Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT
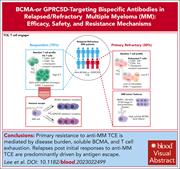
BCMA- or GPRC5D-targeting bispecific antibodies in multiple myeloma: efficacy, safety, and resistance mechanisms
In this Blood Spotlight, Lee and colleagues review the role of bispecific antibodies in the treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Several bispecific antibody therapies have received accelerated approval. The authors focus on their efficacy as demonstrated in clinical trials, the biological mechanisms of resistance leading to relapse, and the optimal sequencing of their use.
REVIEW ARTICLE
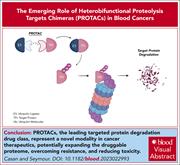
Degraders upgraded: the rise of PROTACs in hematological malignancies
Clinical Trials & Observations
Casan and Seymour provide a state-of-the-art review of proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs), the leading class of targeted protein degradation agents. PROTACs exploit the ubiquitin-proteosome system to degrade targeted proteins, allowing degradation of otherwise “undruggable” proteins required to drive disease. The authors provide an overview of their mechanism of action and the preclinical and clinical explorations of their use in treating hematologic malignancies.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Antitumor efficacy and safety of unedited autologous CD5.CAR T cells in relapsed/refractory mature T-cell lymphomas
Clinical Trials & Observations
Replicating the success of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells in T-cell malignancies has been a challenge, with concerns for shared markers on malignant and normal T cells, CAR T-cell fratricide, and transduction of circulating malignant cells. Hill et al report on a first-in-human study of unedited autologous CD5.CAR T cells in 17 patients with relapsed/refractory T-cell lymphoma. Only 1 patient sustained remission following an allogeneic transplant, with the main impediment being rapidly progressive disease precluding infusion in 8 patients. Response was seen in 4 out of 9 infused patients, including 2 patients with a complete response. Immunodeficiency and fratricide were not seen, encouraging further study of this approach as a bridge to transplant.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
A p53 score derived from TP53 CRISPR/Cas9 HMCLs predicts survival and reveals a major role of BAX in the response to BH3 mimetics
Durand and colleagues established a functional p53 score that better defines survival in multiple myeloma (MM) and predicts response to BH3 mimetics. The authors used CRISPR/Cas9 technology to derive TP53 wild-type and mutant human myeloma cell lines and demonstrate a TP53-specific gene expression profile. The score identified samples with biallelic TP53 inactivation and predicted poorer survival in 2 large clinical trial cohorts of patients with MM. Biallelic TP53 inactivation also engenders relative resistance to BCL2 inhibitors, which can be overcome by combination with MCL1 inhibitors.
Complete responses in AL amyloidosis are unequal: the impact of free light chain mass spectrometry in AL amyloidosis
Clinical Trials & Observations
Bomsztyk et al establish the superiority of mass spectrometric assessment of serum free light chains (FLC-MS) in light chain amyloidosis (AL amyloidosis) and examine its prognostic significance in patients who are in hematologic remission. By sequential assessment by FLC-MS in the context of hematologic responses, the authors report that in patients with complete hematologic response at 6 and 12 months, only 28% and 39%, respectively, were FLC-MS negative. Results have prognostic significance: median overall survival for patients who were FLC-MS negative was not reached vs 108 months in those who were FLC-MS positive. FLC-MS will likely become the gold standard for response assessment in AL amyloidosis.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
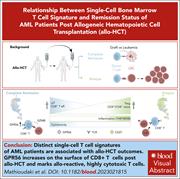
The remission status of AML patients after allo-HCT is associated with a distinct single-cell bone marrow T-cell signature
Cure of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) by allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT) depends on a graft-versus-leukemia effect mediated by transplanted T cells that can destroy residual AML cells. Mathioudaki and colleagues performed single-cell RNA-sequencing on lymphocytes and CD34+ cells from 6 patients with AML 100 days after allo-HCT to identify T-cell signatures associated with relapse (REL) or durable complete remission (CR). The authors identified a population of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells with increased GPR56 surface expression that was increased in patients in CR, while REL patient samples had an inflammatory TNF/NFκB signaling/immunosuppressive signature.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
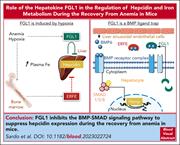
The hepatokine FGL1 regulates hepcidin and iron metabolism during anemia in mice by antagonizing BMP signaling
Although erythroferrone (ERFE) is known to suppress hepcidin, the master regulator of iron homeostasis, during response to anemia it has been suspected that there is a second regulator of hepcidin. Sardo et al report on the identification of that novel regulatory protein, the hepatokine FGL1. The authors demonstrate that while ERFE is induced by erythropoietin in the setting of acute anemic stress, FGL1 is upregulated in the liver in response to hypoxia during prolonged anemia and in thalassemic mice, suggesting that the iron response to anemia occurs in 2 waves of regulation of hepcidin.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
Clearance of VWF by hepatic macrophages is critical for the protective effect of ADAMTS13 in sickle cell anemia mice
Shi et al introduce a new complexity to the pathology of sickle cell disease (SCD) involving macrophage processing of ADAMTS13-cleaved von Willebrand factor (VWF) fragments. Cleaved VWF is cleared from the circulation by a subset of hepatic macrophages and if uncleared, it binds to SCD red cells and promotes vaso-occlusion. Administration of ADAMTS13 to mice with SCD alleviates vaso-occlusion, as does administration of the annexin A1–derived peptide Ac2-26, which enhances macrophage activity; conversely, macrophage depletion exacerbates vaso-occlusion. Manipulation of macrophage activity may offer a new therapeutic option for SCD.
LETTER TO BLOOD
CALR mutation burden in essential thrombocythemia and disease outcome
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
A confocal microscopic image of immunofluorescent staining of von Willebrand factor (red) and sickle red cells (green) in the liver section indicates increased vaso-occlusion of a tumor necrosis factor–challenged sickle cell anemia mouse after depletion of macrophages. Blue marks the cell nuclei. See the article by Shi et al on page 1293.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






T-cell lymphoma: the CAR-T revolution is coming
Clinical Trials & Observations