Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
Determinants of ventricular arrhythmias in sickle cell anemia: toward better prevention of sudden cardiac death
Clinical Trials & Observations
Sudden death is a leading cause of death in patients with sickle cell disease (SCD), but its cause is unknown. In this Plenary Paper, d’Humières et al report on the prevalence and predictors of ventricular arrhythmia (VA) in 100 patients with SCD referred for ambulatory cardiac evaluation. The prevalence of VA was 22% and was associated with male sex, impaired global longitudinal strain, and decreased platelets. Although based on a small cohort of patients specifically referred for cardiac evaluation, these data suggest VA contributes to sudden death in SCD and requires further study.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
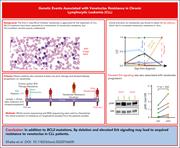
Genetic events associated with venetoclax resistance in CLL identified by whole-exome sequencing of patient samples
Resistance of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) to venetoclax can be attributable to BCL2 mutations, but other mechanisms of progression have been reported. Khalsa and colleagues performed whole exome sequencing of longitudinal samples from 11 patients with disease progression on venetoclax to better elucidate their clonal evolution. The authors report heterogeneous changes including chromosomal changes and changes in mRNA expression that could lead to better treatment choices for patients with venetoclax-resistant CLL.
Decoding the molecular heterogeneity of pediatric monomorphic post–solid organ transplant lymphoproliferative disorders
Salmerón-Villalobos and colleagues examined the molecular landscape of pediatric monomorphic posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders in 31 solid-transplant recipients. This disorder can present as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or as Burkitt lymphoma (BL), which is usually positive for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Patients with DLBCL are heterogeneous and distinct from de novo DLBCL and frequently respond to a reduction of immunosuppression, rituximab, or low-dose chemotherapy. By contrast, BL resembles de novo EBV+ BL and is best treated with combined therapy used for de novo BL.
High karyotypic complexity is an independent prognostic factor in patients with CLL treated with venetoclax combinations
Clinical Trials & Observations
Complex karyotypes (CKT) are associated with inferior outcomes in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treated with chemoimmunotherapy. Fürstenau and colleagues evaluated the clinical implications of complex CLL karyotypes in patients treated with venetoclax-containing regimens. The authors demonstrate that CKT that manifest as 3 or 4 chromosomal abnormalities (CA) is not an independent predictor of poor outcomes; however, highly complex karyotypes (≥5 CA) do predict inferior progression-free survival.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
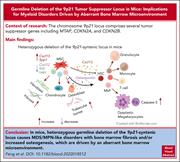
Haplodeficiency of the 9p21 tumor suppressor locus causes myeloid disorders driven by the bone marrow microenvironment
Deletion of chromosome 9p21 is associated with reduced survival in many cancers. Feng et al report that heterozygous deletion of the syntenic region in a mouse model leads to myelodysplastic syndrome/myeloproliferative neoplasm–like disease with marrow fibrosis and/or trabecular bone abnormalities. Using reciprocal transplants, the authors demonstrate that the changes are governed by the marrow microenvironment, highlighting a potential entry point for investigation of targeted therapy for myelofibrosis.
TRANSPLANTATION
Calcineurin inhibitor inhibits tolerance induction by suppressing terminal exhaustion of donor T cells after allo-HCT
Calcineurin inhibitors are a standard part of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis but do not prevent GVHD in a significant number of patients. Senjo et al studied mouse models of GVHD and demonstrate that calcineurin inhibitors inhibit tolerance by suppressing the development of exhausted T cells. They do, however, promote graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) effects, highlighting the complexity of response to immunosuppression in the prevention of GVHD while preserving GVL activity.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Widespread positivity for MUM1 in a monomorphic posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder diffuse large B-cell lymphoma subtype (IRF4/MUM1 immunostain, original magnification at 400×). See the article by Salmerón-Villalobos et al on page 434.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals







Ventricular arrhythmias in sickle cell anemia
Clinical Trials & Observations