Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT
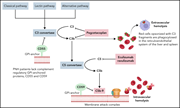
Pegcetacoplan for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
In this Blood Spotlight, Gerber and Brodsky discuss the use of pegcetacoplan, a proximal complement inhibitor that acts at the level of C3, to treat extravascular hemolysis in patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) with inadequate response to C5 inhibitors. The authors review the preclinical and clinical studies leading to its approval and propose an algorithm for sequential use of complement inhibitors for treating PNH.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Follow-up of patients with R/R FLT3-mutation–positive AML treated with gilteritinib in the phase 3 ADMIRAL trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Efficacy and safety of CD19-specific CAR T cell–based therapy in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients with CNSL
Clinical Trials & Observations
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) with central nervous system (CNS) involvement has been hampered by the concern for poor response and treatment-related neurotoxicity. Qi and colleagues report on 48 relapsed/refractory B-ALL patients with CNS leukemia treated with CD19-specific CAR T cells, demonstrating 85-90% response in both marrow and CNS, with manageable neurotoxicity and median overall survival of 16 months. CNS responses are more durable than marrow responses.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
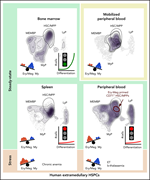
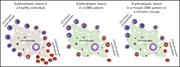
Unique molecular and functional features of extramedullary hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell reservoirs in humans
Rare hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells are found outside the bone marrow, but their role in hematopoiesis is unknown. Mende and colleagues used a combination of RNA-seq and functional assays to provide a detailed picture of the extramedullary stem cell compartments. These reservoirs do not contribute to steady state hematopoiesis but are modulated by stress hematopoiesis and by bone marrow dysfunction.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
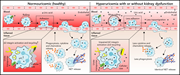
Soluble uric acid inhibits β2 integrin–mediated neutrophil recruitment in innate immunity
Chronic kidney disease is known to be associated with immunodeficiency, partly reflecting neutrophil dysfunction. Ma et al demonstrate that increased soluble uric acid (sUA) is an important contributor to neutrophil dysfunction, impairing neutrophil recruitment, migration, and phagocytosis. This effect, which can be partially reduced with rasburicase to reduce sUA, is in contrast to the impact of crystalline uric acid, which is known to enhance neutrophil function and contribute to inflammation.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Functional mapping of PHF6 complexes in chromatin remodeling, replication dynamics, and DNA repair
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
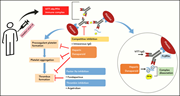
The interaction between anti-PF4 antibodies and anticoagulants in vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia
Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) is a rare life-threatening complication of vector-based COVID-19 vaccination that resembles heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in that it is associated with platelet-activating antibodies against platelet factor 4 (PF4). It has therefore been suggested that a nonheparin anticoagulation is the preferred treatment. Singh and colleagues used an ex vivo flow-based model of several anticoagulants and demonstrated that heparin both inhibits IgG binding and dissociates preformed PF4/IgG complexes, suggesting it is a potential effective therapy for VITT.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
Studies of a mosaic patient with DBA and chimeric mice reveal erythroid cell–extrinsic contributions to erythropoiesis
Doty and colleages describe a transfusion-dependent patient with Diamond-Blackfan anemia (DBA) mosaic for a pathogenic RPS19 haploinsufficiency and define a novel part of the pathophysiology of DBA. Of note, the patient's anemia resolved with eltrombopag (EPAG) despite having no change in her level of mosaicism, and the investigators attribute this to the ability of EPAG to chelate iron and decrease heme synthesis. In DBA, ineffective erythropoiesis partly reflects ferroptotic cell death from excessive intracellular heme.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Illustration of human blood neutrophils expressing the urate transporter SLC2A9. Neutrophils were stained with the anti–human SLC2A9 antibody (red) and DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) (white, nuclei), and confocal microscopy was performed. See the article by Ma et al on page 3402.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






Extramedullary hematopoietic stem cells