Issue Archive
Table of Contents
EDITORIAL
Introduction to a How I Treat series on consultative hematology for inpatients
Associate Editors Hendrickson and Ortel edited a How I Treat series on inpatient consultative hematology. In this timely series of articles, the authors present an approach to bleeding, thrombosis, anemia, and quantitative neutrophil abnormalities.
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
DMF in CTCL: where do we go from here?
Clinical Trials & Observations
HOW I TREAT SERIES
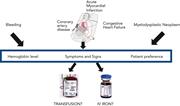
How I approach bleeding in hospitalized patients
Associate Editors Hendrickson and Ortel edited a How I Treat series on inpatient consultative hematology. In this timely series of articles, the authors present an approach to bleeding, thrombosis, anemia, and quantitative neutrophil abnormalities.
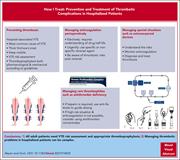
How I approach the prevention and treatment of thrombotic complications in hospitalized patients
Associate Editors Hendrickson and Ortel edited a How I Treat series on inpatient consultative hematology. In this timely series of articles, the authors present an approach to bleeding, thrombosis, anemia, and quantitative neutrophil abnormalities.
How I treat anemia with red blood cell transfusion and iron
Associate Editors Hendrickson and Ortel edited a How I Treat series on inpatient consultative hematology. In this timely series of articles, the authors present an approach to bleeding, thrombosis, anemia, and quantitative neutrophil abnormalities.
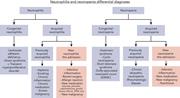
How I manage inpatient consultations for quantitative neutrophil abnormalities in adults
Associate Editors Hendrickson and Ortel edited a How I Treat series on inpatient consultative hematology. In this timely series of articles, the authors present an approach to bleeding, thrombosis, anemia, and quantitative neutrophil abnormalities.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Dimethyl fumarate treatment in relapsed and refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: a multicenter phase 2 study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a challenging disease with limited targeted therapies or curative approaches. Nicolay et al report on a phase 2 study of dimethyl fumarate (DMF), which is known to inhibit NF-κB in CTCL lymphocytes, in 25 patients with stage Ib-IV CTCL. DMF is well tolerated, and 30% of patients have skin responses, with best responses in patients with high skin tumor burden. However, responses in the blood are limited. DMF is a well-tolerated targeted therapy that should be investigated further, probably in combination with other therapies.
DMF in CTCL: where do we go from here?
Clinical Trials & Observations
Risk of male breast cancer after Hodgkin lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Female survivors of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) treated with chest radiation have a markedly increased risk of subsequent breast cancer. de Vries and colleagues report that male survivors of HL who receive chest radiation also have a 23-fold increased rate of breast cancer, although the absolute incidence remains low. Nevertheless, these data suggest that clinicians should be aware of the possible development of male breast cancer after treatment for HL.
GENE THERAPY
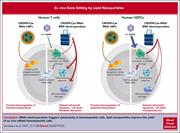
Lipid nanoparticles allow efficient and harmless ex vivo gene editing of human hematopoietic cells
Ex vivo gene editing in T cells and hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (HSPCs) involves delivery of the editing machinery via electroporation. Electroporation and gene editing cause cytotoxicity in T cells and activate a DNA damage response in HSPCs. Vavassori et al report that delivering vectors by lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) reduces cell death, improves cell growth, and improves HSPC clonogenic activity in repopulation assay, suggesting that LNPs may improve efficiency and reduce toxicity of ex vivo gene editing.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
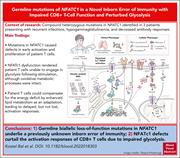
Biallelic NFATC1 mutations cause an inborn error of immunity with impaired CD8+ T-cell function and perturbed glycolysis
The nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) family of transcription factors is important for immunity in murine models, but their role in human immune function is unknown. Kostel Bal et al analyzed 3 members of a family pedigree with germ line biallelic missense mutations in NFATC1 presenting with recurrent infections, hypogammaglobulinemia, and decreased antibody responses. The authors demonstrate a defect in T-cell activation arising from defective glycolysis that is partially compensated by enhanced lipid metabolism.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Representation of the population in need for pivotal clinical trials in lymphomas
Clinical Trials & Observations
Casey and colleagues examined health disparities in clinical trials in lymphoma. By comparing the demographic and geographic diversity of the populations represented in randomized clinical trials to the US census population reflected in the National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program database, the authors confirmed that there are significant health disparities in clinical trial enrollment that may have an impact on translating clinical trial results to the “real world” US population of patients with lymphoma.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
A CODEX 7-color overlay from a skin sample of a representative responder patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma after dimethyl fumarate treatment. The colors are coded as follows: green, CD8; pink, CD163; white, Ki67; red, CD4; yellow, β-catenin; light blue, NF-κB p65; dark blue, nuclear staining. See the article by Nicolay et al on page 794.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals