independent of response to chemoimmunotherapy.
PATCHing platelet data to improve transfusion
The Platelet Transfusion in Cerebral Hemorrhage (PATCH) trial, a trial of platelet transfusion in patients on antiplatelet agents with cerebral hemorrhage, suggested that platelets worsened outcomes. Reanalysis of the data by the investigators revealed that despite randomization, some, if not all, of the adverse effects of platelets reflected worse baseline hemorrhage in patients in the platelet arm.
REVIEW SERIES
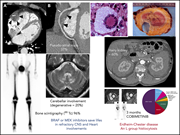
Erdheim-Chester disease
We feature a series of authoritative reviews on a collection of rare systemic hematologic disorders that are frequently difficult to recognize, diagnose, and treat. The series highlights new genomic and proteomic insights that inform our understanding of their pathophysiology and treatment.
Langerhans cell histiocytosis
We feature a series of authoritative reviews on a collection of rare systemic hematologic disorders that are frequently difficult to recognize, diagnose, and treat. The series highlights new genomic and proteomic insights that inform our understanding of their pathophysiology and treatment.
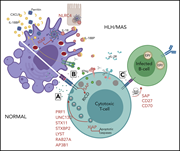
Pediatric hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
We feature a series of authoritative reviews on a collection of rare systemic hematologic disorders that are frequently difficult to recognize, diagnose, and treat. The series highlights new genomic and proteomic insights that inform our understanding of their pathophysiology and treatment.
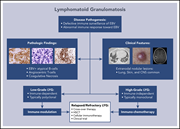
Pathobiology and treatment of lymphomatoid granulomatosis, a rare EBV-driven disorder
We feature a series of authoritative reviews on a collection of rare systemic hematologic disorders that are frequently difficult to recognize, diagnose, and treat. The series highlights new genomic and proteomic insights that inform our understanding of their pathophysiology and treatment.
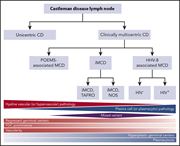
Overview of Castleman disease
We feature a series of authoritative reviews on a collection of rare systemic hematologic disorders that are frequently difficult to recognize, diagnose, and treat. The series highlights new genomic and proteomic insights that inform our understanding of their pathophysiology and treatment.
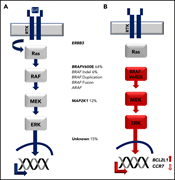
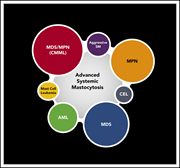
New developments in diagnosis, prognostication, and treatment of advanced systemic mastocytosis
We feature a series of authoritative reviews on a collection of rare systemic hematologic disorders that are frequently difficult to recognize, diagnose, and treat. The series highlights new genomic and proteomic insights that inform our understanding of their pathophysiology and treatment.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosis of recurrent ipsilateral deep vein thrombosis
Clinical Trials & Observations
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
External validation of models for KIR2DS1/KIR3DL1-informed selection of hematopoietic cell donors fails
Clinical Trials & Observations
It has been suggested that modulation of natural killer (NK) cell activity has an impact on relapse and survival in stem cell transplantation for myeloid malignancy. In a retrospective study of over 2200 patients, Schetelig et al demonstrated that modeling donor selection based on advantageous KIR and KIR ligand expression does not predict relapse or survival, thereby confirming that the mechanism of NK-cell mediated alloreactivity is more complex than postulated.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
High total metabolic tumor volume at baseline predicts survival independent of response to therapy
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
In this month’s CME article, Vercellino and colleagues report results of a secondary analysis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients in the REMARC trial who had baseline positron emission tomography scans, thereby demonstrating that metabolic tumor volume combined with performance status allowed risk stratification of patients before treatment and predicted survival independent of response to chemoimmunotherapy.
Predicting the future for DLBCL
In this month’s CME article, Vercellino and colleagues report results of a secondary analysis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients in the REMARC trial who had baseline positron emission tomography scans, thereby demonstrating that metabolic tumor volume combined with performance status allowed risk stratification of patients before treatment and predicted survival independent of response to chemoimmunotherapy.
LETTER TO BLOOD
PATCH trial: explanatory analyses
PATCHing platelet data to improve transfusion
The Platelet Transfusion in Cerebral Hemorrhage (PATCH) trial, a trial of platelet transfusion in patients on antiplatelet agents with cerebral hemorrhage, suggested that platelets worsened outcomes. Reanalysis of the data by the investigators revealed that despite randomization, some, if not all, of the adverse effects of platelets reflected worse baseline hemorrhage in patients in the platelet arm.
BLOOD WORK
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Pericardial localization of Erdheim-Chester disease. Pericardial infiltrate made up of histiocytes positive for CD68 (immunostaining with a KP1 clone). See the review series on rare systemic hematologic disorders in this issue.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals




Something old, something new…
Clinical Trials & Observations
Recurrent ipsilateral deep vein thrombosis has major clinical ramifications, but is often difficult to distinguish from residual clot by ultrasound. van Dam et al demonstrated that magnetic resonance direct thrombus imaging can accurately distinguish the two, with a low risk of venous thromboembolism recurrence after a negative study.