Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PERSPECTIVE
Mitigating inequity: ethically prioritizing patients for CAR T-cell therapy
The growing population of patients eligible for chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies presents a dilemma for physicians deciding which patients to prioritize for the limited slots available. In this Perspective, Bell and colleagues discuss the process developed at their institution to try to ensure fair and equitable decision-making around this issue, focusing on 4 major criteria: medical benefit, safety/risk of complications, psychosocial factors, and medical urgency.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Effective treatment with the selective cytokine inhibitor BNZ-1 reveals the cytokine dependency of T-LGL leukemia
Clinical Trials & Observations
T-cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia (T-LGLL) is a chronic clonal disorder of cytotoxic T cells that is most often manifested as neutropenia, anemia, or pancytopenia. There is preclinical evidence that interleukin-15 (IL-15) is important in its pathogenesis. Brammer and colleagues report on a phase 1/2 trial of BNZ-1, a pegylated peptide that inhibits IL-15 and other cytokines to their receptor complex, demonstrating partial clinical response in 20% of patients with resolution of cytopenias. This was correlated with increased toxicity of T-LGLL, confirming a role of IL-15 in T-LGLL pathogenesis and suggesting a potential targeted therapy to treat cytopenias in that disease.
GENE THERAPY
Outcomes of hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
Clinical Trials & Observations
Labrosse et al report on a phase 1/2 trial of stem cell gene therapy for 5 patients with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS) using a self-inactivating lentiviral vector expressing the human WAS gene under its autologous promoter. Gene-corrected cells were administered after busulfan/fludarabine conditioning. Clinical results are encouraging, with resolution of eczema, infections, and bleeding in all patients. Correction of thrombocytopenia associates with high transduced copy number. Two patients had recurrent autoimmune flares, which correlate with poor recovery of T cells and regulatory T cells.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Analysis and therapeutic targeting of the IL-1R pathway in anaplastic large cell lymphoma
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) is an aggressive subtype of T-cell lymphoma. Song and colleagues report on a genome-wide CRISPR screening in ALK+ and primary cutaneous (pC) ALK- ALCL that reveals a role for IL-1R inflammatory pathway signaling in the viability of pC ALK- ALCL, which promotes JAK-STAT3 signaling even in the absence of STAT3 mutation. Pacritinib, a JAK2/IRAK1 inhibitor, is highly active against pC ALK- ALCL with IL-1R activation in cell lines and mouse xenografts, offering a potential novel therapeutic strategy for this aggressive lymphoma.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
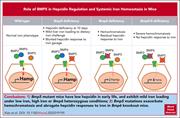
BMP5 contributes to hepcidin regulation and systemic iron homeostasis in mice
Hepcidin is the master regulator of iron homeostasis and is regulated by bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling in response to iron loading, iron deficiency, and erythropoietic drive. This regulation is largely a reflection of BMP6 and BMP2, but the role of BMP5 has not been defined. Xiao et al probed the contribution of BMP5 signaling to iron homeostasis, demonstrating that it also has a role in hepcidin regulation. BMP6 heterozygous or homozygous-null mice have increased iron loading that is further amplified with concomitant BMP5 knockout. This further elucidates the complex process of hepcidin regulation and iron metabolism.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Venetoclax with decitabine as frontline treatment in younger adults with newly diagnosed ELN adverse-risk AML
Clinical Trials & Observations
Xie et al present results of a multicenter, single-arm phase 2 trial of venetoclax and decitabine as frontline treatment in 42 younger adults (median age 39 years) with newly diagnosed adverse risk acute myeloblastic leukemia (AML). Remission was achieved in 39 of 42 patients (93%), 36 of whom went on to allogeneic stem cell transplant. Efficacy is encouraging, with estimated 12-month overall survival, event-free survival, and duration of response being 82%, 61%, and 65% respectively.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Confocal images of human monocytes differentiated into dendritic cells after culturing with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and IL-4, depicting colocalization of actin (red), vinculin (green), and Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (purple) in podosomes (yellow). See the article by Labrosse et al on page 1281.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






CAR Traffic jam: who can use the fast lane?